Epiglottitis
Bacterial Infection

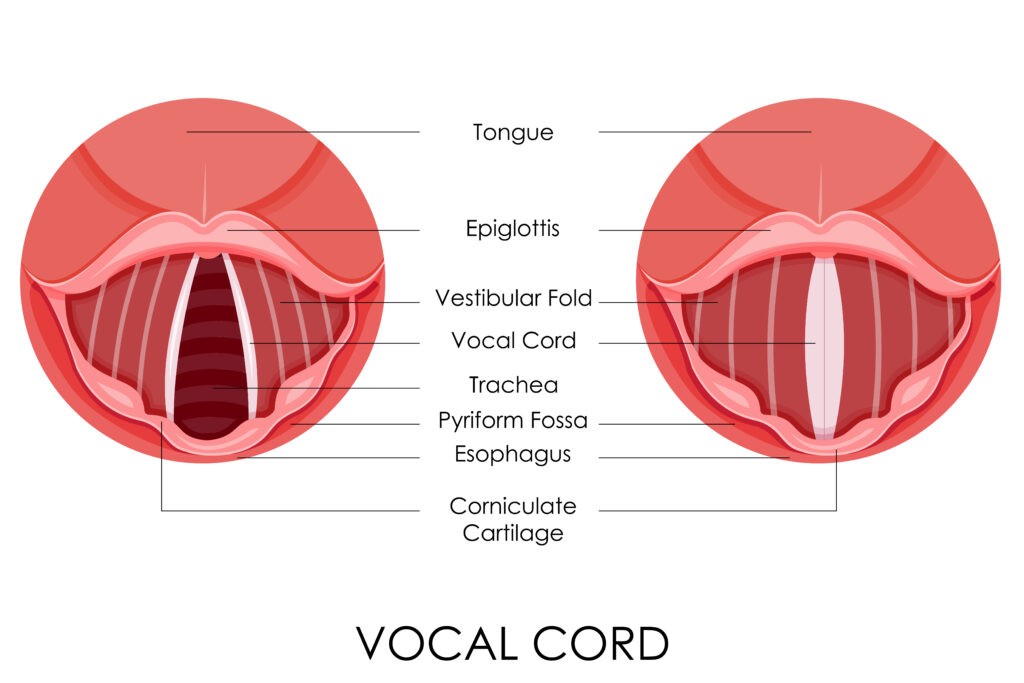
Epiglottitis is a emergency medical condition in which the epiglottis, a flap of tissue that prevents food and liquid from entering the windpipe during swallowing, becomes inflamed and swollen. This can result in a blocked airway, making it difficult to breathe. Most commonly caused by a bacterial infection, but can also result from a viral infection or injury to the throat. Organisms: Haemophilus Influenzae typbe B and Streptococcus pneumoniae.



Symptoms
- High fever
- Sore throat
- Cherry red epiglottis
- Difficulty swallowing
- Painful swallowing
- Absent of cough
- Drooling
- Muffled voice
- Rapid breathing
- Stridor (a harsh, raspy sound when breathing)
- Cyanosis if airway is obstructed
- Anxiety
- Restlessness
- Tripod position with chin thrusted forward and mouth open to keep airway open
- Severe: hypoxia, hypercapnia, tachycardia, ↓ LOC
- Sudden death

Treatment
- Maintain airway
- Assess respiratory status
- Monitor temperature. DO NOT DO ORAL TEMPERATURE
- No throat culture. Avoid inspecting epiglottis
- NPO with IV fluids
- IV antibiotics followed by oral once swelling is reduced
- Corticosteroids may be used
- Acetaminophen for fever
- Have tracheostomy/intubation tray at the bedside
- Maintain calm/quiet environment
- Make sure children have Haemophilius influenzae type B (Hib) vaccine to prevent epiglottitis

