
Causes
Trauma. GI Bleeding. Postpartum. Severe. Dehydration. Fluid shifts. (Edema/Ascites). Burns

Trauma. GI Bleeding. Postpartum. Severe. Dehydration. Fluid shifts. (Edema/Ascites). Burns
Blood products if bleeding, Crystalloids, LR and NS, Colloids (Stay in vascular space, e.g., Albumin), 2 Large IV’s
Weak Pulses, Tachycardia, Hypotension, ↓ Cardiac Output, ↓ CVP ↓ PCWP, ↓ CFT, Pale Skin, Confusion, Agitation
Lactated Ringer’s is an isotonic crystalloid with electrolytes similar to plasma. Used for fluid resuscitation to perfuse organs and increase urine output. Does not have dextrose. It has K+ so monitor K and do not give to clients with renal problems.

Acidosis, Dysrhythmias, Cardiac Tamponade, Severe Hypoxemia, Acute MI, & CHF
Oxygen, Vasopressors, (Epinephrine, Dobutamine, & Dopamine), Intraaortic Balloon Pump, Pulmonary Artery Catheter for management
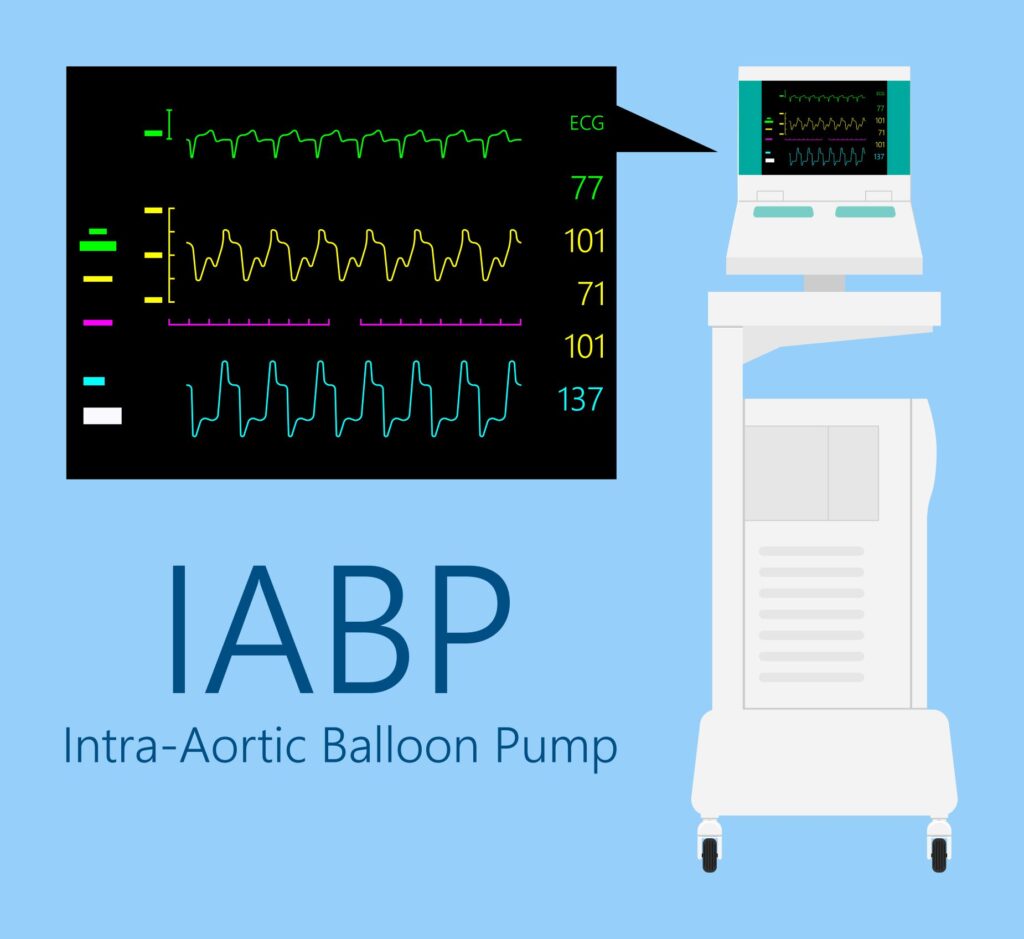
↓ Cardiac Output, ↑ Central Venous Pressure, Tachycardia, Hypotension, Hypoxia (↓ O2 Saturations), Weak Pulses, ↑ Capillary Filling Time, JVD, Oliguria (Late sign), Dyspnea, Confusion (early symptom). Watch for dysrhythmias (Major complication!).
Wound Infections, Invasive Procedures, Catheters, Pneumonia, Urosepsis (most common) & Peritonitis
Oxygen, Fluids first then Vasopressors, Monitor for Organ dysfunction, Get blood cultures , Before giving antibiotics, Start with broad spectrum, Antibiotics, Prevent stress ulcers, Enteral nutrition if possible


Early= Warm, Late = Cold, Tachycardia, Hypotension, Fever, Restlessness, Oliguria, Coma, ↑ Lactic acid, & Acidosis
Early septic shock: ↑ CO, ↓ PCWP, ↓ CVP. Always send blood cultures before administering antibiotics. Vasodilation lowers SVR and PCWP. The increased CO and HR are a compensatory mechanisms. In early shock, the increased Oxygen saturation happens because tissues are not extracting oxygen. In septic shock, monitor for DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy) = Impaired clotting (e.g., prolonged PT).
Foods (Peanuts), Medications, Bees, Latex, Insects, &Blood Products
EPINEPHRINE, Diphenhydramine, Albuterol, Corticosteroids, Fluids, & Stay with client and monitor


Occur within 2 to 30 minof exposure to antigen, Rapid weak pulse, Hypotension, Vasodilation ↓ SVR, Hypoxia & Wheezing, Bronchoconstriction, Redness & Hives, Dyspnea, Impending doom, Dysrhythmias, & Cardiac Arrest
Keep in dark room. Given IM in the thigh. Give immediately after first sign of reaction. Do not wait! Side effects: Dizziness, palpitations, & tachycardia

Spinal cord injury above T6, Spinal anesthesia, and nervous system damage. Parasympathetic system takes over leading to vasodilation. Loss of adrenergic/sympathetic stimulation
Airway, intubate, IV fluids, and vasopressors. Blood pools so check for clots (e.g. thrombosis in legs or DVT).


↓ CO. ↓ CVP, ↓ Heart rate, ↓ BP, ↓SVR, ↓ Oxygen Saturation. Everything is relaxed.
| Type | CO | HR | CVP | PCWP | SVR | O2 Sat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiogenic |  |  |
||||
| Hypovolemic |  |  |  |  |
||
| Septic (Early) |  |  | ||||
| Neurogenic |  |  |  |  |  |
|
| Anaphylactic |  |  |  |  |

0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 1 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
For each sign or symptom, put/type an X to specify if it a sign or symptom of hypovolemic, cardiogenic, anaphylactic, neurogenic, and/or septic shock. Each sign or symptom may belong to more than one shock.
| Sign and symptom | Septic | Cardiogenic Shock | Hypovolemic | Anaphylactic Shock | Neurogenic Shock |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bradycardia | |||||
| ↓ PCWP | |||||
| ↑ CO | |||||
| ↓ SVR | |||||
| ↑ SVR | |||||
| ↓ O2 Sat | |||||
| ↓ CO |
