Disaster Triage, Prioritizing, and Delegation
4 Topics | 2 Quizzes
Neurological System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
MS, MG, and Guillain Barré
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The Cardiovascular System
12 Topics | 1 Quiz
Pulmonary System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cushing Versus Addison Disease
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Thyroid Disorders
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Parathyroid Disorders
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
DI and SIADH
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Diabetes
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Burns
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Anemias, Aplastic Anemia, Polycythemia Vera, Thrombocytopenia and DIC
9 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Oncological Emergencies
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Leukemias, Hodgkin’s Disease, and Multiple Myeloma
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The GI system
16 Topics | 1 Quiz
Renal and Genitourinary Problems
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Infection and Isolation Precautions
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
NCLEX Pharmacology
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
TPN, IV Solutions, & Blood Products
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Lab Values
9 Topics
Leukemias
Before we start, remember that cancer is confirmed with biopsies. Look at the actual cancer cells.
Leukemia
- Uncontrolled production of immature WBCs
Treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation
- Stem Cell Transplant
- Bone Marrow Transplant
- Biological Therapy
Risk Factors
- Smoking
- Genetic/family history
- Previous cancer treatment
- Environmental/Chemical exposure
Symptoms
- Fever
- Fatigue (Anemia) and weight loss
- Infections (Neutropenia)
- Petechiae & easy bleeding (Thrombocytopenia)
- Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
- Hyperplasia of gums
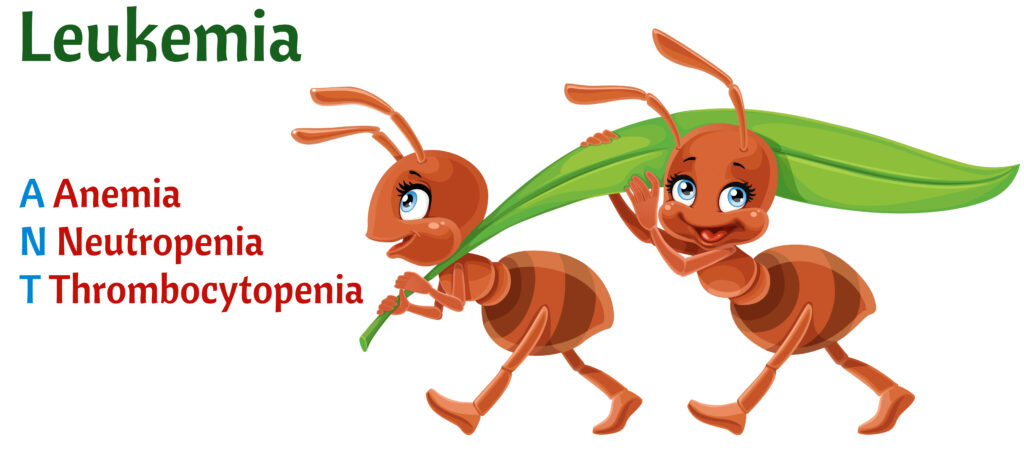
4 major types of leukemia
- Lymphocytic: involves abnormal cells from the lymphoid pathways
- Myelogenous: involves abnormal cells from myeloid pathways
- Affect bone marrow causing: anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia
AML
- Older Adults > 60 years
- Stem cells differentiate into myeloid cells

CML
- Occurs in ages 55 to 60 years
- May be asymptomatic at first
- Confusion & SOB due to WBCs > 100,000 due to leukostasis in which leukemic cells obstruct blood vessels.
- Prognosis 3 to 5 years
- Treated with Imatinib a type of chemotherapy drug. Main side effect: myelosuppression (neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia)l
ALL
- Common in children < 15 years
- Prognosis good with early treatment
- Accumulatioin of immature lymphocytes in bone marrow.
- Leukemia invades meninges: headaches, seizures, blurred vision, facial weakness.
- Treatment: Imatinib: signals leukemic cells to stop expressing the cancer protein
CLL
- Most common Malignancy of older adults
- Malignant mature B lymphocytes escape apoptosis and accumulate in organs.
- May be asymptomatic
- Treatment: In early stages: monitored only. Chemotherapy & Monoclonal antibodies
Remember!
- ALL or Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia is the leukemia of Children. ALL Children
- and CLL Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia is the leukemia of older people. CLL= Chronic=Older adults have chronic problems
Leukemia Symptoms (again)
- Anorexia, weight loss, and weakness
- Bleeding: nose bleeds, hematuria, occult bleeding, ⇑ menstrual bleeding, ecchymosis, and petechiae
- Fever, enlarged nodes, hepatomegaly, and splenomegaly
- Tachycardia and SOB
- Bone pain
- Anemia, thrombocytopenia, changes in WBC (either high or low, sometimes normal)
Nursing Interventions: Infection
- Infection is the major cause of death
- Monitor closely
- Use protective isolation
- Handwashing
- Avoid sick visitors
- Strict aseptic technique
- Private room with door closed
- No fresh foods, no flowers, plants
- Good environmental cleaning
- Use antimicrobial soap to bathe client
- Prevent constipation
- Assess wounds/mucous membranes/lungs/vital signs/sputum/urine for infection
- Avoid crowds
- No Live virus vaccines for client and family.
- Low bacteria diet. No fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Send cultures and give antibiotics as ordered
Nursing Interventions: Bleeding
- Remember thrombocytopenia
- < 50,000 risk for bleeding
- < 20,000 risk for spontaneous bleeding; may need transfusion
- Handle client gently
- Monitor for internal bleeding: abdominal distension, increased abdominal girth and tachycardia
- Avoid injections
- Apply pressure for at least 5 minutes after needle sticks
- Avoid rectal suppositories, enemas, and rectal thermometers
- Watch for excessive menstrual bleeding
- Electric razors
- Avoid NSAIDs and aspirin
- Restrict activity to prevent falls. Bedrest
- Use soft toothbrush
Fatigue and Nutrition
- Well-balanced diet
- Small frequent meals w/high calories, high protein, high carbs
- Food easy to chew to reduce energy used to eat
- Help client in self-care
- Adequate rest periods and naps
- Encourage fluid intake 3-4 L/day
- Analgesics: Tylenol is best
Treatment of Neutropenia
Filgrastim (Neupogen) is given to increase the absolute neutrophic count or treat neutropenia.
- It is stopped when ANC is > 1000 cells/mm3.
- It is a granulocyte colony stimulating factor or (G-CSF)
- Side effects: bone pain, fever, diarrhea, weakness, and rash.
NCLEX Alert
Leukemia
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
You got {{SCORE_CORRECT}} out of {{SCORE_TOTAL}}
Your Answers
