Growth and Development


Grows 1/2 to 1 inch every month

Teeth: First to show at about 10 months are lower central incisors
Erikson's Developmental Stages

Trust vs. Mistrust
- Teach trust by: Holding infant, feeding infant, & create mother-infant attachment.
- Toys: Rattles, teething toys & mobile.
- Priority is to avoid aspiration

Autonomy vs Shame & Doubt
- Parallel Play
- Push/pull toys
- Fill/empty containers
- Finger paint
- Large crayons (Be careful with aspiration!)

Initiative vs Guilt
- Associate and cooperative play
- Tricycles (3 years= tricycle)
- Imaginary play
- Dress up
- Puzzles
- Collect things/toys

Industry vs Inferiority
- Develops social, learning and physical skills

Growth and Development

2 to 3 Months
- Raises head and chest
- Smiles, cries, turns head to sound
- Better head control
- Coos and makes gurgling sounds
- Posterior fontanelle closes
- Colicky: unexplained crying
- Big issue: shaken baby syndrome
- Teach parents to put baby in crib and walk away or rock baby

4 to 5 Months
- At 4 can roll over on the floor (Rhymes) from stomach to back
- Can grasp and switch objects from one hand to another
- Babbles and copies sounds
- Calms by parent’s voice. Unaware of unfamiliar surroundings
- Give solid foods: Iron-fortified rice cereal, fruits, vegetables, and meats
- Introduce new food one at a time (every week) to look for allergies.

6 to 7 Months
- Teething
- BIRTH WEIGHT DOUBLES AT 6 MONTHS
- Creeps (pushes around with stomach
- Sits with support
- Imitates and babbles
- Stranger anxiety
- Holds arms out
- Waves bye-bye

8 to 9 Months
- Crawling
- Sits unsupported
- Pincer grasp
- Can eat finger foods
- Stands straight at 8 months
- Object permanence (objects out out of sight still exist)
- Mama & dada Nonspecifically
- Choking risk: No nuts, seeds, popcorn, grapes and hot dogs

10 to 12 Months
- Whole milk at 12 months
- Lead test at 12 months
- Can speak 3-5 words and understand “no”
- Remember: up to 12 months only breastmilk, no cow!
- BIRTH WEIGHT TRIPLES AT 12 MONTHS
- Separation anxiety
- Follows simple directions & understands “no”
- By 12 to 13 months, the child can take a few steps without falling.
- Drinks from a cup

15 Months
- Walks alone
- Crawls upstairs/climbs
- Pulls toys
- Feeds self finger foods
- Full fincer grasp is developed
- Understands 100-150 words
- Babbles sentences

18 Months
- Throws ball overhand & Jumps in place
- Helps undress
- Builds tower of 3-4 blocks
- Scribbles
- Eats with a spoon
- Vocab: 15-20 words. Names familiar objects
- Temper Tantrums
- Ownership “mine”
- Explores with parents closeby
- Follows 1 step verbal command.

24 Months
- Terrible 2’s
- Kicks ball
- Runs without falling
- Builds 6-7 blocks tower
- 2-3 word phrages. 300+ vocab
- Parallel play
- Scribbles; draws line

3 Years
- Walks alternating feet
- Follows 2-3 step instructions
- Speaks simple sentences
- Rides a Tricycle (3 is for tricycle)
- Draws a circle & Holds a pencil
- Turns pages one at a time
- Uses 3-4 word sentences
- Associative play & Imaginary friends
- Screws and unscrews lids
- Knows name, age, and gender
- Wants to know “Why”
- Toilet trained

4 Years
- Hops on one foot
- Throws ball overhead
- Uses scissors & knows at least one color
- Copies capital letters
- Draws circles, squares and traces a cross or diamond
- Draws a person with 2-4 body parts
- Laces shoes & memorizes songs
- Uses complete sentences
- 75% of speech understood by outsiders
- Would rather play with others
Car Seat Safety
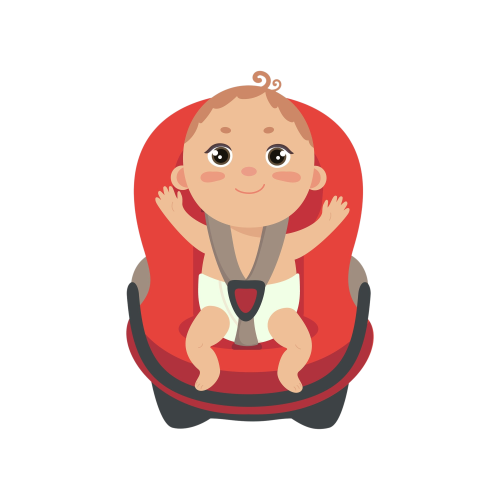

Car seat facing to the back of the car if < 20 lbs or < 1 year old
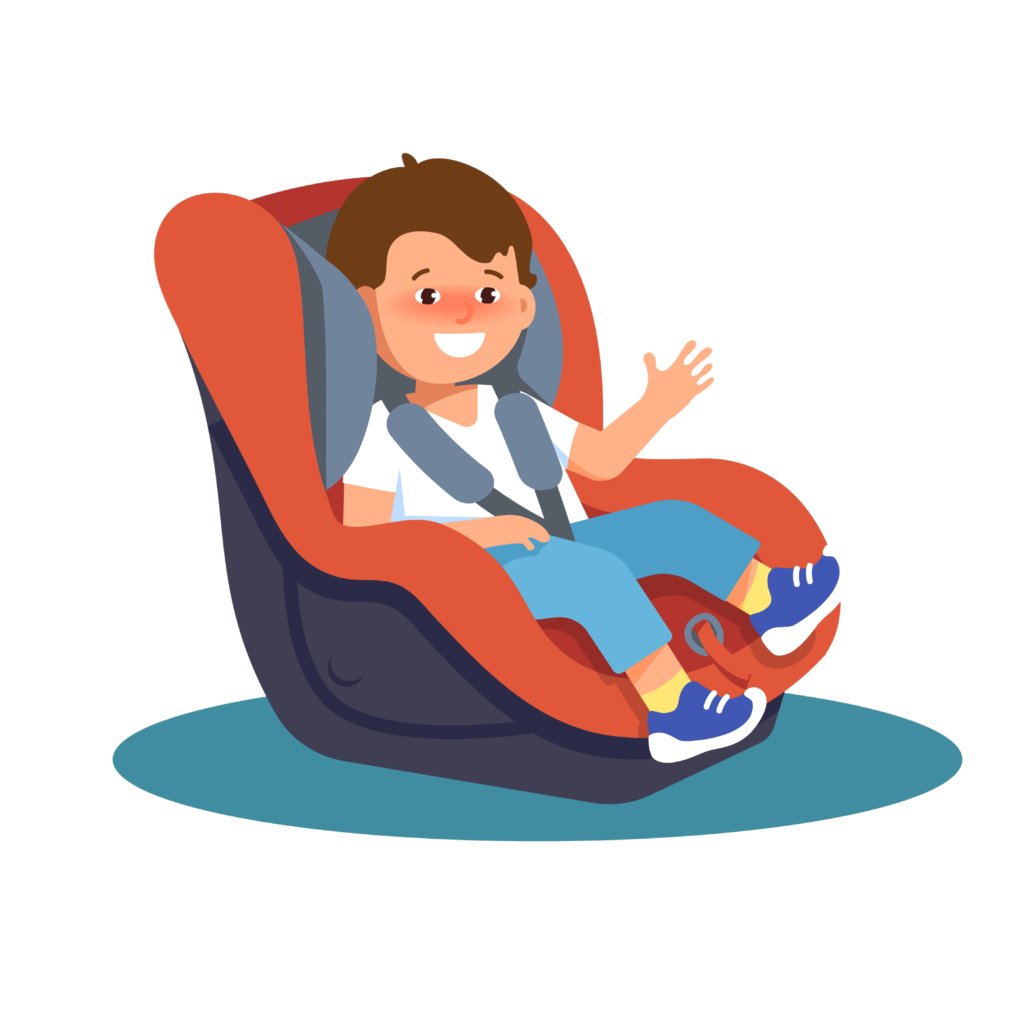

When the child is > 20 lbs or > 1 year, car seat can now face foward.
The child should remain in booster seat until 8 years and at least 4 feet 9 inches tall. Wow, that’s old! But that’s what sources recommend.
Normal Findings in Neonates

Normal vital signs in a newborn include:
- Heart Rate 120-160 beats per minute
- Respiratory rate of 30-60 breaths per minute
- Blood pressure of 60-90/20-60 mm Hg
- Axillary temperature of 36.5-37.5°C
Key words you should know:
- Lanugo,
- Vermix
- Acrocyanosis
- Acrocyanosis, which is a bluish discoloration of the hands and feet due to immature circulation.
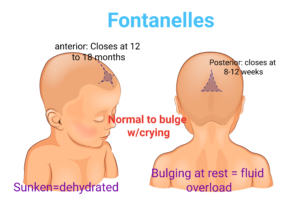
- The fontanelles, or soft spots on the baby’s head, should be flat and not bulging or sunken. It is normal if they bulge when crying.
- Skin should be pink and dry with no rashes or unusual markings, unless they have some acrocyanosis.
- Vernix, a white, waxy substance that covers their skin and can help protect against infection.
- Lanugo, a fine hair that covers their body but typically falls out within a few weeks. Premature babies have more lanugo than term babies.
Caput succedaneum causes swelling (edema) on the top of the scalp that is usually noticeable at birth. This swelling causes the scalp to feel spongy, does cross suture lines, and starts to go down soon after birth. Cephalohematoma is a buildup of blood (hemorrhage) underneath a newborn’s scalp. A cephalohematoma does NOT cross suture lines.
What car seat should a 7-year-old child who is 4 feet tall use?
Believe it or not, children should use booster seats until they are 4 feet 9 inches tall or 8-years of age.
The nurse is monitoring the anterior fontanelle of a 2-month-old with hydrocephalus. It feels soft and flat. What should be the nurse's action?
The anterior fontanelle should be flat and soft. It is normal to bulge with crying. If the child is at rest and the anterior fontanelle is bulging, think increased intracranial pressure. A sunken fontanelle = dehydration.
What is the best toy for a 3-year-old?
Think swallowing when you have to decide which toy is the most appropriate. The child can swallow the small marbles. A 50-piece puzzle is too advanced. At this age, the best toys are push-pull toys.
Is it concerning that a hospitalized 5-year-old begins to suck his thumb?
Regression occurs due to the stress of hospitalization. The best action is to ignore it and praise acceptable behavior.
What is the best activity for a teenager who is hospitalized?
Teenagers are all about peers.
What is the best activity for a hospitalized 5-year-old on bedrest?
Remember this: Hospitalized pre-schoolers: crayons, coloring books, puppets, and Play-Doh are good choices. Talking on the phone and music videos are more appropriate for teens
How does a 5-month old communicate?
2-3 months: coos and gurgling sounds. 4-5 months: babbles. 6-7 months: babbles and can wave bye-bye. 8-9 months: mama and dada non-specifically. 10-12 months: understands "no" and can say 3 to 5 words. Can say mama and dada specifically. 15 months: babbles sentences. 18 months: can say up to 20 words. 24 months: makes 2 to 3 word phrases. 3 years: makes 3 to 4 word phrases.
What is the best developmental approach for a hospitalized 4-year-old?
Should a toddler be allowed to fall asleep with a bottle?
Toddlers should not nap or go to bed with a bottle that contains milk, juice, soda and sugar water to prevent bottle mouth (cavities). A bottle with water is ok.
At what age can a child begin to eat with a spoon?
At what age should a child be toilet trained?
At what age does birth weight doubles?
A nurse is caring for a newborn infant with elevated bilirubin levels who is breastfeeding every 3 hours with good intake. Which intervention can the nurse implement to help reduce the newborn's bilirubin levels?
A premature newborn is diagnosed with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Which of the following would be the most effective intervention to support the newborn's respiratory function?
A nurse is providing discharge teaching to parents of a male newborn. Which statement by the parents indicates a need for further teaching?
"Back to sleep" to prevent SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome). Babies should sleep on their back
During the newborn assessment, the nurse should palpate the fontanels for which reason?
The fontanelles can tell you about fluid/volume status. The fontanelle will bulge in hydrocephalus or increased intracranial pressure. The fontanelles will sunken in dehydration
