Magnesium
Hypomagnesemia under 1.5 mg/dl
Causes of HYPOmagnesemia
Click on the headings to expose content: The MAFIA of the causes of hypomagnesemia
- Malabsorption: Diseases that cause poor absorption of nutrients such as Celiac and Crohn’s DiseaseMalnutrition: e.g., Pregnancy
Alcoholism leads to increased magnesium excretion. Remember that alcohol acts like a diuretic!
Fluid Losses such as NG tube to suction, Nausea, Vomiting, diarrhea, and Diuretics
- Simple. Not enough magnesium in the diet.
- Foods with magnesium: Chocolate, Cauliflower, Veggies, Avocados, peas, bananas, oranges, milk, peanut butter, pork, and nuts.
Aminoglycosides: Gentamicin, Tobramycin, Amikacin, and Streptomycin

Signs and Symptoms Hypomagnesemia
Click on the headings to expose content. The D’s of hypomagnesemia
Breathing goes wild. Increased, shallow breathing.
Wild poop
- If may be hypomagnesemia, but DTR’s are wild and increased.
- Tetany and tremors
- Clonus- rhythmic, spasmic reflexes
- Low magnesium also causes numbness and tingling (like low calcium!)
Hypomagnesemia EKG changes to remember: Depressed ST segment, inverted T wave and Torsades
- Increased Heart rate.
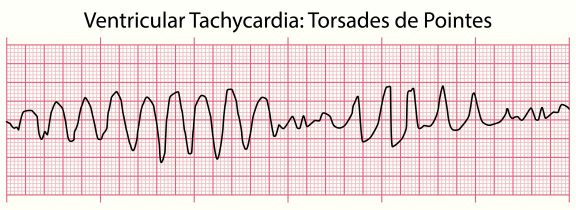
- Here is what low magnesium is famous for- torsades!
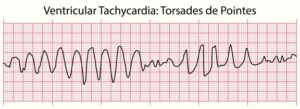
- A variation of ventricular tachycardia that is polymorphic (changes in form)
Wild Seizures, confusion, and insomnia. You want to sleep better after studying, take a magnesium supplement. Pacify the Wild D’s of hypomagnesemia.
Confusion
Difficulty swallowing

Low magnesium is famous for Torsades
Nursing Interventions
- Assess respiratory status
- Administer Magnesium supplements (IV or PO)
- Monitor EKG rhythm (Torsades!)
- Seizure precations
- Give foods high in magnesium: Chocolate, Cauliflower, Veggies, Avocados, peas, bananas, oranges, milk, peanut butter, pork, and nuts.
Foods high in Magnesium
Click on the letters to expose the content: MOBCAP foods high in magnesium
HYPERmagnesemia over 2.5
Causes of HYPERmagnesemia
Click on the letters to expose the content: HARD the causes of hypermagnesemia
Signs and symptoms of HYPERmagnesemia
RELAXATION
Click on the headings to expose content: Did I say magnesium relaxes you?

- Hypotension and bradycardia
- Prolonged PR interval and Widened QRS
- It is a sedative
- CNS depression
- Causes decreased energy, lethargy, drowsiness, and even coma
- Given to pregnant patients with pre-eclampsia to prevent seizures because it RELAXES brain.
Decreases respiratory rate. Think Decreased shallow respirations
Relaxes/decreases bowel sounds
Decreases Deep Tendon Reflexes. Good way to monitor toxicity! Check DTRs
facial flushing

Nursing Interventions
- Diuretics
- IV Calcium Gluconate or IV Calcium Chloride in severe hypermagnesemia with cardiac and respiratory consequences.
- Diet: Limit foods with high magnesium
- Avoid laxatives and Antacids with magnesium
- Hemodialysis
- Monitor DTR’s for signs of toxicity. Pregnant women with pre-eclampsia get magnesium infusions to prevent seizures/eclampsia. For these clients, monitor respiratory status and DTRs to check for toxic hypermagnesemia. The goal of therapy is a magnesium level of 4 to 7 mg/dl.
- The symptoms of pre-eclampsia are epigastric pain, blurred vision, and a headache. Magnesium is excreted by the kidneys for monitor kidney function/urine output. If signs of renal failure develop, stop the infusion.
- Once the baby is born, monitor the baby for respiratory depression and the mother for bleeding (hypermagnesemia causes uterine atony).
- The antidote for magnesium is calcium gluconate.


