What is it?
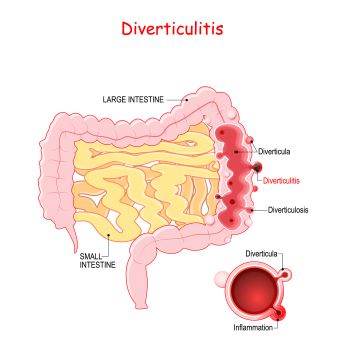
Diverticulitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation or infection of small pouches called diverticula that can form along the walls of the colon (large intestine). These pouches typically develop in weakened areas of the colon, particularly where blood vessels pass through the muscular walls. When these pouches become inflamed or infected, it leads to diverticulitis.