Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip

What is it?
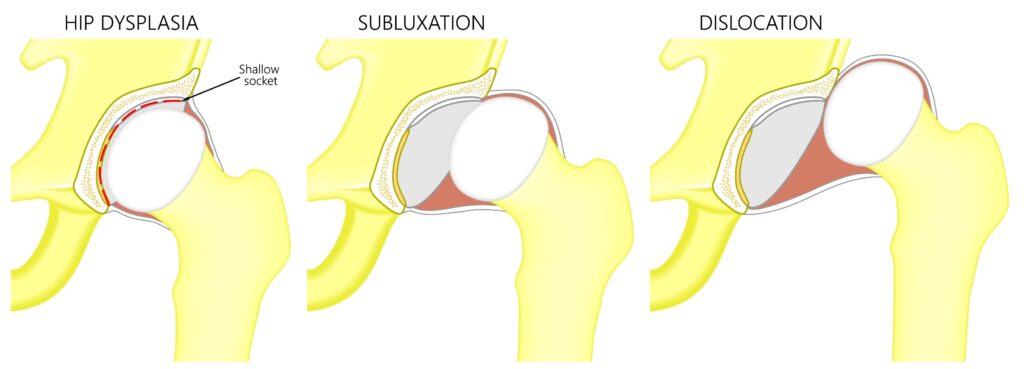
The hip joint is considered dysplastic when the ball (femoral head) and the socket (acetabulum) do not fit properly together. It lead to dislocation or subluxation of the hip, instability of the joint, and uneven leg length.
Symptoms

- Shortening of affected hip
- Restricted abduction of the affected hip
- Unequal gluteal folds
- Positive Ortolani’s test: Examinaer abducts hip, applies gentle pressure over greater trochanter and feels a “clicking” sensation which indicates a dislocated femoral head moving into the acetabulum.
- Positive Barlow’s test: Examiner adducts hips, applies pressure down and back with thumbs. Examiner can feel head move out of the acetabulum.
- Older children: Limping, waddling gait, lordosis, affected leg is shorter.

Interventions
- Birth to 6 months: Pavlik harness to maintain flexion, abduction, and external rotation of the hips.
- 6 to 18 months: gradual reduction, a spica cast for 2-4 months, and then a flexion-abduction brace for about 3 months.
- Notice the order of treatment.
