Disaster Triage, Prioritizing, and Delegation
4 Topics | 2 Quizzes
Neurological System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
MS, MG, and Guillain Barré
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The Cardiovascular System
12 Topics | 1 Quiz
Pulmonary System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cushing Versus Addison Disease
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Thyroid Disorders
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Parathyroid Disorders
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
DI and SIADH
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Diabetes
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Burns
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Anemias, Aplastic Anemia, Polycythemia Vera, Thrombocytopenia and DIC
9 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Oncological Emergencies
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Leukemias, Hodgkin’s Disease, and Multiple Myeloma
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The GI system
16 Topics | 1 Quiz
Renal and Genitourinary Problems
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Infection and Isolation Precautions
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
NCLEX Pharmacology
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
TPN, IV Solutions, & Blood Products
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Lab Values
9 Topics
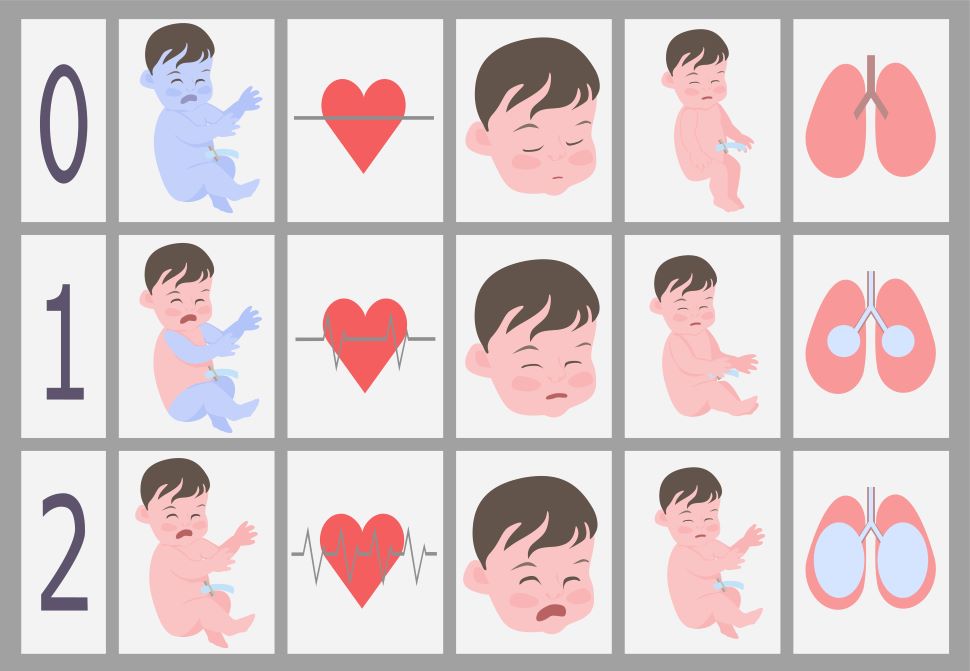
Assessments

- Appearance or Skin Color
- Pulse or Heart Rate
- Grimace or Cry
- Activity or Tone
- Respiratory Effort


- Rectal surgery
- Rectal bleeding
- Fecal impaction
- Cardiac clients (Vagal stimulation may occur leading to bradycardia or cardiac arrest)
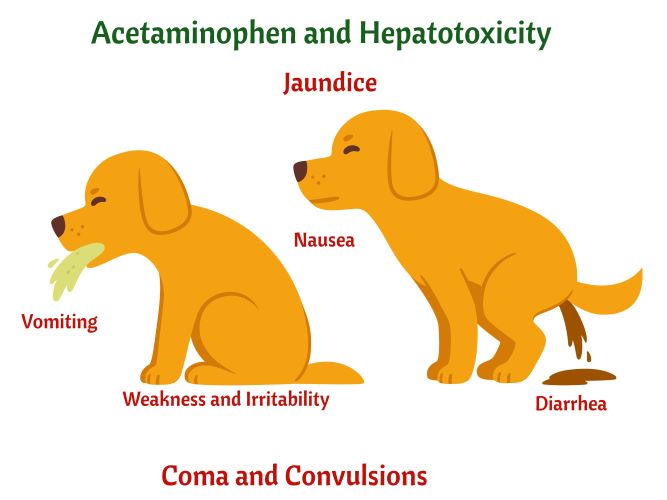
- Watch for hepatotoxicity:
- Abdominal pain.
- Irritability.
- Generalized weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Jaundice (yellow appearance of skin and eyes)
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting
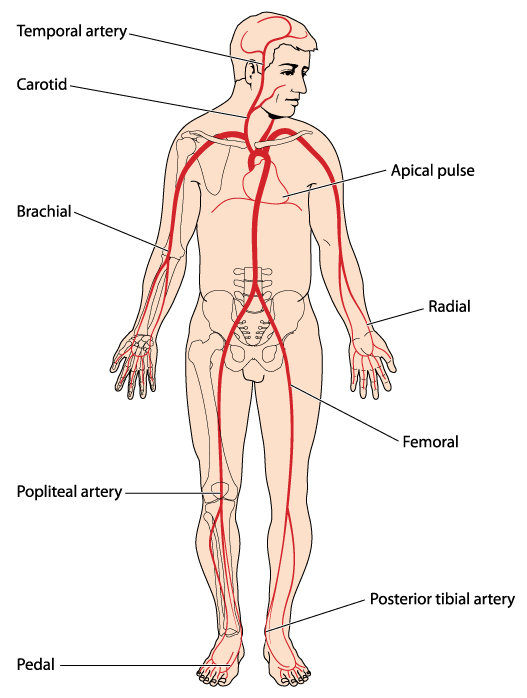
- In infants and young children, the apical pulse is located at the fourth intercostal space at the left midclavicular line.
- In adults, the apical pulse is located at the fifth intercostal space at the left midclavicular line.
- Check for a full Minute
- Check before giving digoxin and beta blockers
- Check in clients with irregular pulse or heart condition

- It’s ok to count for 30 seconds and multiply by 2 except for clients who are critically-ill or have irregular breathing.

- Too small, BP will be falsely high
- Too large, BP will be falsely low

- In clients on chemotherapy, monitor platelets and place on bleeding precautions
- Clients having a liver biopsy, check coagulation studies and platelet count.
- Consider the disease process and how it affects nutrition
- Monitor Albumin levels
- Assess ability to swallow and promote regular oral intake. It is the best!
- Count calories to check if the client is getting enough nutrition.
- Do not feed clients with no bowel sounds
- No bowel sounds may be = paralytic Ileus
- Abdominal assessment: Inspect, Auscultation, percussion, and palpation.
- Note that palpation is last!
- Monitor for neutropenia.
- Place on neutropenic precautions if ANC < 500
- Neutropenic precautions: no sick visitors, no live plants, no fresh fruits and vegetables, visitors must wear a mask.

