Burns
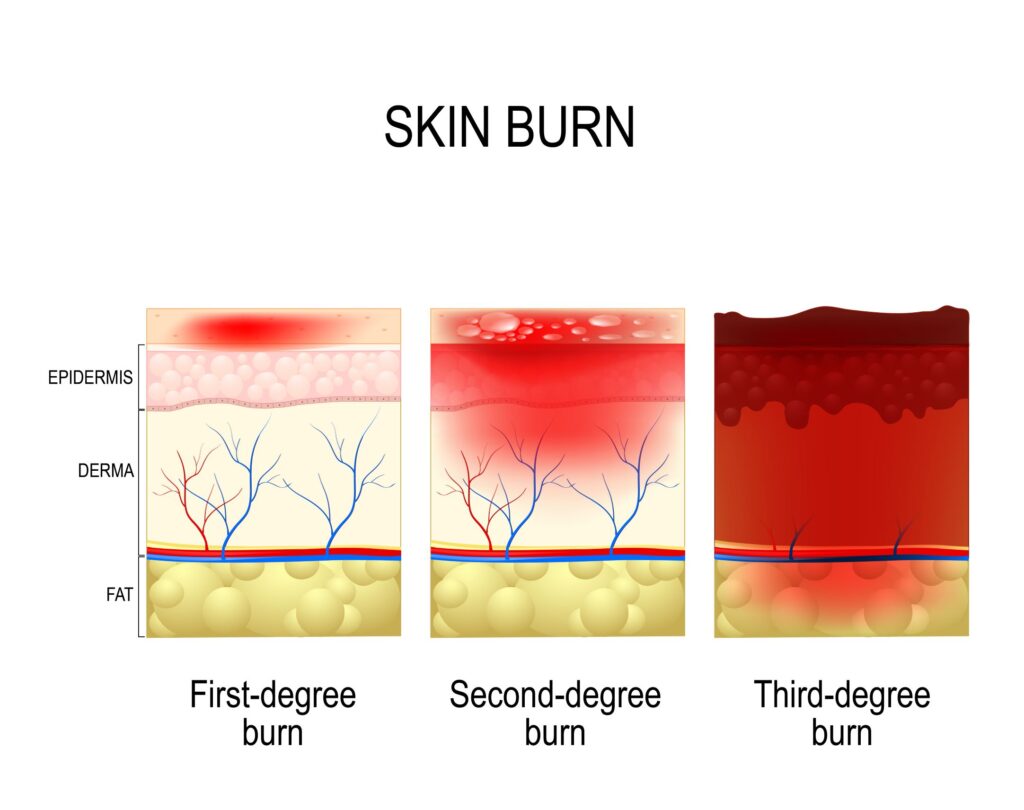
- There are three main types of burns: first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree burns.
- First-degree burns are the least severe and only affect the top layer of the skin, causing redness, pain, and mild swelling.
- Second-degree burns affect the top two layers of the skin and can cause blisters, severe pain, and swelling.
- Third-degree burns are the most severe and penetrate all layers of the skin, causing extensive tissue damage. These burns can lead to a loss of sensation in the affected area, as well as scarring and disfigurement.
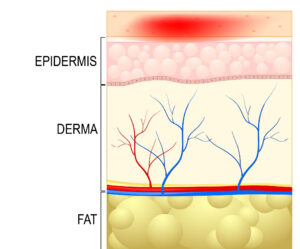
First Degree Burns
First Degree Burns
Minor injuries to the skin that involve only the top layer of skin, the epidermis. Caused by brief exposure to heat, such as touching a hot object or sunburn.
Symptoms
Redness, mild swelling, and pain.

Treatment
Heal within a few days to a week without medical intervention, over-the-counter pain relief medications, running cool water over the affected area, applying aloe vera or other topical medications, and avoiding further exposure to heat.
Nursing Priorities
Cooling the affected area with running water or a cool compress to reduce inflammation and pain.

Second Degree Burns
Second Degree Burns
Affects the second layer of the skin, known as the dermis. It has broken through the skin
Symptoms
Redness, pain, swelling, and blisters. Exposure to flames, hot liquids or steam, chemicals, electricity, or prolonged exposure to the sun.

Treatment
Cooling of the affected area with cool running water for 10-15 minutes. The wound should be covered with a sterile gauze to protect from dirt and infection.

Nursing Priorities
Airway, Manage pain, Prevent infection, Tetanus prophylaxis, & Wound care

Third Degree Burns
Third Degree Burns
A third degree burn is a type of burn that affects the deepest layers of the skin, including the fatty tissue, muscle, and bone.

Symptoms
Waxy white, brown or black burnt skin that feels dry and leathery, blisters that do not rupture easily due to the loss of fluid, Difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath if the burn affects the respiratory system, and in severe cases, shock or loss of consciousness due to fluid loss and electrolyte imbalance.
Treatment
Skin grafting, topical or IV antibiotics, & pain management. Skin grafting involves removing skin from another part of the body & placing it over the affected area.

Nursing Priorities
Airway, Manage pain, Prevent infection, Tetanus prophylaxis, & Wound care, minimize disfigurement, IV fluids, watch for electrolyte imbalances.
Emergent phase of burns
Burn to 24-48 hrs
Plasma/albumin/sodium shift to interstitial space. Edema but fluid deficit in vascular space
Priorities
ABC, ABC, IV fluids to treat hypovolemic shock. Again, fluids, fluids, fluids.
Monitoring
Urine output, potassium exits cell so monitor for deadly hyperkalemia, BUN/creatinine & edema

IV fluids
LR & crystalloids. Hypovolemic shock (tachycardia, hypotension)

Acute phase of burns
48 to 72 hours post burn
From stabilization of capillary permeability to wound closure
Infection & Nutrition
Vitamin C and high protein diet to promote healing. Tetanus Vaccine and Antibiotics

GI & GU
Foley due to diuresis, H2 blockers to prevent Curling's ulcer, NG tube, watch for paralytic ileus, & monitor bowel sounds
Nursing Priorities
IV fluids, prevent infection, pain management, wound care, and nutrition for wound healing.

