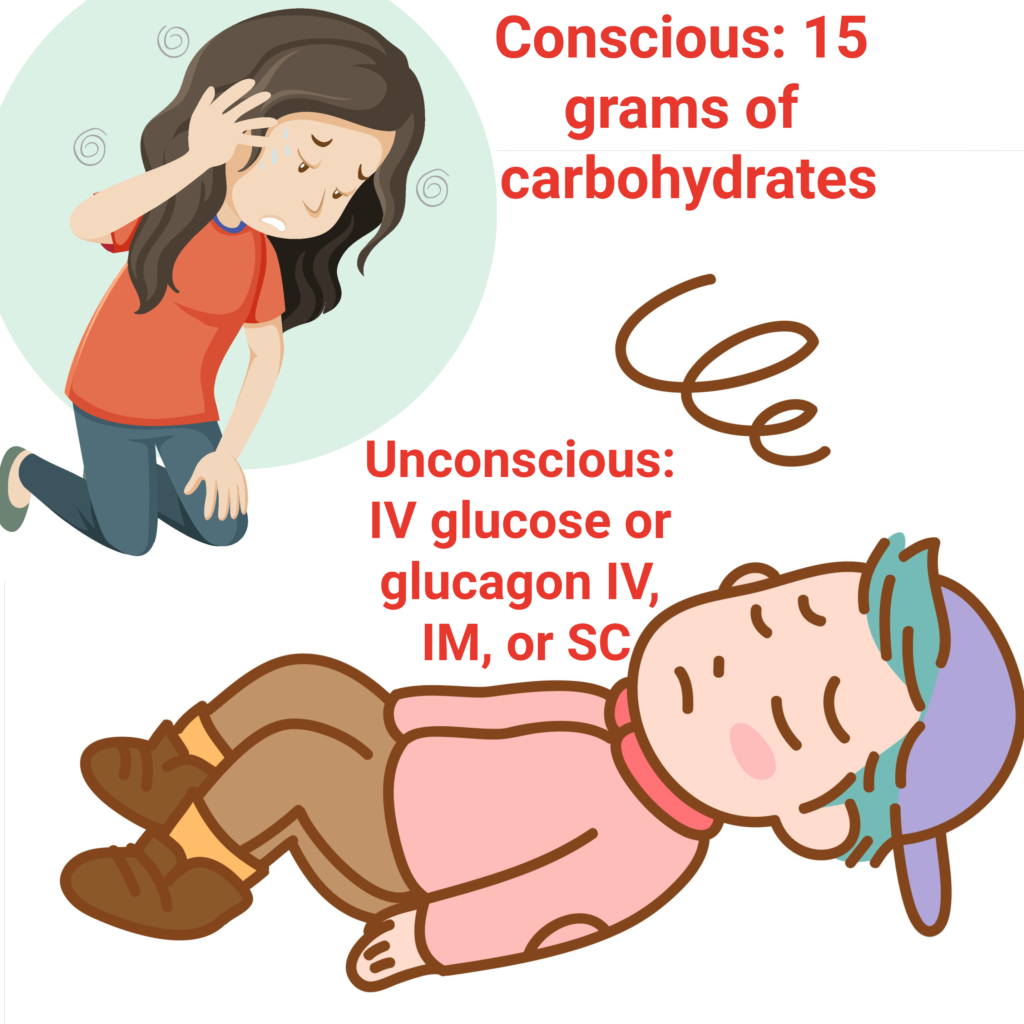
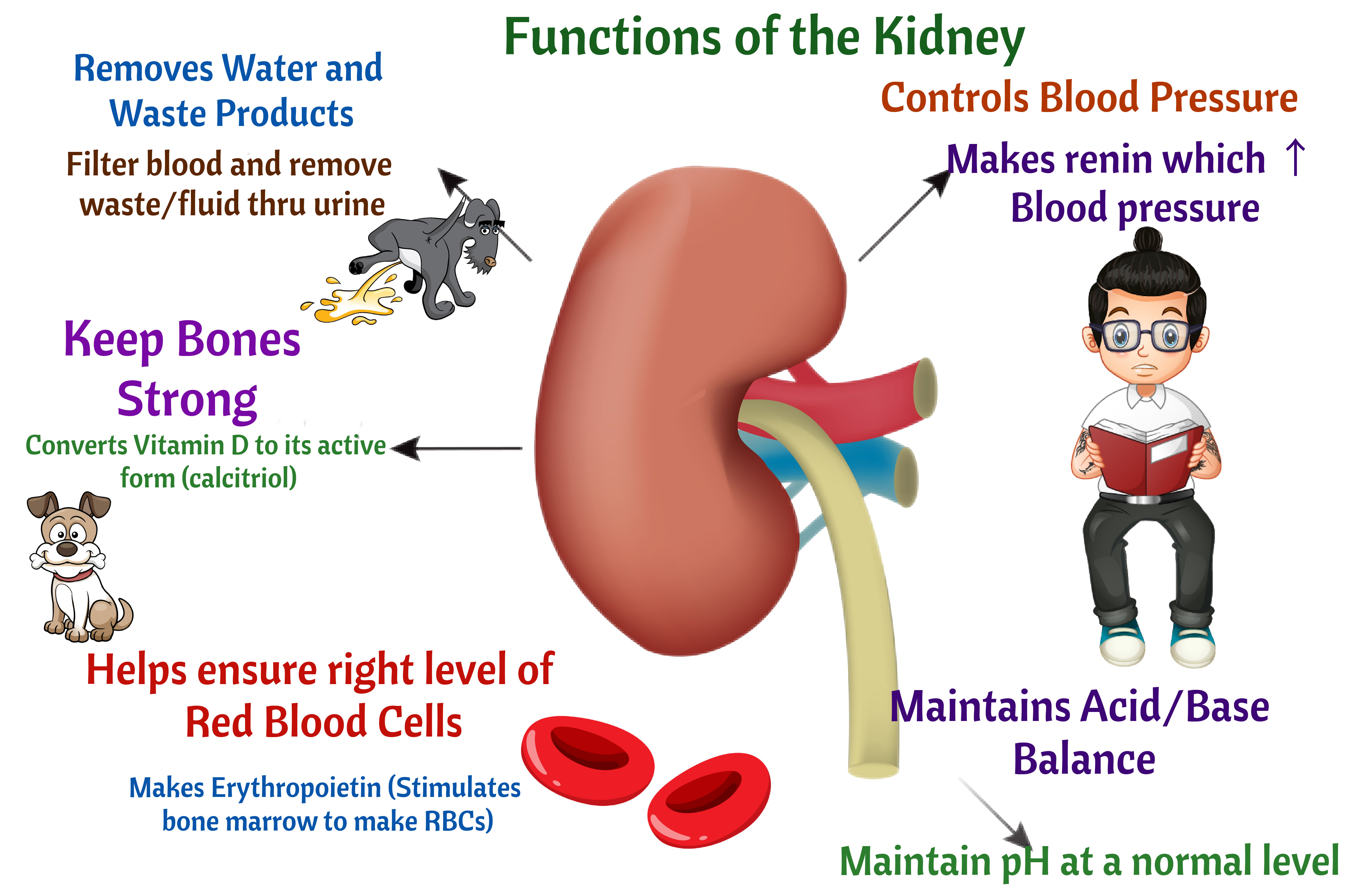
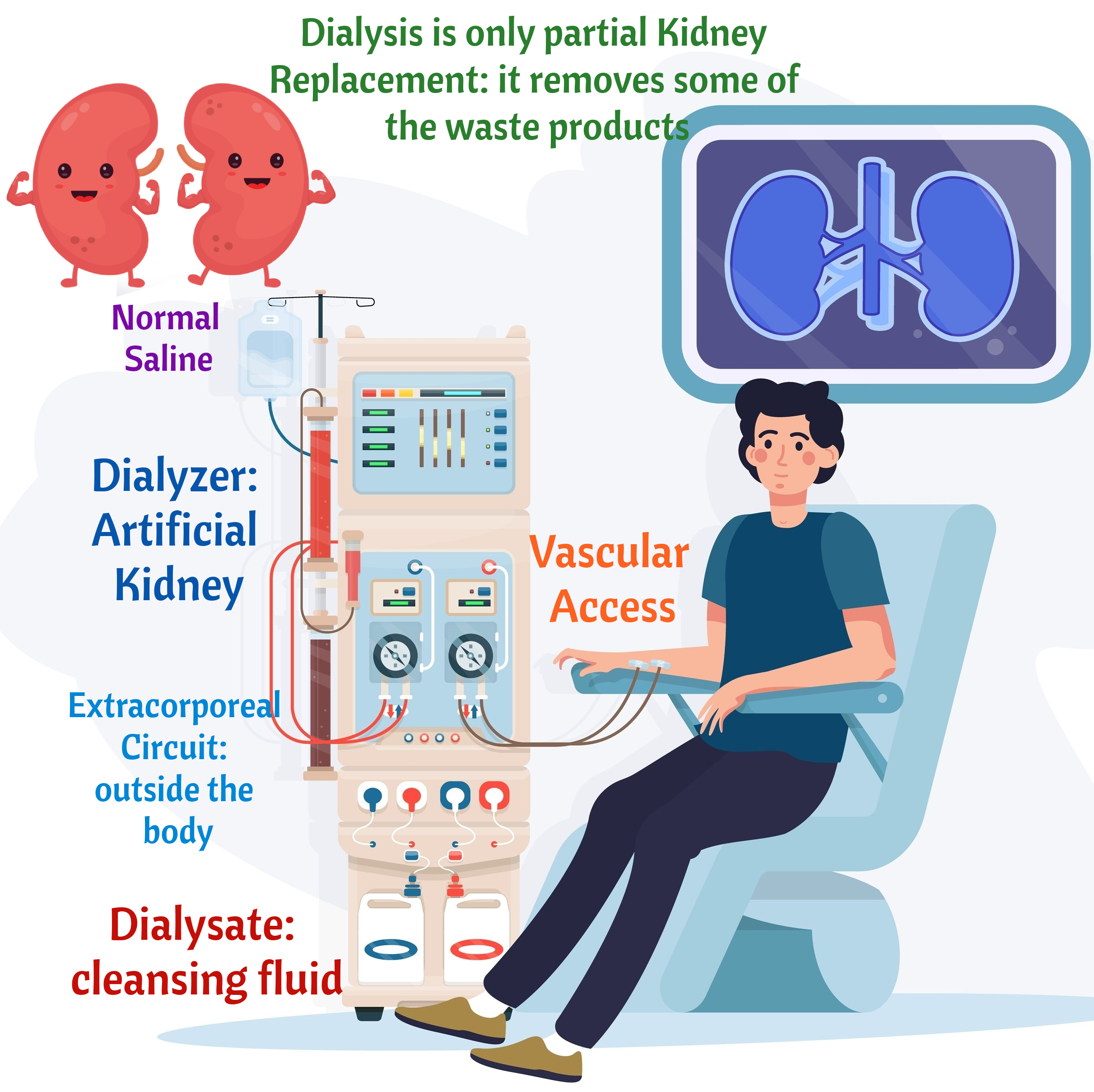
Flashcards!
 Weight with same scale before breakfast
Weight with same scale before breakfast
- Diarrhea
- Hemorrhage
- DKA
- Hyperventilation (We lose moisture through our breath)
- Polyuria
- Sensorium (LOC)
- Urine output
- Skin turgor
- CFT
- Think tissue perfusion as best indicators.
- E.g., BP would not be a good indicator. You can have a good BP as a compensatory mechanism, but not good tissue/renal perfusion.
We lose about 1 Liter/1Kg of fluid daily (GI tract, perspiration)
 Have low oncotic pressure, low albumin, low protein stores. There are NO large molecules keeping fluid/water inside the vascular space. Oncotic pressure is the pressure exerted by large molecules in the blood to keep fluid inside the vessels.
Have low oncotic pressure, low albumin, low protein stores. There are NO large molecules keeping fluid/water inside the vascular space. Oncotic pressure is the pressure exerted by large molecules in the blood to keep fluid inside the vessels.
 Think restlessness, agitation, confusion
Think restlessness, agitation, confusion
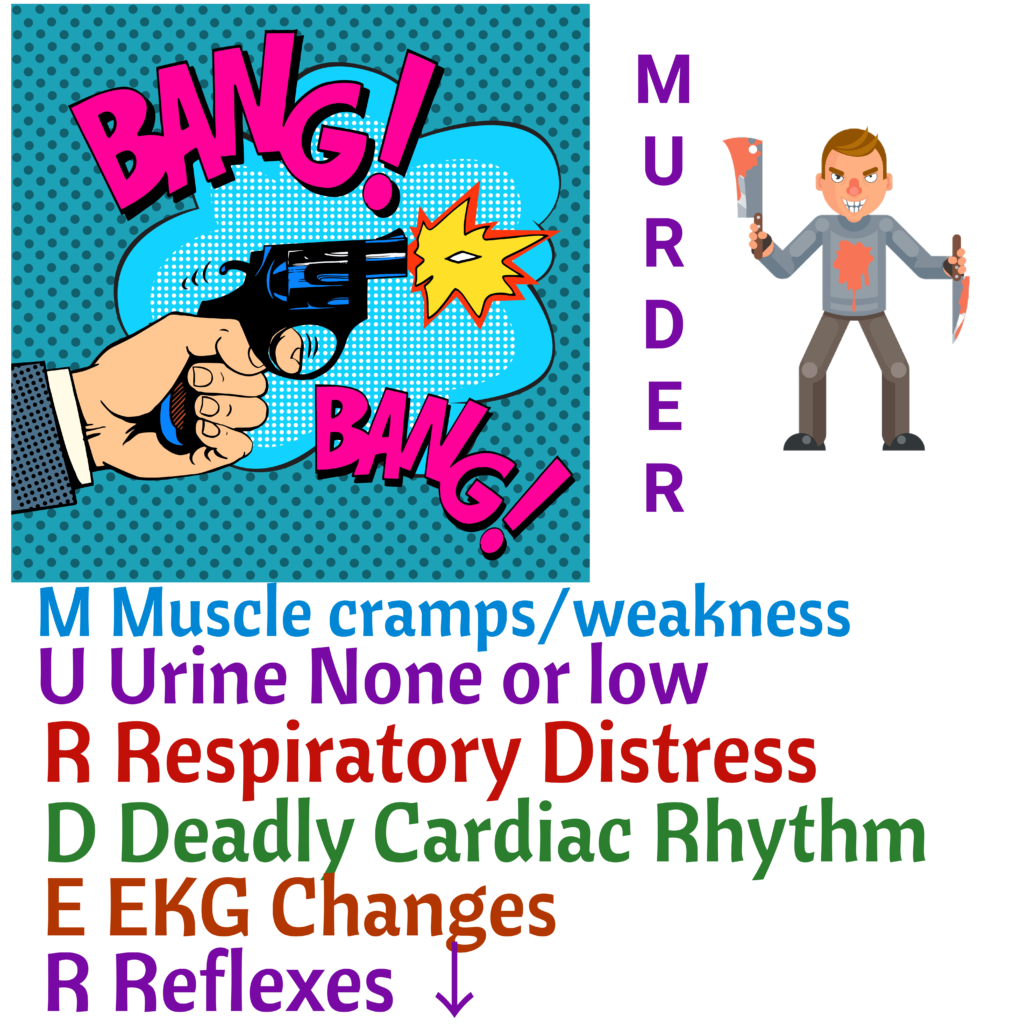
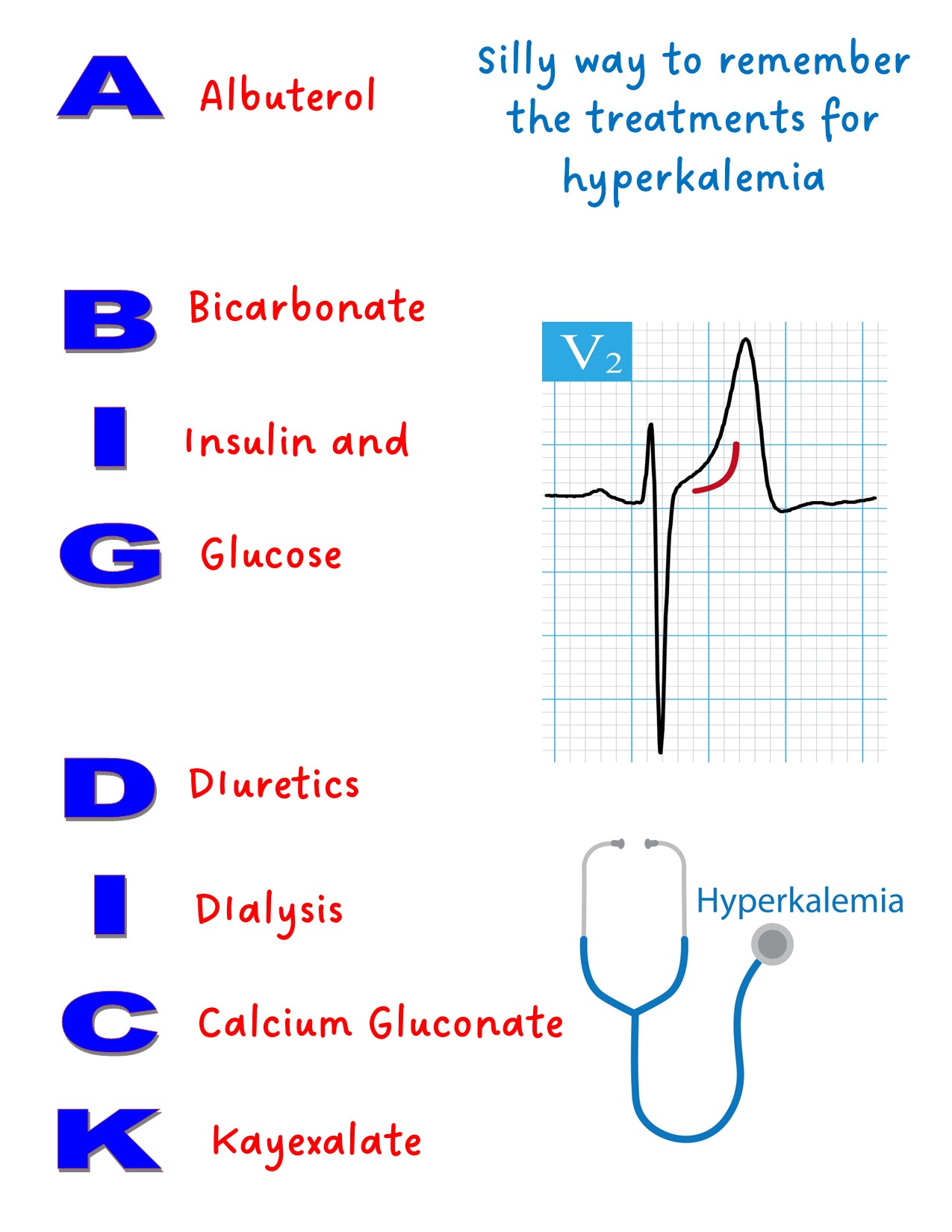
Hyperkalemia = high potassium
Fluid volume deficit
- Sodium, potassium and chloride.
- Two hormones that affect BP are Renin and Aldosterone
- Aldosterone ↑ sodium and chloride and ↓ potassium. High sodium tends to increase BP
- Chloride and sodium are roommates. They change together. They go up together and go down together. Think of sodium
 chloride (NaCl)
chloride (NaCl)
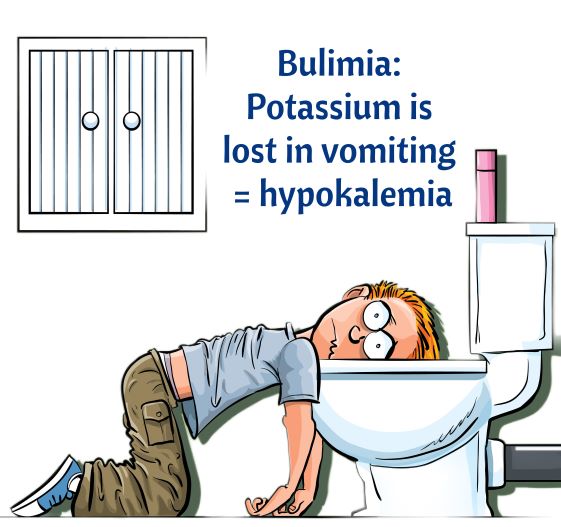
- Hypokalemia
- Hyponatremia
 Swollen/edematous
Swollen/edematous
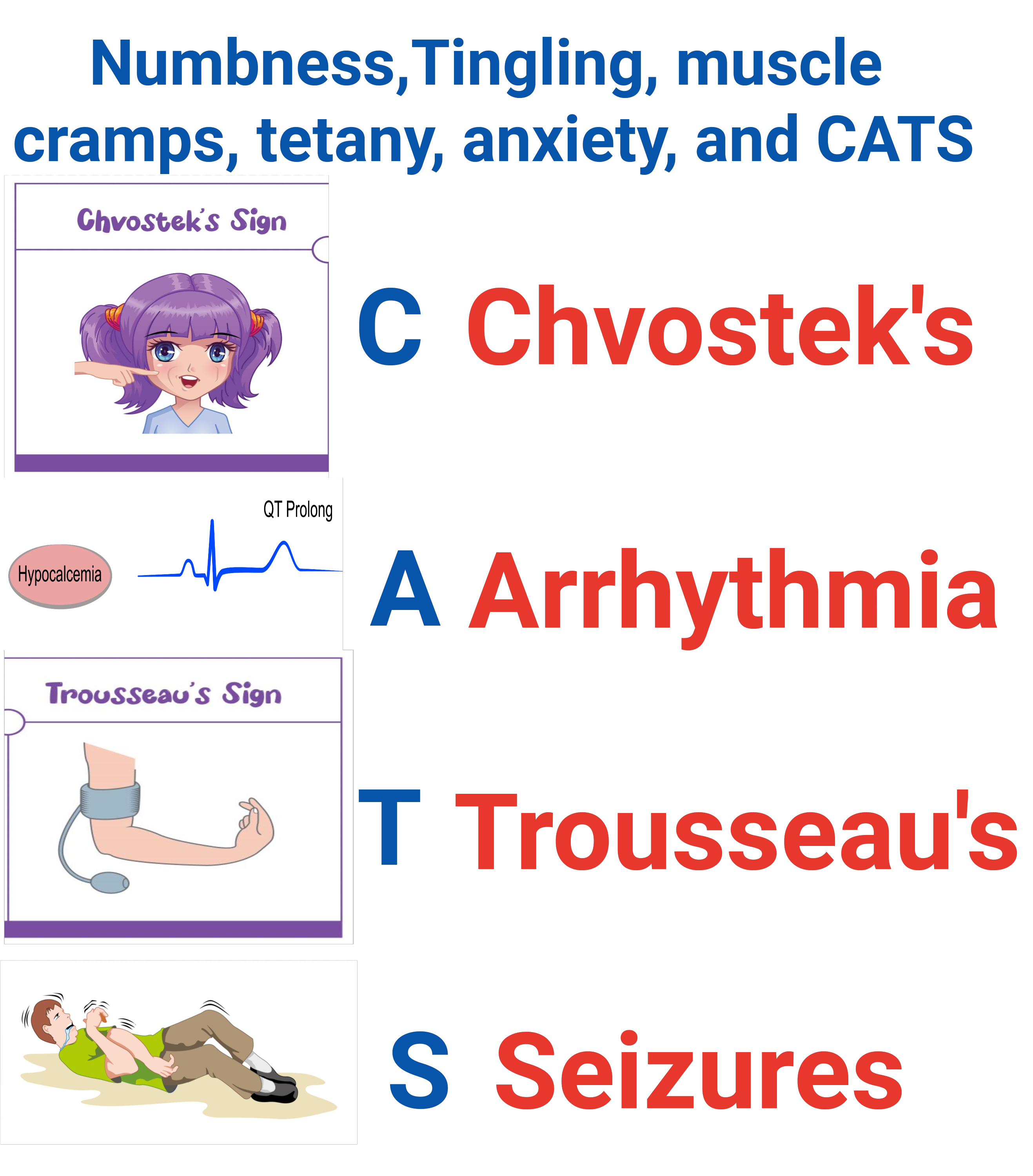
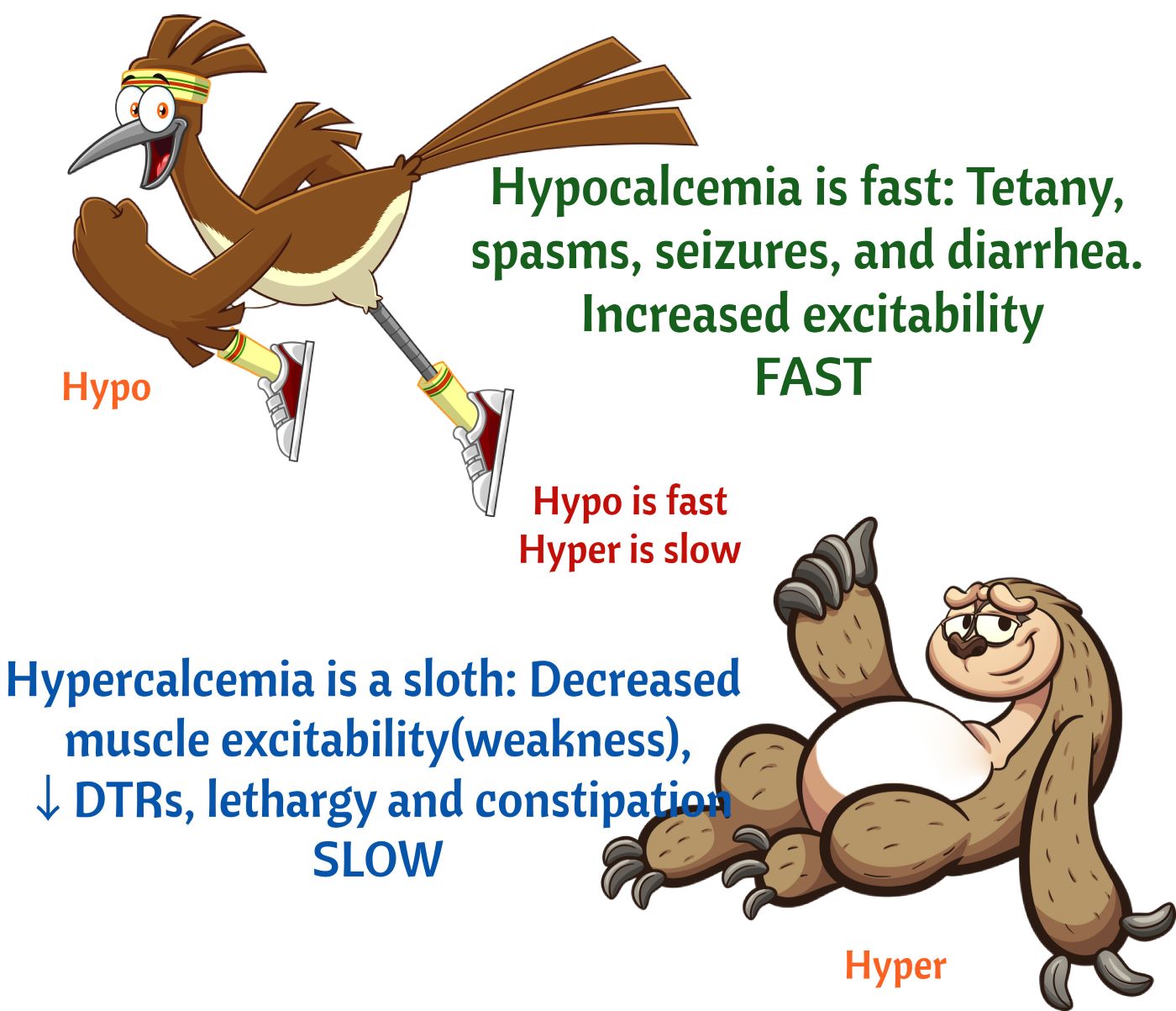
 Neurological symptoms such as restlessness, agitation, seizures, lethargy, and even coma.
Neurological symptoms such as restlessness, agitation, seizures, lethargy, and even coma.
 Muscle weakness, headache, confusion, abdominal cramping.
Muscle weakness, headache, confusion, abdominal cramping.
- Potassium
- Watch for low potassium if giving Furosemide or Hydrochlorothiazide (potassium-wasting diuretics).
- Watch for HIGH potassium if giving Spironolactone (a potassium-sparing diuretics)
 Infants and older adults
Infants and older adults
- Hyponatremia (low sodium)
- Fluid overload
- Kidney Failure
- Heart Failure (CHF)
- Via an infusion pump
- Never IV push
- Give 10 mEq/Hour or per protocol
- If given via a peripheral IV, it will burn.
- Administer potassium to clients with good kidney function and good urine output only.
- Make sure you know the client’s potassium level before administering it.
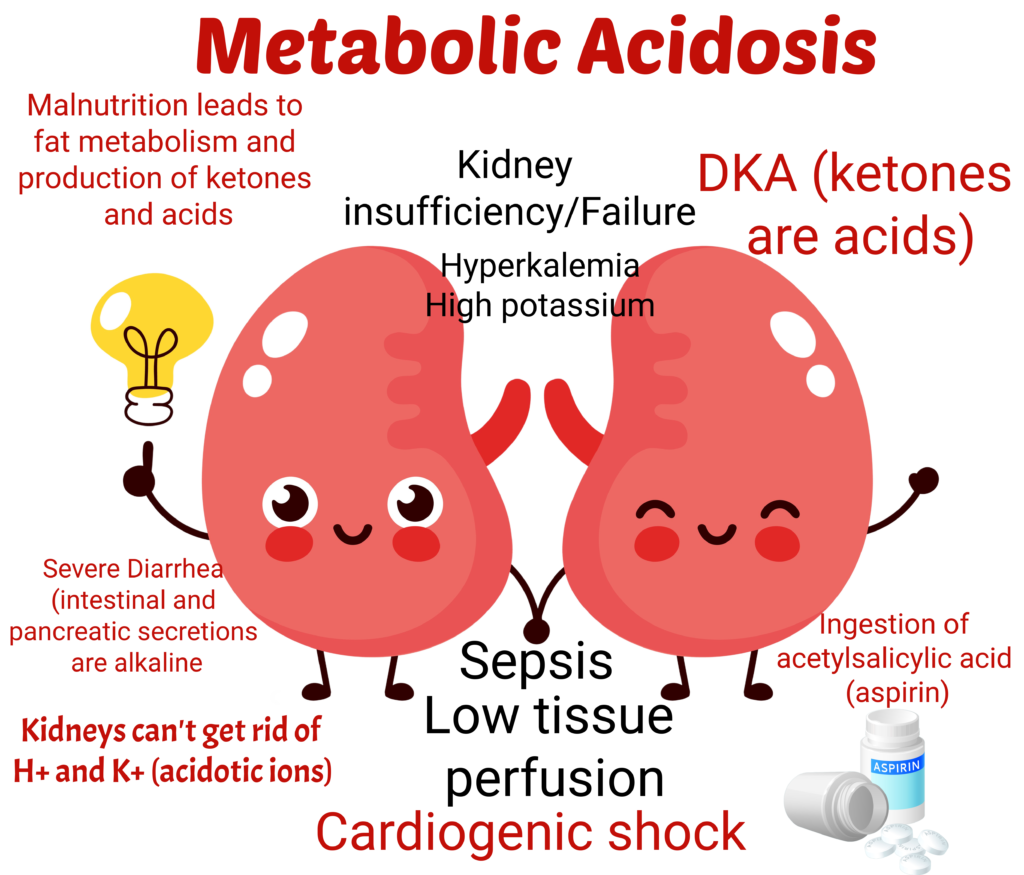
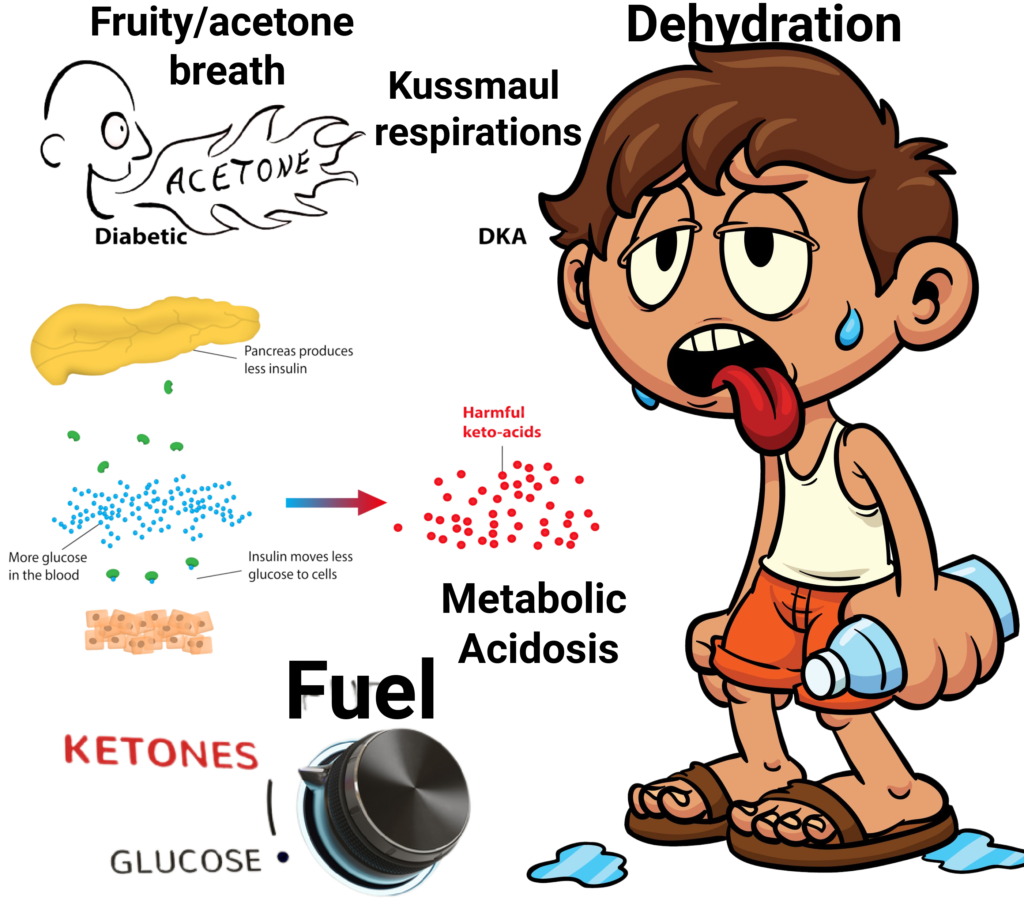 Metabolic Acidosis due to an inadequate supply of insulin occurs in DKA
Metabolic Acidosis due to an inadequate supply of insulin occurs in DKA
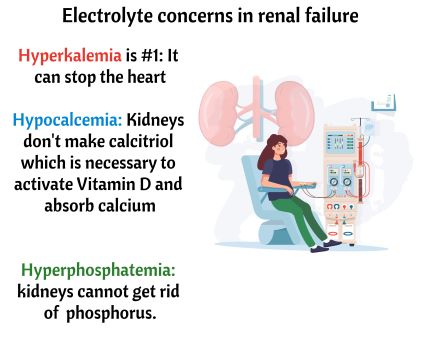
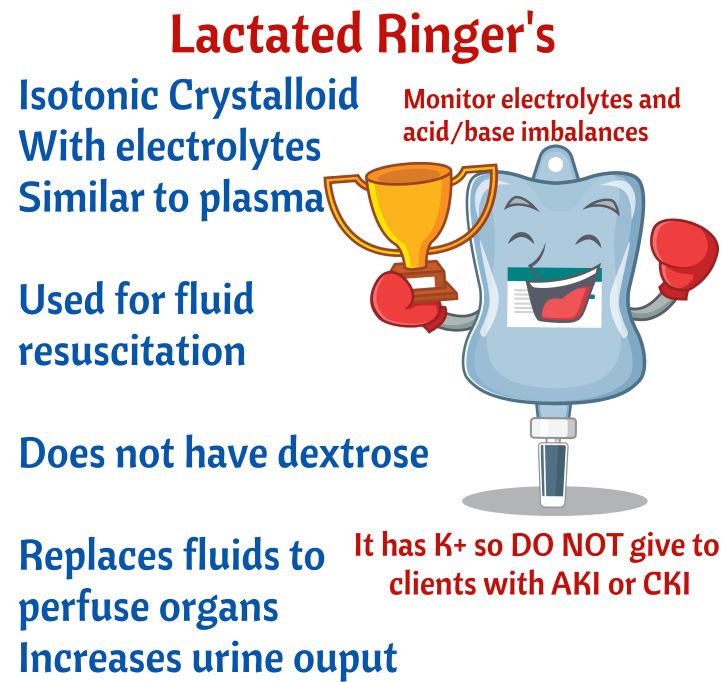 Do not give to clients with Chronic or Acute renal failure due to potential hyperkalemia. It has K+
Do not give to clients with Chronic or Acute renal failure due to potential hyperkalemia. It has K+
Hyponatremia precipitates Lithium toxicity!

- Volume excess.
- They retain fluid due to low urine output.
- Restrict fluids

- Never increase rate to catch up. Keep it at the rate ordered by MD

- Sit upright
- Dangle feet (feet dependent position)
- Slow IV fluids


Remember that in acid/base imbalances, potassium moves either in or out of cell to maintain balance.
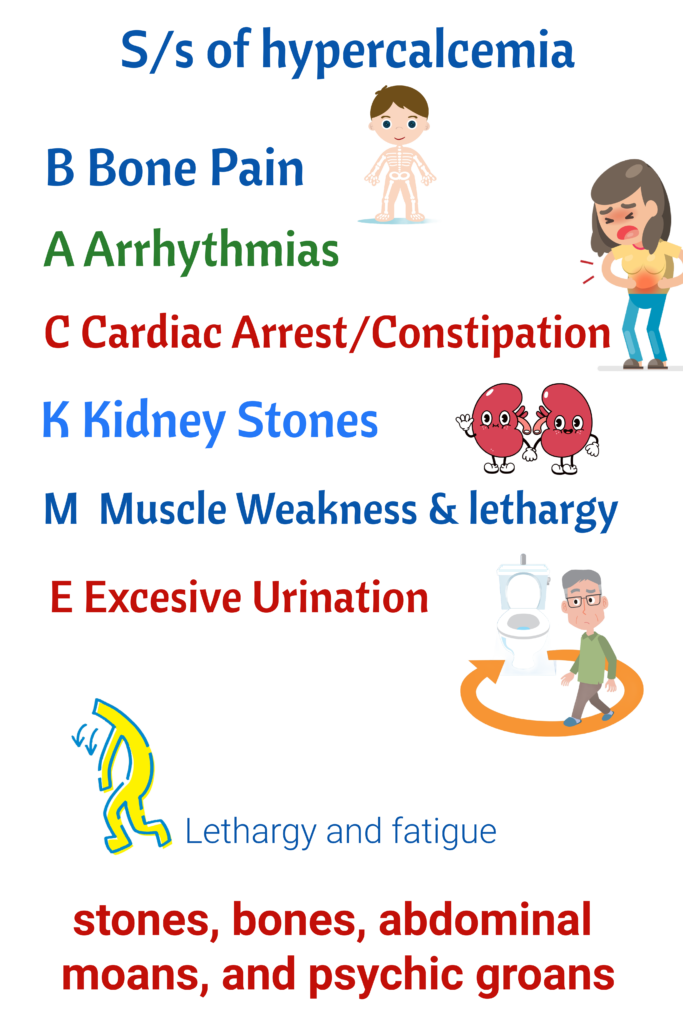
- Monitor for fractures.
- Handle client with care
- Assist with ambulation

Metabolic Acidosis
Metabolic Alkalosis

Anything that suppresses respiratory function, monitor for respiratory acidosis. E.g., Opioid or Benzodiazepine overdoses
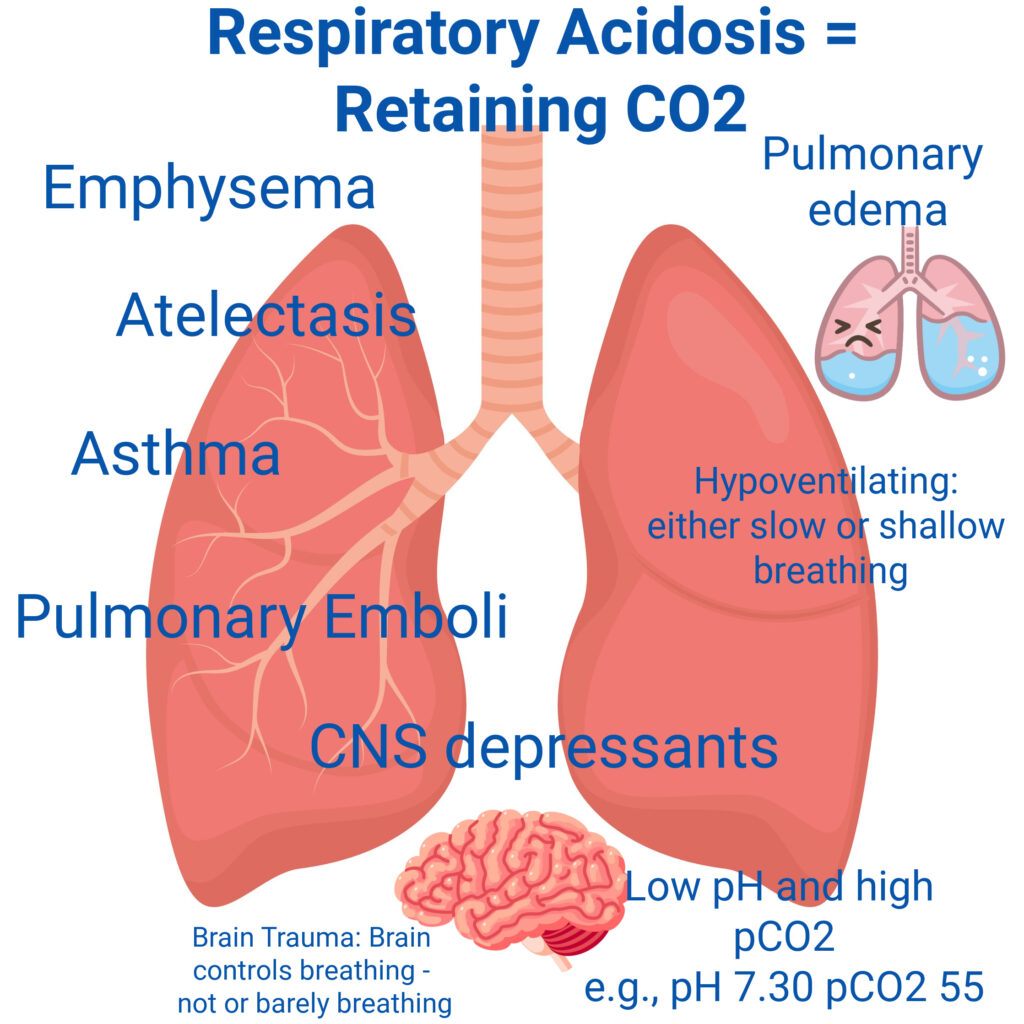
Overstimulation of the respiratory system leading to fast and deep breathing.

- Think Compensatory mechanism!
- In metabolic acidosis, breathing will increase/become deeper to blow off CO2 (exhale acids) to compensate for the acidosis or normalize pH. Example, in DKA, the client is acidotic so breaths fast (Kussmaul respirations).
- In metabolic alkalosis, the client will breath slower/shallow to retain CO2 and balance pH.
Metabolic Alkalosis
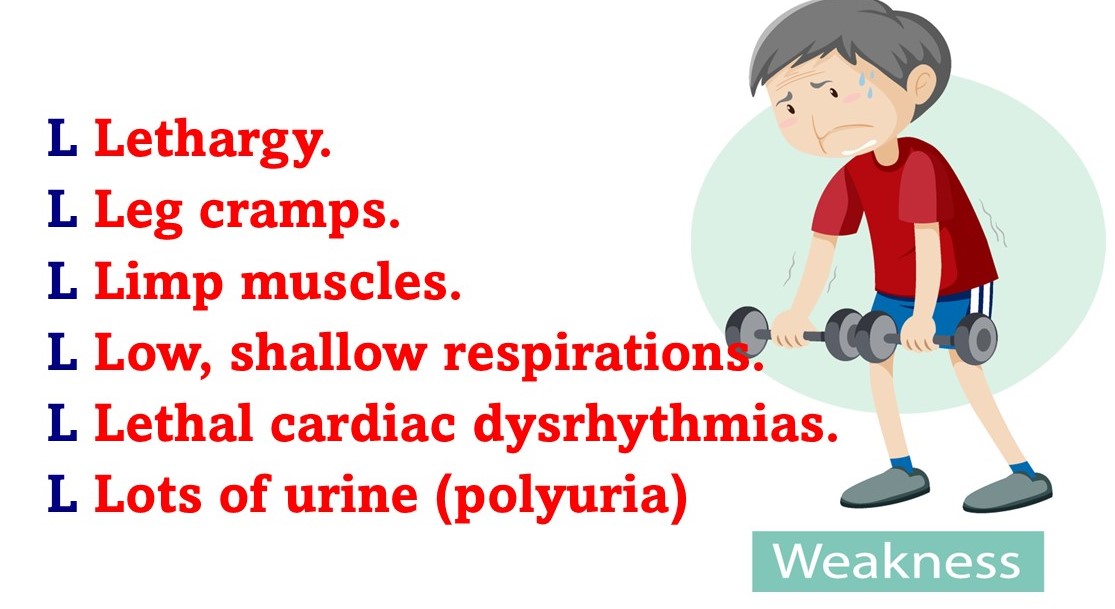
Hypokalemia Signs and Symptoms
Lethal Arrhythmias

Watch for Cardiac Dysrhythmias
- Calcium gluconate is the antidote of magnesium overdose.
- Clients with eclampsia get infusion of magnesium sulfate so have calcium gluconate ready in case of overdose. Hypermagnesemia causes depressed respirations and ↓ Deep Tendon Reflexes.
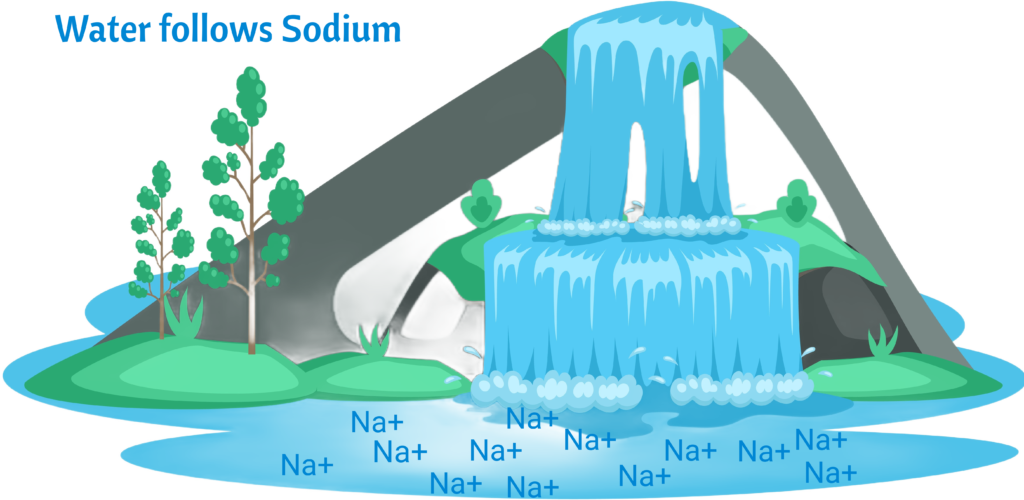
Water follows sodium so sodium restriction in clients with CHF and Renal Failure to prevent fluid overload
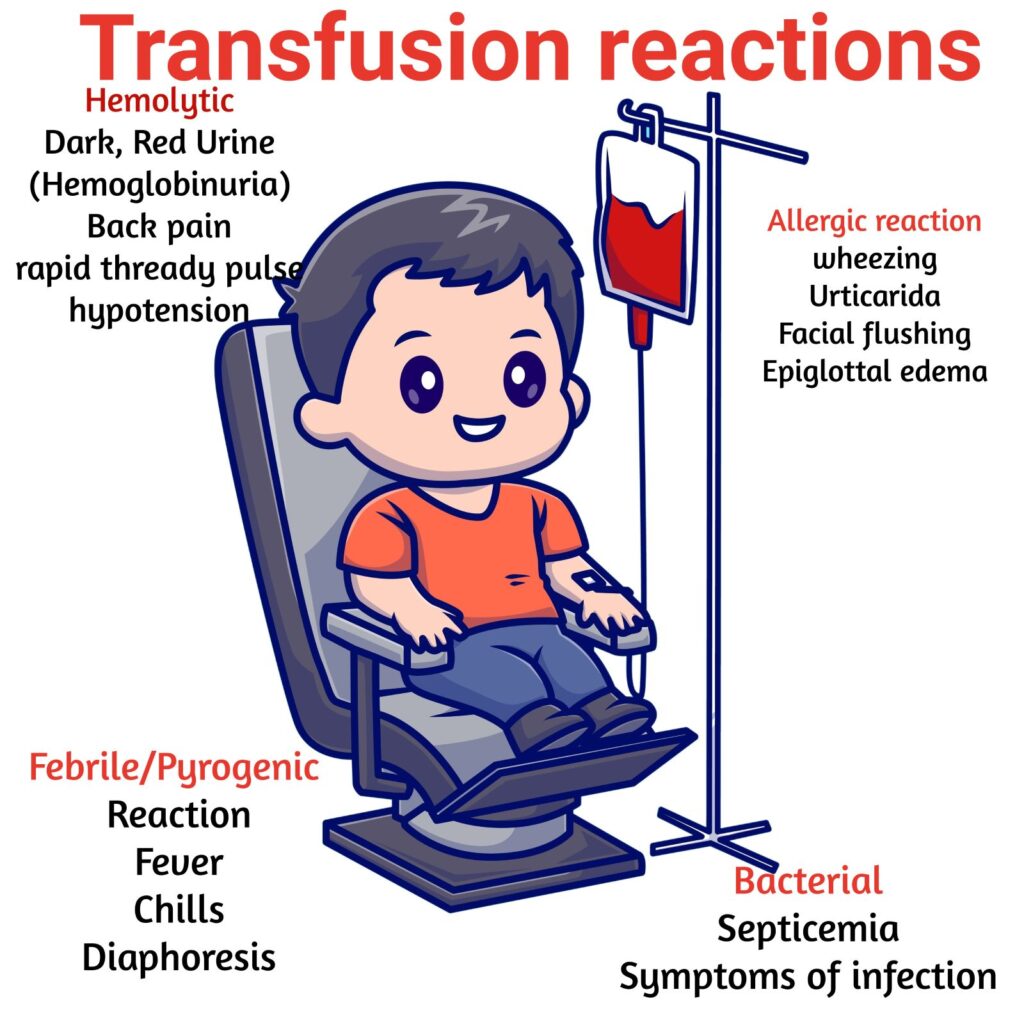
- Stay with client at least for the first 15 minutes. This is when a reaction is most likely to occur.
- Monitor vitals every 30 minutes or per protocol.
- Stop transfusion is reaction occurs.
- Only use warming devices for blood products. Never use microwave or hot water!
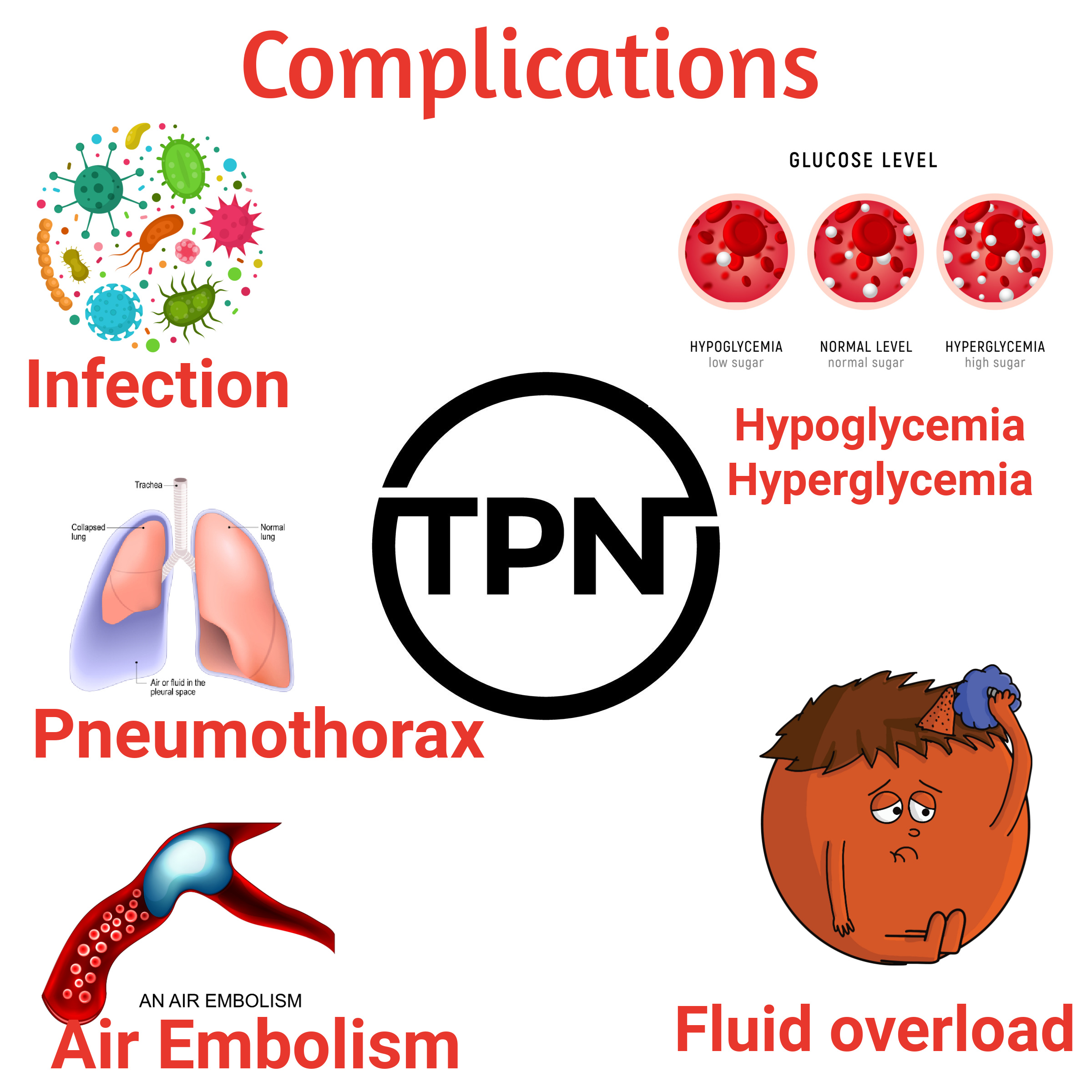
- TPN is hypertonic and may cause sclerosis, phlebitis, or swelling if given peripherally. Must be given through a central catheter or peripherally-inserted central catheter.
- PPN or Peripheral Parenteral Nutrition may be given through a peripheral IV. It is isotonic or mildly hypertonic since it has < 12.5% glucose.
- NG or oral feeds are preferrable to TPN or PPN.
- May be given peripherally
- May be mixed with TPN or given separately
- Check for egg allergy since contain egg yolk phospholipids.
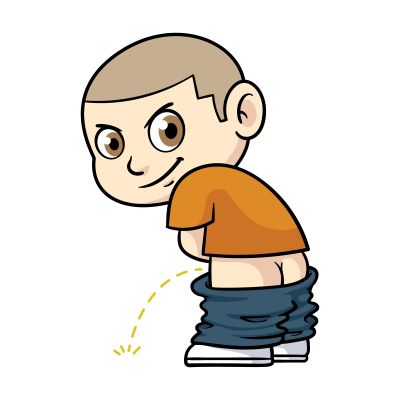
- Notify Provider of Urine output < 30 ml/hr