Calcium
Hypocalcemia Under 8.4 mg/dl
Causes of hypocalcemia
Hypoparathyroidism
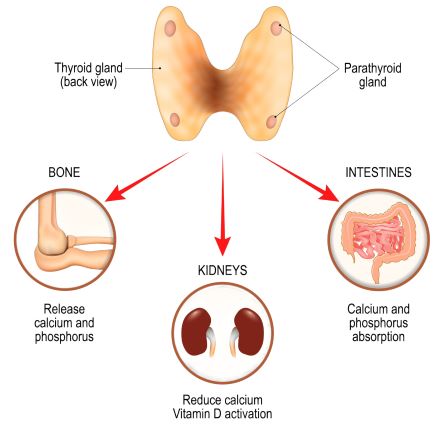
- The goal of the parathyroid is to ↑ Calcium.
- If it is underworking, calcium will be low.
Medications
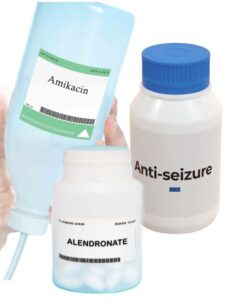
- Anticonvulsants: Phenobarbital & Phenytoin
- Aminoglycosides: Amikacin & Tobramycin
- Biphosphoates (Alendronate): Causes the bones to stop releasing calcium into the blood.
- Laxatives with phosphorus: Remember phosphorus & calcium have opposite relationship. ↑ Phosphorus = ↓ Calcium
- Loop diuretics such as furosemide
Surgery
- Parathyroidectomies
- Thyroidectomies (Accidental damage of parathyroid)
Diseases
- Kidneys produce Calcitriol, which activates Vitamin D for calcium absorption. These clients need Vitamin D & Calcium supplements
- Acute Pancreatitis
- Crohn’s Disease
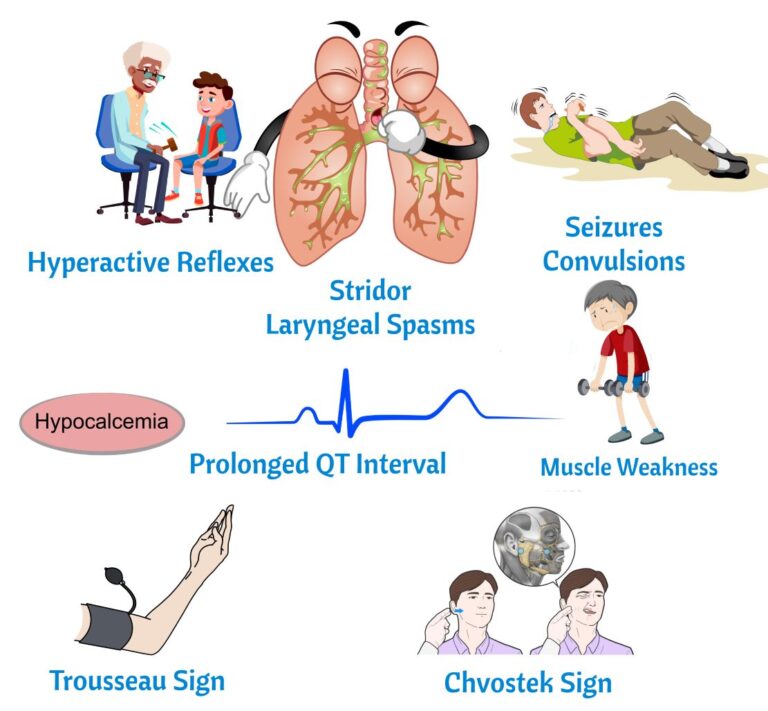
Signs and Symptoms of Hypocalcemia
Accordion: Click on the letters to expose the content
Chvostek’s Sign: Tap on facial nerve by ear⇒ Tetany/spasms of all facial muscles

- Arrhythmias
- Prolonged QT interval
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Trousseau’s Sign/Tetany
- Inflate BP cuff to 20mm Hg above systolic, hold x 3 min ⇒Tetany/spasms of the hand
- Seizures/Spasms/Stridor
- Laryngospasms and dyspnea
- Slow clotting factors: Bleeding
- Remember Calcium is one of the clotting factors
- ALOC, Confusion.
- Hypocalcemia, think respiratory
Click on the headings to expose the content.
Nursing Interventions for hypocalcemia
Click on the headings to expose the content
Calcium acetate or Phoslo is a phosphorus binder often used in renal failure patients. It binds phosphorus when taken with meals. Remember the inverse relationship of phosphorus and calcium. As phosphorus goes down, calcium goes up.
Monitor phosphorus levels!
Remember that vitamin D is needed to absorb calcium in the gut. You want to increase calcium, take vitamin D
IV calcium gluconate is given to patients in the hospital. Give slowly. Monitor EKG. Give via a central line because infiltration can cause phlebitis.
Monitor for dysrhythmias and prolonged QT interval
- Big one.
- For patients with hypocalcemia, the answer is most likely “Initiate seizure precautions”
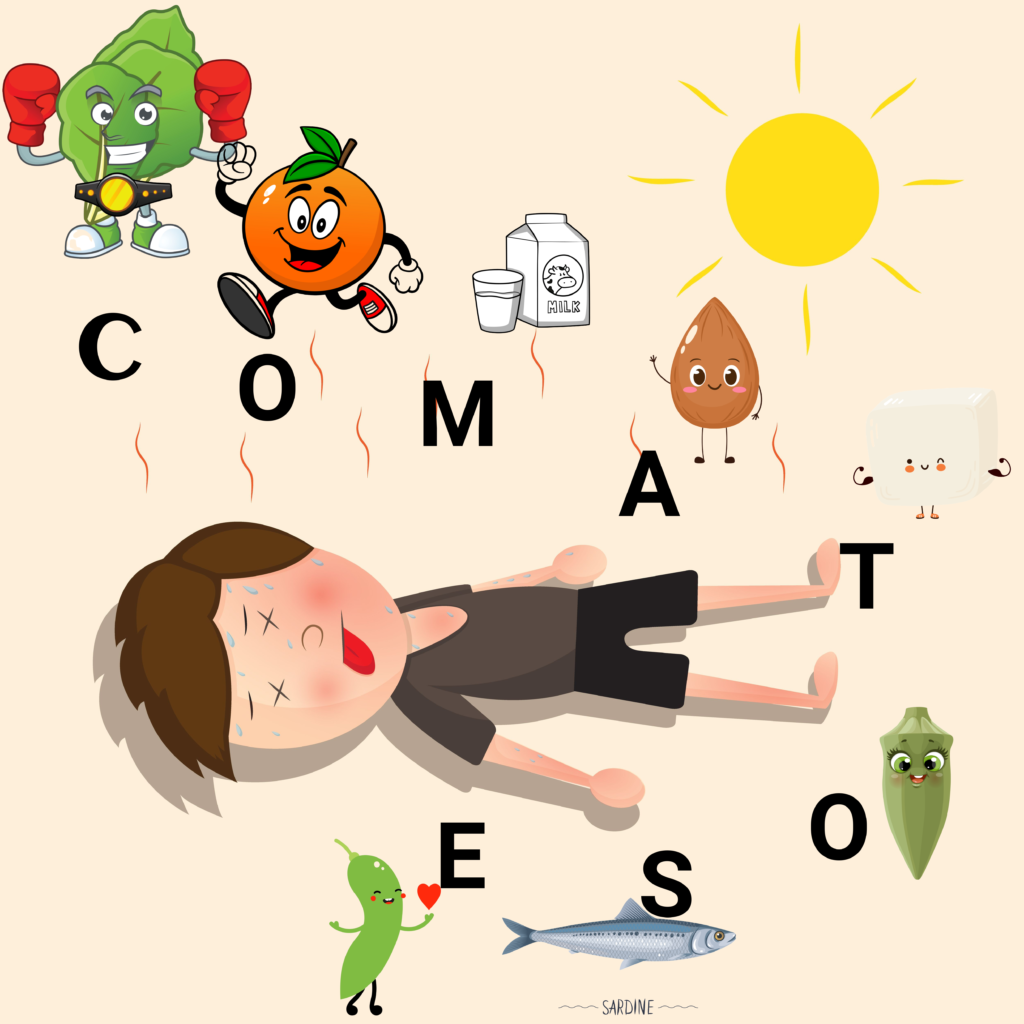
Remembering Foods High in Calcium. Think Comatose
Click on the letters to expose the content
Hypercalcemia over 10.4
Mnemonic for the causes of hypercalcemia
Click on the headings to expose the content
Chimpanzees


C Calcium Supplements
Too much calcium can cause hypercalcemia. Makes sense!
H Hyperparathyroidism
Remember, the ultimate goal of the parathyroid gland is to raise calcium. Yup, that simple!
I Immobilization
Due to prolonged bedrest the bones begin to release their calcium into the blood stream
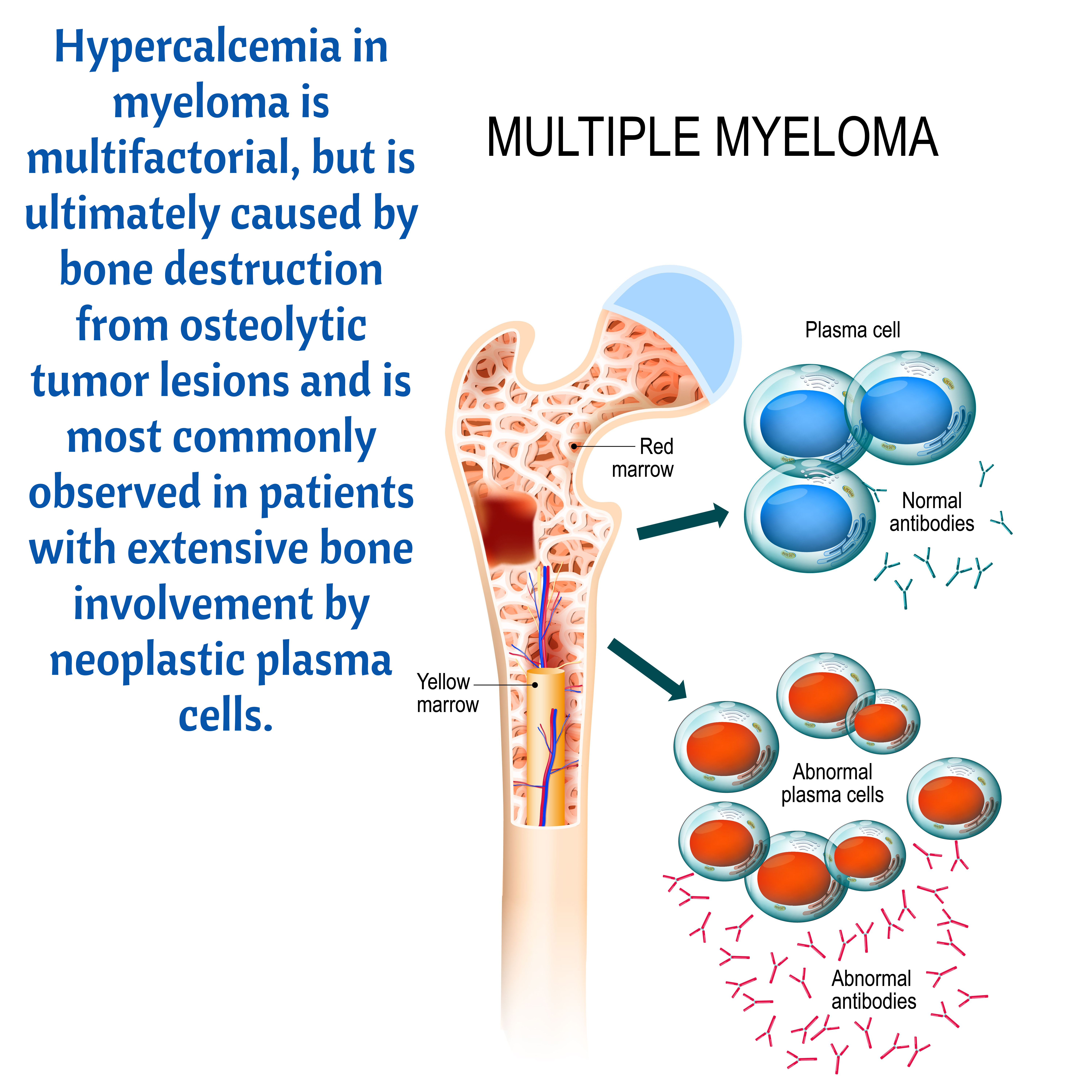
M Multiple Myeloma
- Due to malignancy, bones release calcium into the bloodstream.
- NCLEX: Hypercalcemia occurs in multiple myeloma.
P Phosphorus low
Remember that calcium and phosphorus are opposites.
High calcium⇒ low phosphorus
A Antacid with calcium (TUMS)Adrenal Insufficiency
- Makes sense. You take too much calcium and end up with hypercalcemia
- Adrenal insufficiency causes hypercalcemia! Remember! Adrenal insufficiency = hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and hypercalcemia
- Opposite is true. Too much adrenal hormone or Cushing Syndrome = HYPOCALCEMIA.
- Remember that steroids can lead to osteoporosis (which is due in part to hypocalcemia).
- So if a client tells you they have joint pain and they are taking steroids, think osteoporosis!
N Neoplasms
Cancer again.
Z Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Increased gastrin levels in this syndrome is associated with hypercalcemia
E Excessive Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps calcium be absorbed in the gut. Too much vitamin D and more calcium is absorbed.
E Excessive Vitamin A
Chronic ingestion of vitamin A beyond the recommended daily amount can be associated with increased bone resorption, reduced bone formation, hypercalcemia, and increased risk of fractures.
S Sarcodoisis
Sarcoidosis is a condition that develops when cells in your immune system form lumps, called granulomas, in the body’s organs. This is due to increased production of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D. There is that vitamin D again. Repeat after me: Vitamin D increases the absorption of calcium and can cause hypercalcemia.
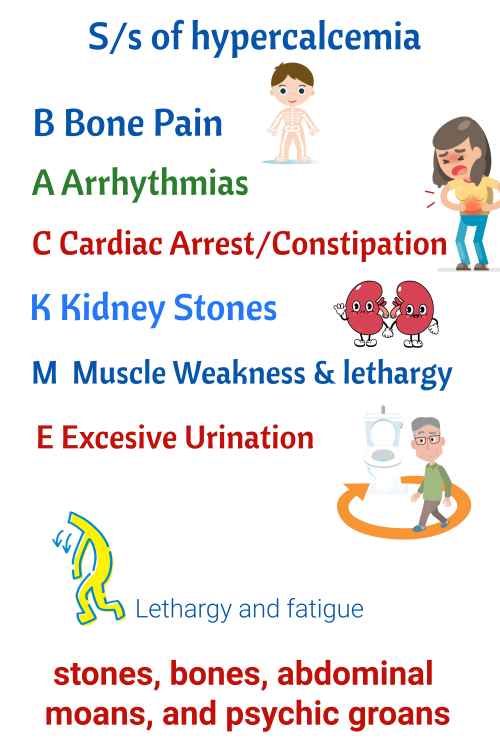
Stones, Bones, Abdominal Moans and Psychic Moans
GenitoUrinary
- Kidney Stones
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
Muscles/Bones
- Bone pain
- Joint pain
- Bone fractures
- Muscle weakness
Digestive
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Anorexia
- Weight Loss
- Abdominal Pain
- Constipation
Brain
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Lethargy
- Confusion
- ↓ Deep Tendon Reflexes
Think Low and Slow
- Profound muscle weakness (slow and low)
- ↓ DTRs (low and slow)
- Lethargy and coma (Slow Brain)
- Hypoactive bowel sounds and constipation
- Monitor respiratory status (weak breathing muscles).
- Hypercalcemia is an oncological emergency (bone metastasis).
- Serious signs in hypercalcium due to metastatic cancer: ↓ DTRs, paralytic ileus, dehydration from polyuria, EKG changes, severe muscle weakness, and renal impairment.
Interventions for hypercalcemia

Pay Attention
- Discontinue calcium and Vitamin D (Vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium).
- NO thiazide diuretics (INCREASE calcium)
- Loop diuretics DECREASE calcium.
- Administer phosphorus, calcitonin, bisphosphonates (Alendronate Fosamax), and prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors: all ↓ calcium
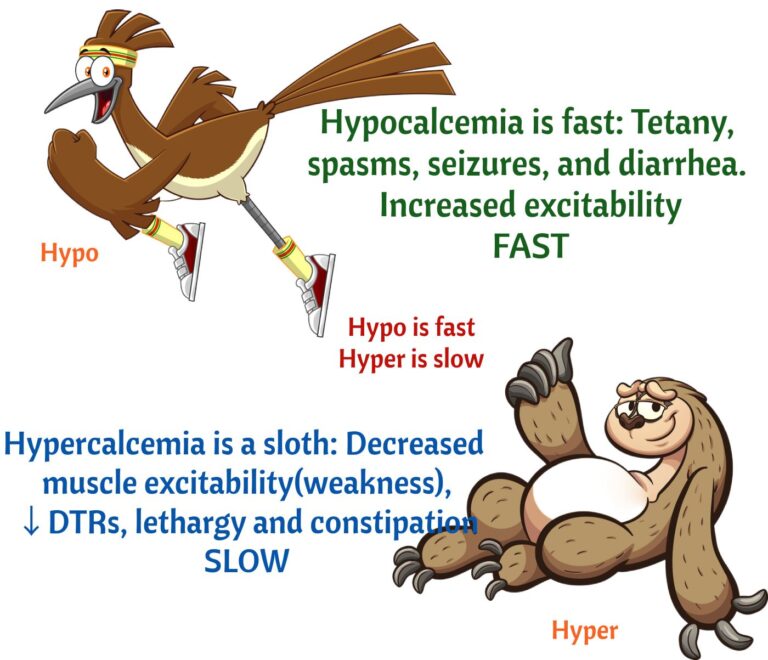
Difference between hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia
Let's test your knowledge
Quiz Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 1 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
Specific by typing an X whether it is describing hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia. ( You do know that the new NCLEX exam will have matrix multiple response questions. This question is as complex as it gets. After doing this matrix multiple choice, you should know every thing there is to know about hypercalcemia and hypercalcemia)
-
Description Hypocalcemia Hypercalcemia Must eat sadines, tofu, rhubard, and collard greens Getting too much Vitamin D Must avoid sardines, tofu, and collard greens Muscle cramps and hyperactive DTRs Hypoactive DTRs Trousseau’s Sign Chvostek’s Sign Renal Calculi Decreased Bowel Sounds Diarrhea Constipation Tx is calcitonin Give phosphorus Metastatic Cancer Pancreatitis Crohn’s Disease Chronic Adrenal Insufficiency Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism Stridor/watch airway Tetany After thyroidectomy watch for… treated with calcium gluconate Fractures Cardiac Arrhythmias
CorrectIncorrect -
Prevent Bone Fractures
- Hypercalcemia complications can include: Osteoporosis. If the bones continue to release calcium into the blood, the bone-thinning disease osteoporosis develops, which could lead to bone fractures, spinal column curvature and loss of height.
- Hypocalcemia can cause poor bone formation and brittle bones that are prone to fractures.
- Both hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia may lead to bone fractures!
- FALL PRECAUTIONS!




 Oranges
Oranges
 Almonds
Almonds
 Okra
Okra Sardines
Sardines
