Disaster Triage, Prioritizing, and Delegation
4 Topics | 2 Quizzes
Neurological System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
MS, MG, and Guillain Barré
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The Cardiovascular System
12 Topics | 1 Quiz
Pulmonary System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cushing Versus Addison Disease
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Thyroid Disorders
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Parathyroid Disorders
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
DI and SIADH
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Diabetes
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Burns
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Anemias, Aplastic Anemia, Polycythemia Vera, Thrombocytopenia and DIC
9 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Oncological Emergencies
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Leukemias, Hodgkin’s Disease, and Multiple Myeloma
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The GI system
16 Topics | 1 Quiz
Renal and Genitourinary Problems
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Infection and Isolation Precautions
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
NCLEX Pharmacology
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
TPN, IV Solutions, & Blood Products
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Lab Values
9 Topics
Famous Clinical Signs
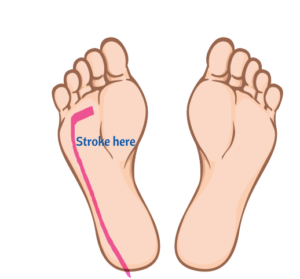
- Dorsiflexion of the big toe after stimulation of the lateral sole.
- It is normal for toes/great toe to curl down (flexion), but positive Babinski if toes curl up (dorsiflexion)
- Normal in children up to 2 years of age.
- Associated with corticospinal tract lesions in adults
- In newborns, reddening of one side of the body while the other is pale or has no color change. It is due to temporary vasomotor disturbance.
- Benign due to autonomic nervous immaturity in infants.
- Abnormal in adults. Needs MRI to find neurological problem.
- Name comes from this funny looking clown character who wears clothes with different color on each side.

- Severe neck stiffness that causes a patient’s hips and knees to flex when the neck is flexed.
- Due to meningeal irritation (Meningitis).
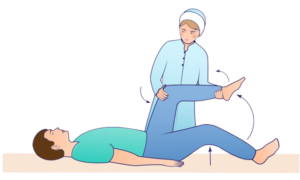
- Patient is kept in supine position, hip and knee are flexed to a right angle, and then knee is slowly extended by the examiner. Pain during extension of the patient’s knees beyond 135 degrees constitutes a positive Kernig’s sign meningeal irritation (meningitis)
- Bluish Discoloration around the umbilicus
- Seen in acute pancreatitis
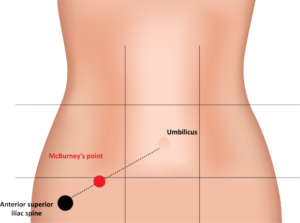
- Deep Tenderness at the Mcburney’s point.
- Sign of appendicitis
- Pain in the right lower quadrant when pressure applied to left lower quadrant.
- A sign of appendicitis
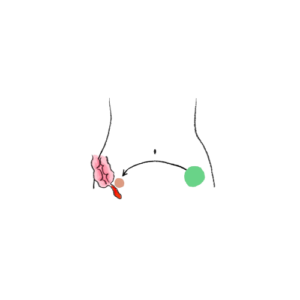
- Softening of the fundus of the uterus.
- Associated with first trimester pregnancy
- The fundus is the top area.
- Cyanosis of vaginal and cervical mucosa.
- Associated with pregnancy.

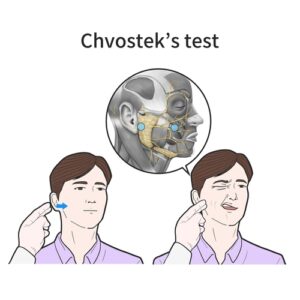
- Facial muscle spasm induced by tapping on the facial nerve (in front of earlobe) due to hypocalcemia
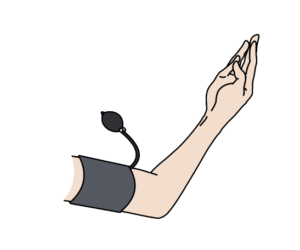
- Carpopedal spasms by inflatting blood pressure cuff.
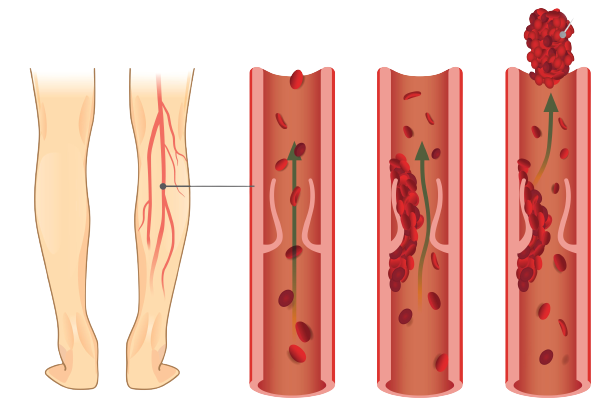
- Pain behind the knee, induced by dorsiflexion of the foot.
- Indicates possible deep vein thrombosis.
- The pain is caused by the compression of the clot against the vessel with dorsiflexion.