Hypertension
Hypertension
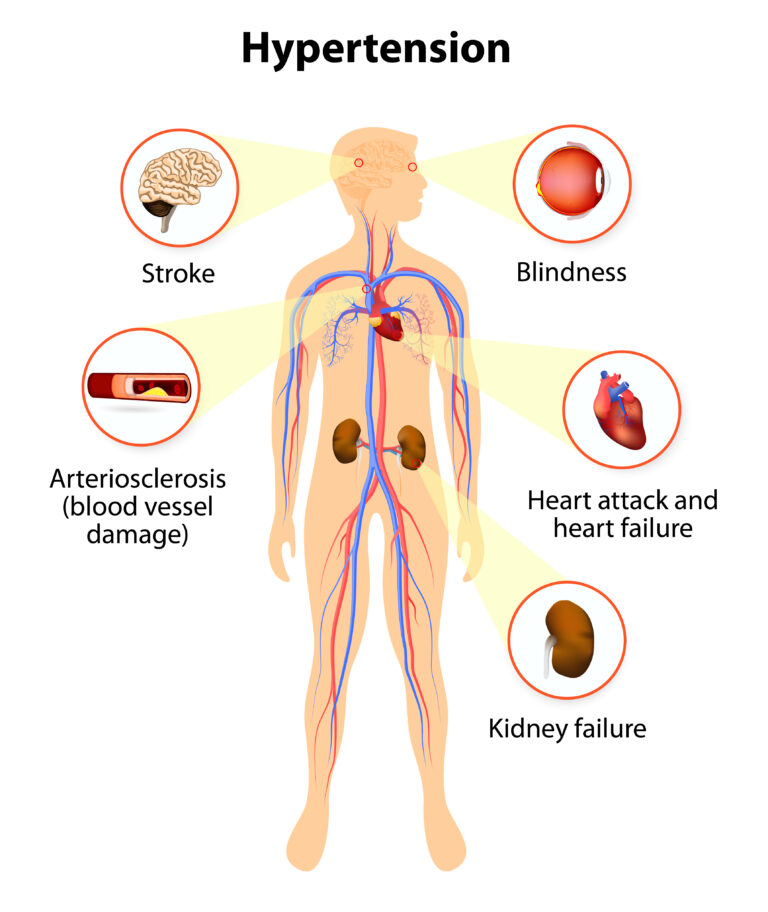
- Hypertension is a modifiable risk for coronary artery disease and stroke. Also modifiable is cigarette smoking and hyperlipidemia.
Modifiable and Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- How to modify risk:
- Hypertension: Control BP with meds/exercise/diet
- Smoking: Stop
- Hyperlipidemia: exercise/diet/meds
- Diabetes can also lead to CAD/Stroke/kidney disease. Diabetes can also be controlled.
- Non-modifiable risks: Age, genetics, gender, and ethnicity.
Patient education: NCLEX Alert
- Low-sodium diet. Not moderate. LOW
- Watch out: Salts substitutes have potassium. If the client has kidney disease or is taking ACE inhibitors, that’s a problem. The client may be taking salt substitutes to stick with low sodium diet, but now they will have hyperkalemia (DEADLY).
- Home monitoring of BP at least once weekly (Weekly, weekly, weekly).
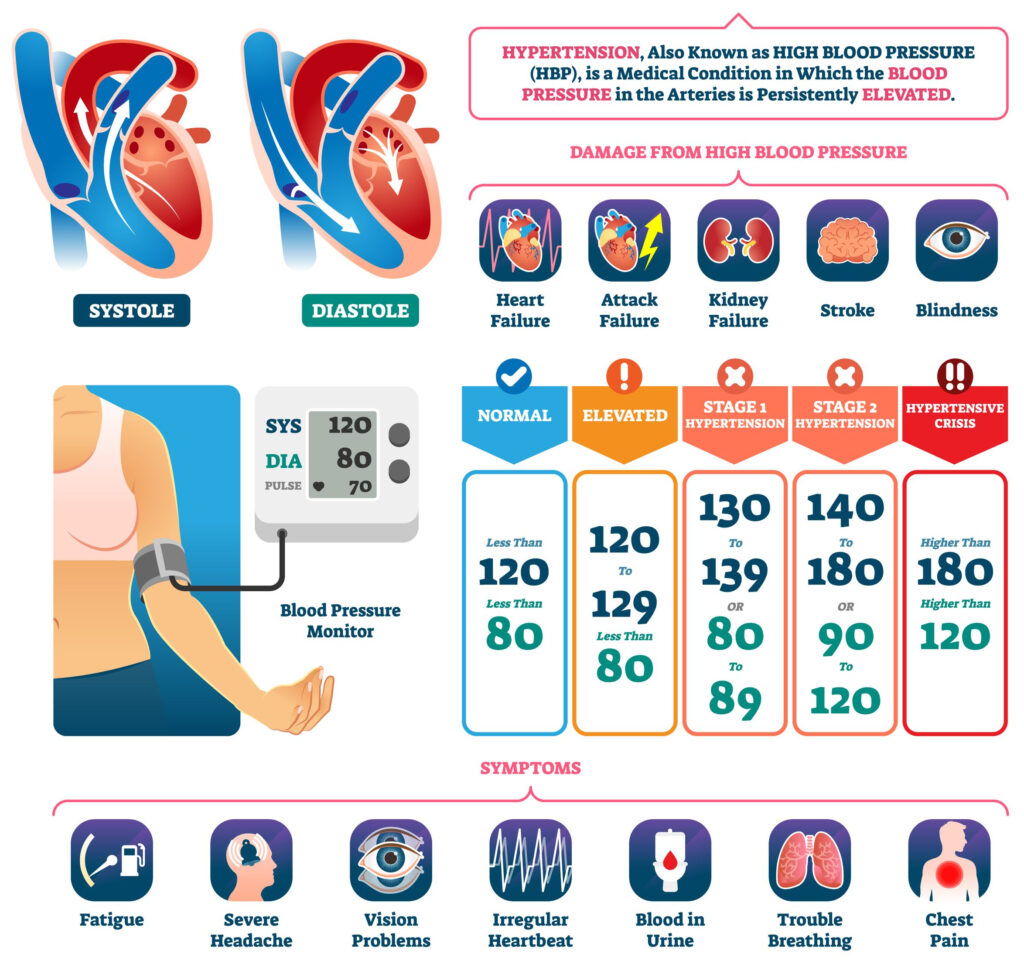
- Goal BP <140/90
- Orthostatic Hypotension. Most, if not all, antihypertensives cause orthostatic hypotension. Change position slowly. Let me say that again. Ok, I won’t. Just read it again.
- Beta blockers (metoprolol and the other -lol meds) also cause erectile dysfunction. Compliance with beta blockers is a problem due to erectile dysfunction. Compliance is essential for the treatment of hypertension
- What has sodium? Canned foods, crackers, & frozen pizza.
- Low sodium: stick with fruits and vegetables.
A little sense of humor

Antihypertensives
The diuretics
Note the area of the nephron where each diuretic works on.
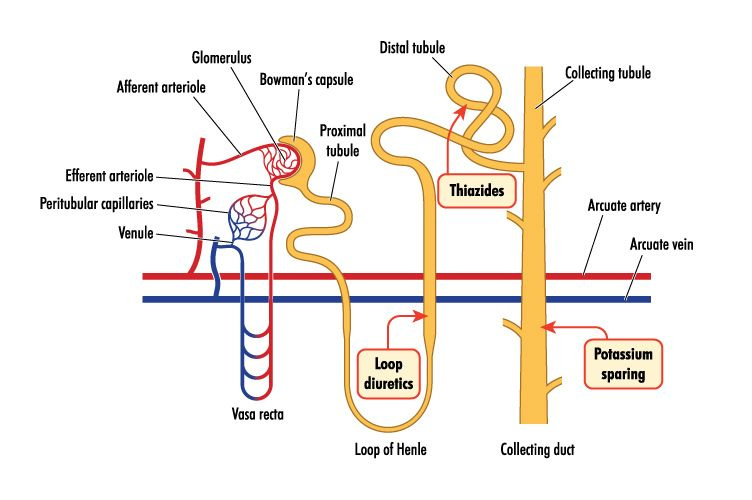
Loop Diuretics (Furosemide)
Loop Diuretics: Furosemide and Bumetadine. Watch for HYPOkalemia & HYPOcalcemia


Reduce blood volume to decrease blood pressure.
Give loop diuretics slowly (over 1 to 2 minutes) to prevent tinnitus/hearing loss.
Loop diuretics are often used in hypercalcemia since they reduce calcium
Medications interactions: Watch for digoxin toxicity due to hypokalemia. Lithium levels may decrease due to hyponatremia.
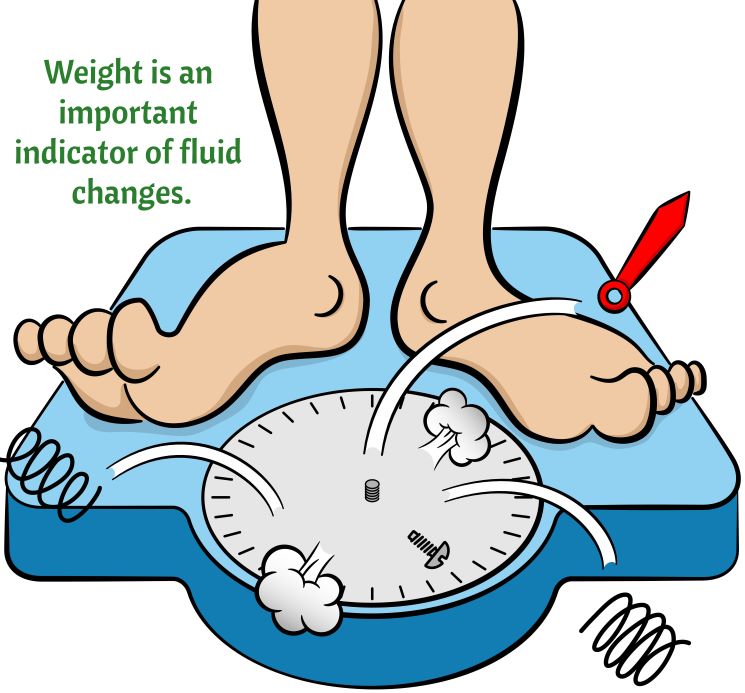
Nursing interventions: Monitor weight (#1 indicator of changes in fluid status). Monitor intake and output. Teach client how to minimize orthostatic hypotension (change position slowly). NCLEX Alert
Thiazide Diuretics
- A common Thiazide Diuretic is Hydrochlorothiazide.
- Usually first-line antihypertensive
- Watch for hypokalemia
- Monitor weight
- Watch for orthostatic hypotension
- Increase calcium by increasing its reabsorption.
- Pay attention: Furosemide decreases calcium and hydrochlorothiazide increases calcium. NCLEX Alert
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
- One potassium-sparing diuretic is Spironolactone.
- It increases the excretion of sodium. Potassium is retained.
- Watch for HYPERkalemia
- Notice that Spironolactone acts as an aldosterone antagonist. Spironolactone ↓ Na+ and ↑ K+.
- Memorize that aldosterone ↑ Na+ & ↓ K+
- An antagonist such as spironolactone will have the opposite effect (↓ Na+ & ↑ k+)

NCLEX Alert: If a client is on both, an ACE inhibitor and Spironolactone, watch out for hyperkalemia. Both increase potassium
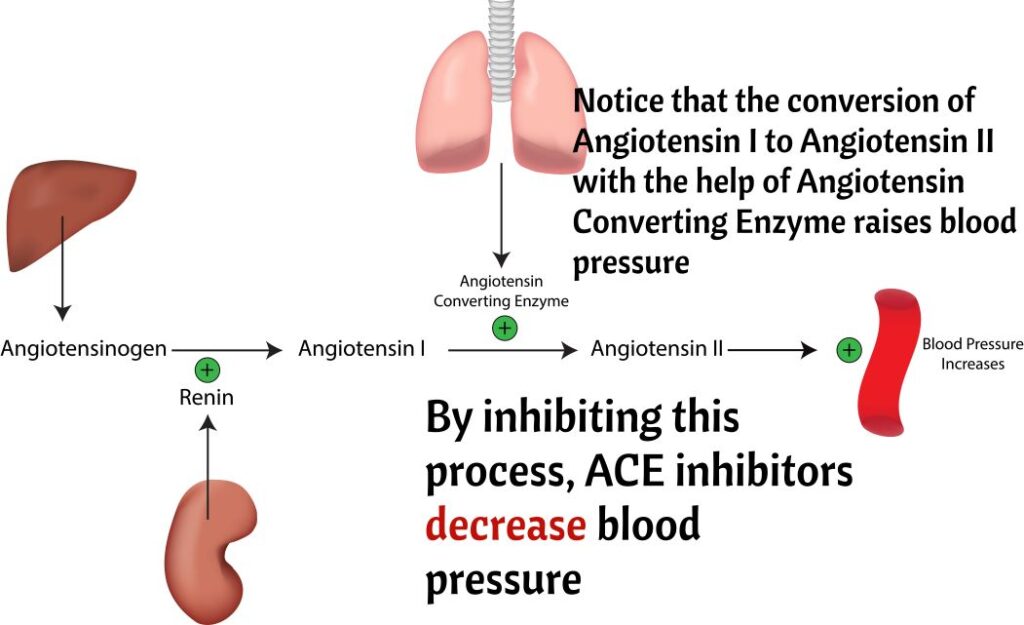
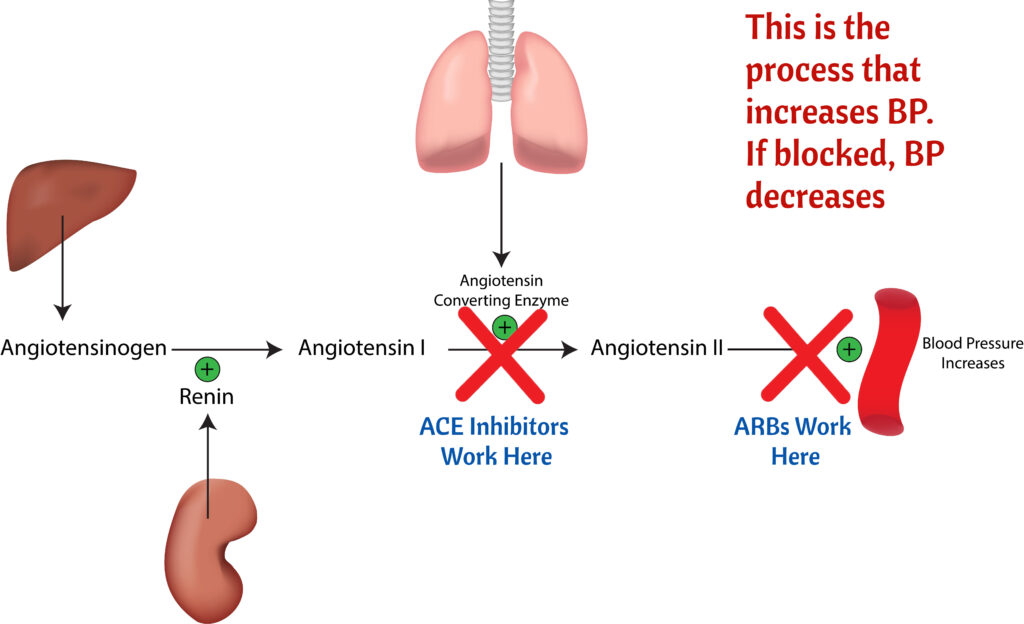
ACE Inhibitors end with -pril
- Treatment of hypertension and Congestive Heart Failure.
- Captopril
- Enalapril
- Lisinopril
- And the other -prils
- Common side effect: COUGH (benign, goes away), orthostatic hypotension, dizziness & fatigue.
- Adverse effects: ANGIOEDEMA AND HYPERKALEMIA.
- Angioedema: Be concerned if the client has swollen/Itchy lips, tongue, or throat. It can lead to airway swelling and respiratory failure.
- Adverse effect: something very bad such as angioedema. May close airway.
- Side effect: something that is not so bad such as cough, which usually goes away after a while.

Beta Blockers end with -lol
- Selective beta blockers only affect the heart and do not cause bronchospasms. There are not contraindicated in Asthma. Metoprolol, Atenolol, esmolol, and Nevibolol.
- Non-selective beta blockers are contraindicated in Asthma because they cause bronchospasms. Propranolol, labetalol, sotalol and carvediolol.
- Ii is important to remember that beta blockers
- ↓ HR and ↓ afterload to ↑ the contractility of the heart.
- Cause Impotence which can be a problem with compliance.
- NCLEX Alert: cause depression and mask the effects of hypoglycemia.
- Never give in cardiogenic shock.

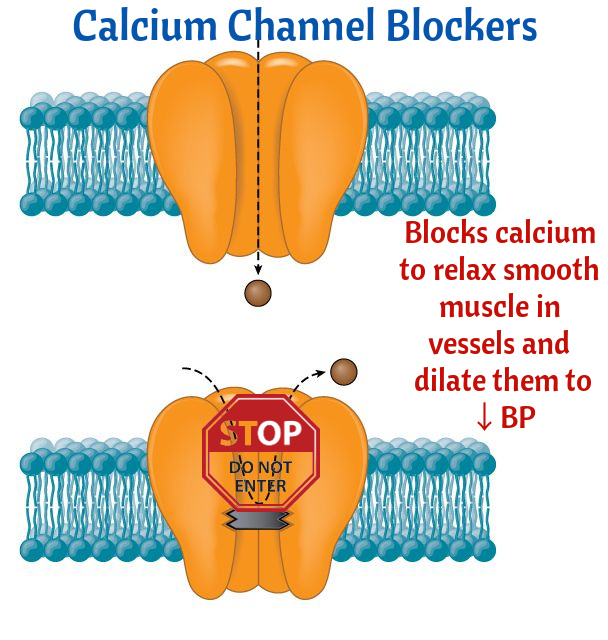
Calcium Channel Blockers the "-dipines" and the others
They have multiple uses:
- Amlodipine and Nifedipine are used for hypertension. Side effects: Headache, Reflex Tachycardia, and Peripheral Edema.
- Diltiazem and Verpamil are Class IV antiarrhythmics. Used in Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter and SVT. Side effects: Bradycardia and AV BLOCK.
- Nimodipine is used in subarachnoid hemorrhage to improve neurological outcome.
- Avoid Grapefruit with Calcium Channel blockers. Grapefruit increases blood levels of CCB (toxicity).
- Grapefruit also increases statins levels

Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) The Sartans
- End with -sartan
- Losartan
- Valsartan
- Side effects: First dose hypotension, dizziness, Angioedema (less frequent than ACE inhibitors), hyperkalemia, and renal impairment)
Vasodilators
- Arterial Vasodilators: Hydralazine, Minoxidil, & Diazoxide.
- Arterial and Venous: Sodium Nitroprusside (Potent antihypertensive given IV).
- Side effects: Reflex tachycardia, fluid retention, headache, and angina.
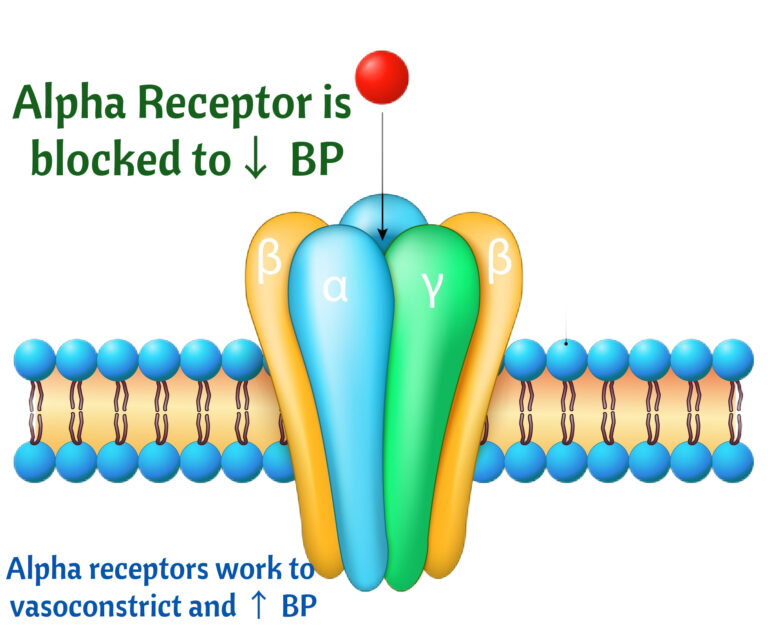
Central-Acting Adrenergics
- Central-Acting Adrenergics are Alpha antagonists that reduce sympathetic outflow to the central nervous system leading to reduction of BP
- Side effects: Dry Mouth, Impotence and Sleep disturbances.
- Cause rebound hypertension if stopped.
- Example: Clonidine (Catapress).
Nitrates
- Nitroglycerin and Isosorbide Dinitrate
- Cause relaxation of vascular smooth muscles, causing arteriolar and venous dilatation
- Side Effect Headache
- Used for chest pain.
- 3 Nitroglycerins and chest pain persists= likely a myocardial infarct.
- Sublingual tablets should be kept in the original glass bottle. Screw the cap on tightly after each use and store the bottle at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light. NCLEX Alert
Orthostatic Hypertension
Causes:
- Antihypertensives
- Anemia
- Alcohol
- Dehydration
- Fever
- Pregnancy
- Narcotics/Sedatives
Symptoms:
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Reports of seeing spots
- Pallor
- Tachycardia
- Drop of Systolic BP > 15 mm Hg
- Drop of Diastolic BP > 10 mm Hg
Intervention:
- Change position slowly