Remembering Important Information
Here is some sample content
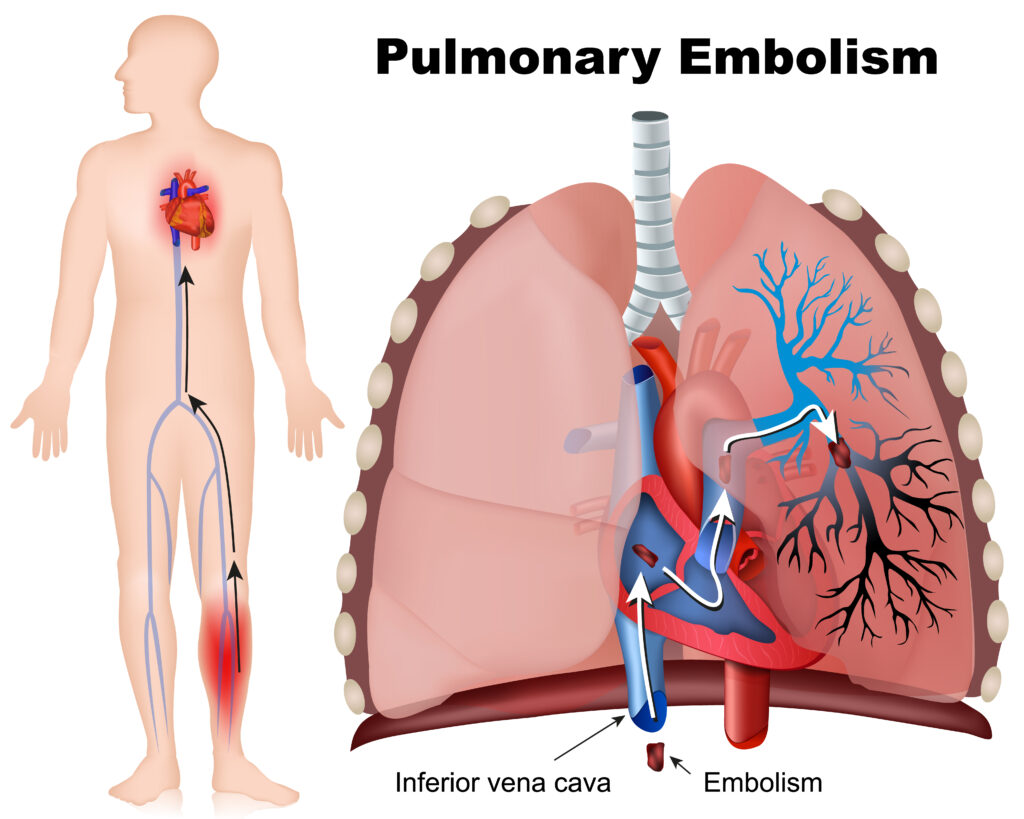
Pulmonary Embolism
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
Pulmonary Embolism
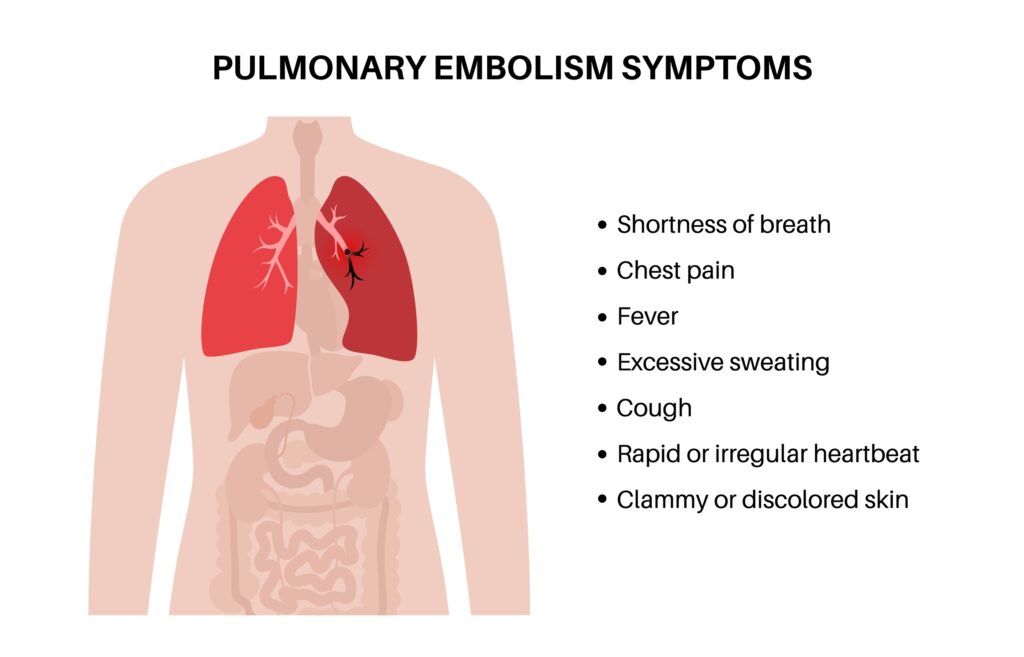
“PE CLOTS” Signs & Symptoms
- P: Pleuritic chest pain (sharp, worsens with breathing)
- E: Elevated heart rate (tachycardia)
- C: Cough (may produce blood-tinged sputum)
- L: Low oxygen levels (hypoxia, shortness of breath)
- O: Onset sudden (symptoms appear quickly)
- T: Temperature elevation (fever, mild)
- S: Swelling in one leg (deep vein thrombosis sign)
“CLOTS” Treatment
- C: Clot-busting drugs (thrombolytics for severe cases)
- L: Low molecular weight heparin (anticoagulant therapy)
- O: Oxygen therapy (to improve oxygen levels)
- T: Treat the cause (e.g., underlying DVT)
- S: Surgical intervention (embolectomy or filters in severe cases)
Meningitis
“SMART Neck Flexion”
- S: Stiff neck (nuchal rigidity)
- M: Mental changes (confusion, irritability, lethargy)
- A: Aching head (severe headache)
- R: Rash (especially petechial in meningococcal meningitis)
- T: Temperature (fever)
- Neck: Brudzinski’s sign (neck flexion causing hip and knee flexion)
- Flexion: Kernig’s sign (pain/resistance when flexed hip is extended at the knee)
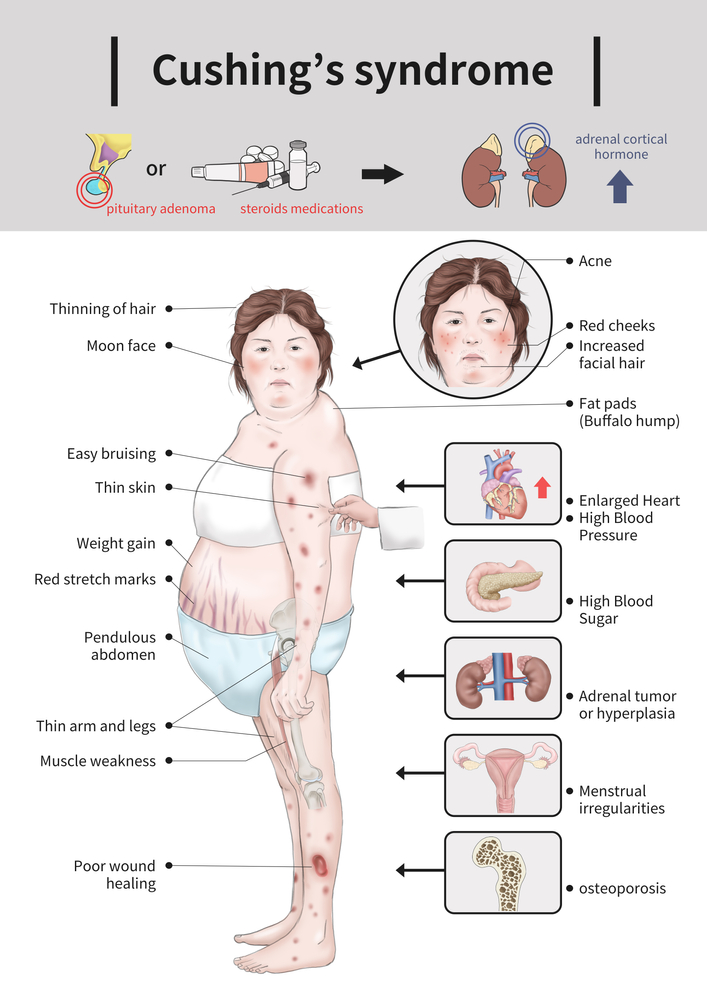
Cushing's Syndrome: High Cortisol
“CUSHING”
- C: Central obesity (weight gain around the abdomen)
- U: Unusual hair growth (hirsutism in women)
- S: Skin changes (thin skin, stretch marks, bruising)
- H: High blood sugar and hypertension (diabetes and high BP)
- I: Infections (weakened immune system)
- N: Neck fat pad (buffalo hump)
- G: Glucose intolerance (hyperglycemia)
Addison's Disease: Low Cortisol
“ADDISONS”
- A – Anorexia (loss of appetite and weight loss)
- D – Darkening of skin (hyperpigmentation)
- D – Dizziness (due to low blood pressure)
- I – Increased potassium (electrolyte imbalance)
- S – Salt craving (due to low sodium levels)
- O – Overall fatigue (tiredness, weakness)
- N – Nausea (gastrointestinal issues)
- S – Syncope (fainting due to low blood pressure)

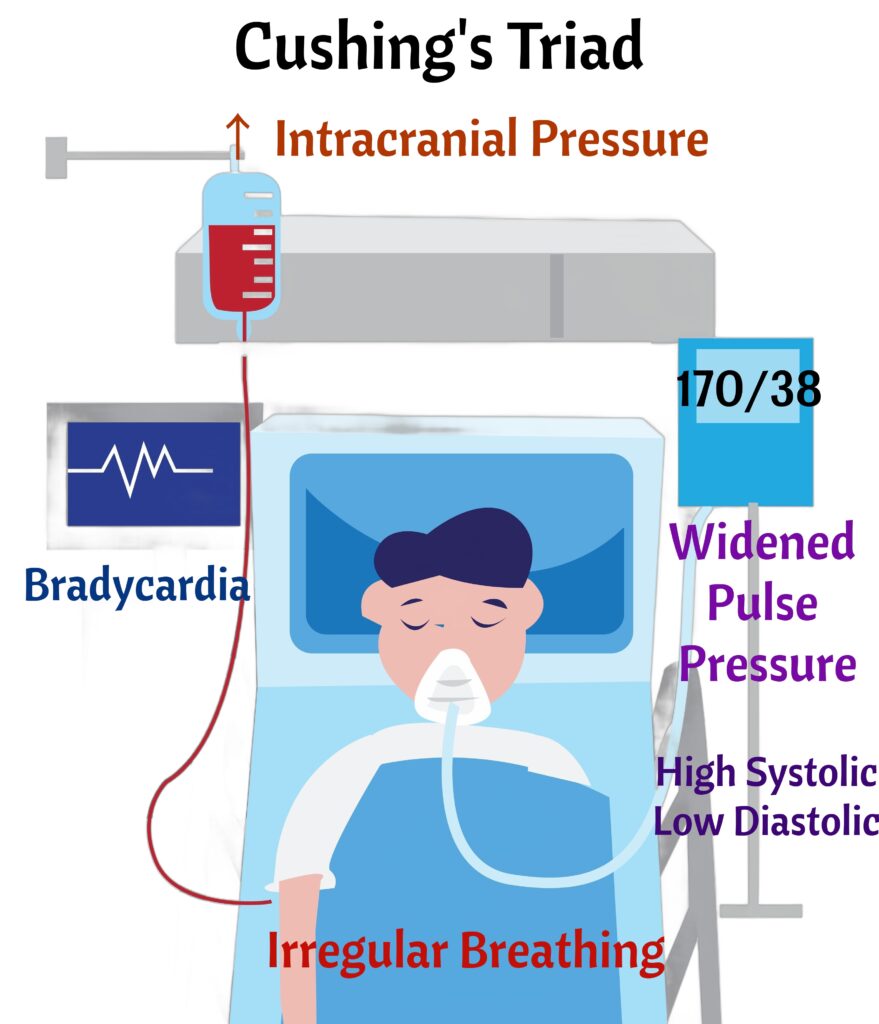
↑ Intracranial Pressure
“PRESSURE”
- P: Projectile vomiting (without nausea)
- R: Reduced level of consciousness
- E: Edema of the optic disc (papilledema)
- S: Slurred speech or difficulty speaking
- S: Slow pulse and irregular breathing (Cushing’s triad)
- U: Unusual posturing (decorticate or decerebrate)
- R: Reactive pupils become abnormal (sluggish or unequal)
- E: Elevated systolic blood pressure (widened pulse pressure)
Quiz Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 1 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- TPN nurising 0%
- 1
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
A nurse is caring for a patient who has been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. Which of the following signs and symptoms are most consistent with hyperthyroidism?
CorrectIncorrect
Hyperthyroidism
“S.W.E.A.T.I.N.G.”
- S – Sweating: Excessive sweating and heat intolerance.
- W – Weight loss: Despite an increased appetite.
- E – Exophthalmos: Bulging eyes (common in Graves’ disease).
- A – Appetite increase: Increased hunger despite weight loss.
- T – Tachycardia: Rapid heart rate or palpitations.
- I – Irritability: Increased nervousness or mood swings.
- N – Nervousness: Anxiety, tremors, and restlessness.
- G – Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid gland.
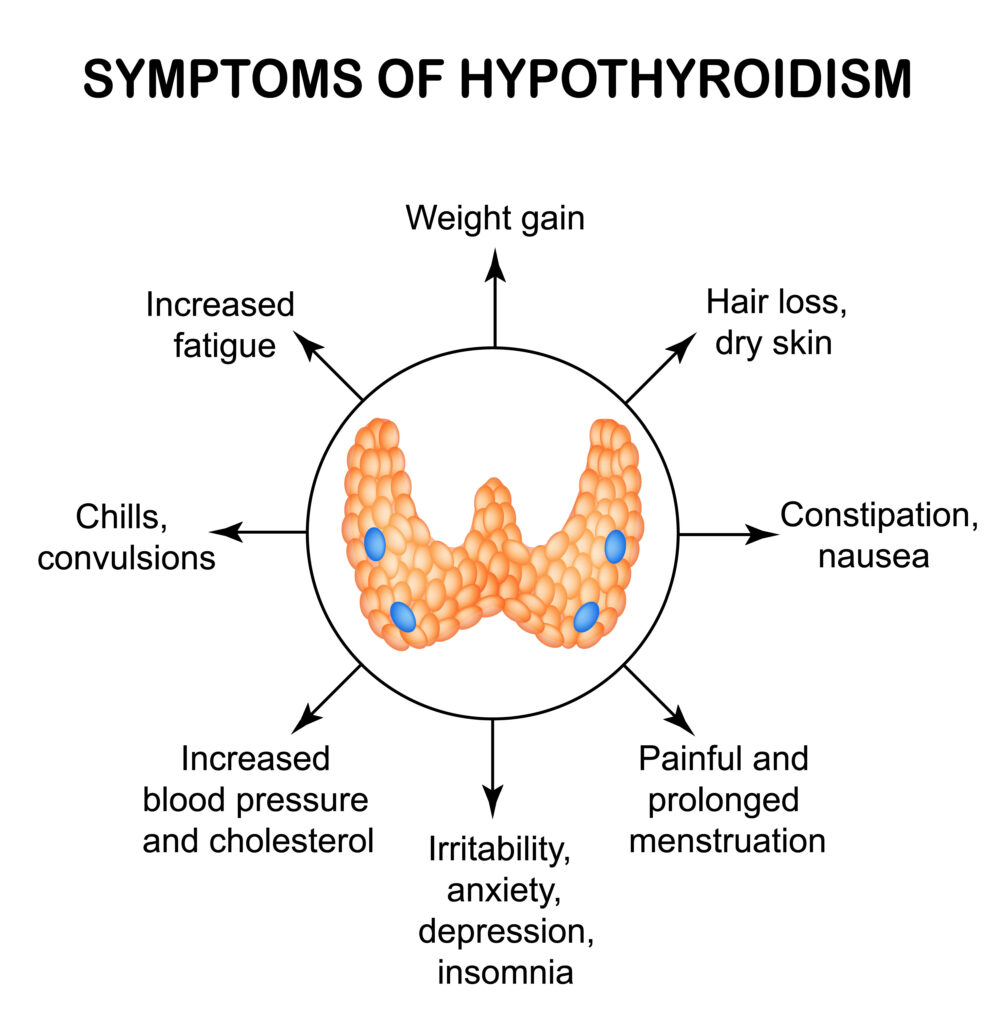
Hypothyroidism
“HASHIMOTO’S”
- Hypothermia (cold intolerance)
- Apathy (depression)
- Slow heart rate
- Hair thinning
- Increased weight
- Memory problems (brain fog)
- Obsession with sleep (fatigue)
- Thin skin, dry skin
- Observed constipation
- Swelling (myxedema)
Asthma Symptoms
“WHEEZY BREATH”
- Wheezing
- Hyper-resonance (on percussion)
- Exertional dyspnea (difficulty breathing during activity)
- Episodic shortness of breath
- Zero relief from triggers (e.g., allergens, cold air, exercise)
- Yearning for air (feeling breathless)
- Bronchospasm
- Respiratory distress (severe cases)
- Expiration prolonged (harder to breathe out)
- Accessory muscle use
- Tight chest feeling
- Hypoxemia (low oxygen in blood, severe cases)

Asthma Treatment
“ASTHMA PLAN”
- Albuterol (short-acting bronchodilator for quick relief)
- Steroids (inhaled or systemic for inflammation control)
- Trigger avoidance (dust, pollen, smoke, etc.)
- Humidifier (can help with dryness and irritation)
- Monitor peak flow (to track lung function)
- Anticholinergics (e.g., ipratropium for bronchodilation)
- Prevention medications (e.g., long-acting beta-agonists, inhaled corticosteroids)
- Leukotriene modifiers (e.g., montelukast)
- Action plan (personalized plan for managing exacerbations)
- Nebulizer use (for severe attacks or young children)

Prioritizing
“Always Be Calm During Emergencies” (ABCDE):
- A: Airway (Is the airway clear?)
- B: Breathing (Is the patient breathing adequately? Drug overdose?)
- C: Circulation (Is the heart functioning? Check for bleeding or shock.)
- D: Disability (Is there decrease blood flow to an extremity? Potential for amputation?)
- E: Exposure (Ensure the patient is safe from environmental threats, such as cold or heat.)

Drugs
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
