Disaster Triage, Prioritizing, and Delegation
4 Topics | 2 Quizzes
Neurological System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
MS, MG, and Guillain Barré
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The Cardiovascular System
12 Topics | 1 Quiz
Pulmonary System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cushing Versus Addison Disease
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Thyroid Disorders
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Parathyroid Disorders
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
DI and SIADH
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Diabetes
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Burns
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Anemias, Aplastic Anemia, Polycythemia Vera, Thrombocytopenia and DIC
9 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Oncological Emergencies
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Leukemias, Hodgkin’s Disease, and Multiple Myeloma
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The GI system
16 Topics | 1 Quiz
Renal and Genitourinary Problems
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Infection and Isolation Precautions
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
NCLEX Pharmacology
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
TPN, IV Solutions, & Blood Products
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Lab Values
9 Topics
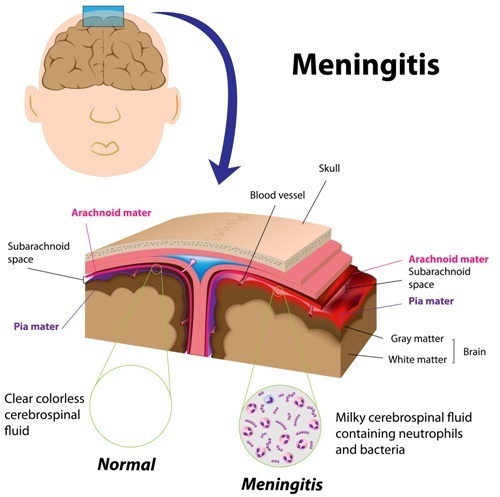
Meningitis
Infection
- Inflammation of the meninges (arachnoid and pia mater of the brain and spinal cord)
Causes
Mostly bacterial or viral, but may also be fungal.
Transmission
- Transmission by droplet and direct contact
- Occurs in crowded areas such as college dorms and prisons
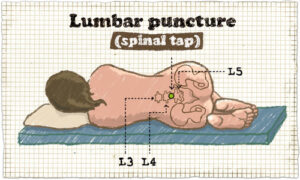
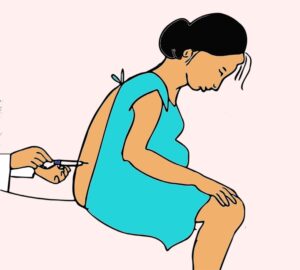
Diagnosis
CSF obtained via lumbar puncture. CSF will be Cloudy with high protein, low glucose, culture of organisms. After lumbar puncture, keep the client flat to prevent headache.
Symptoms
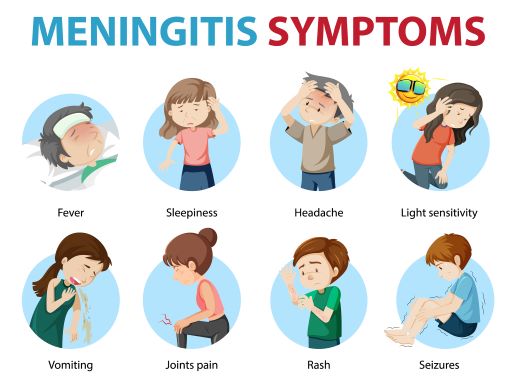
Symptoms
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Changes of LOC
- Headaches
- Stiff neck
- Photophobia and phonophobia
- Meningeal irritation: Positive Kernig’s sign and Brudzinski’ sign
- Red macular rash is meningococcal meningitis
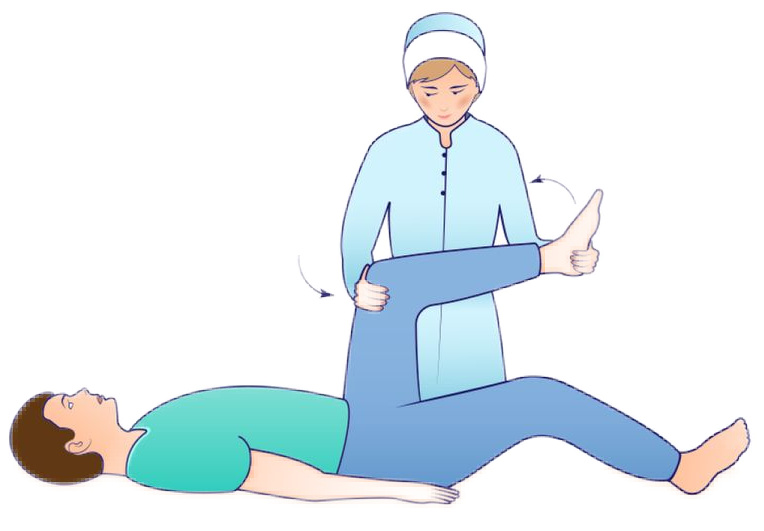
Kernig's Sign
Knee and hip at a right angle. Extend the knee and the client will experience pain.
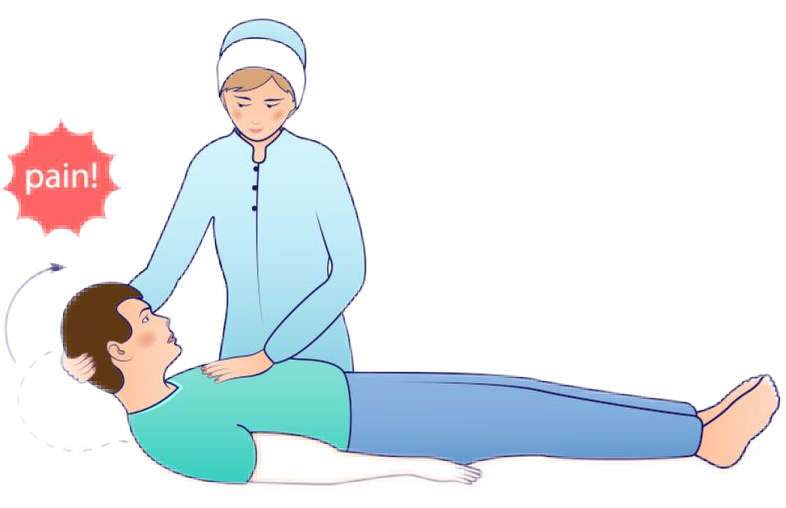
Brudzinski's Sign
Placing the client in supine position, the nurse attempts flexion of the neck, but it causes pain.
Nursing Interventions
- Assess for ↑ ICP, meningeal irritation, and cranial nerves
- Seizure precautions
- Isolation precautions with bacterial meningitis (Droplet precautions, wear surgical mask, good handwashing) for at least 24 hours after the initiation of treatment.
- Maintain quiet environment
- Administer analgesics and antibiotics as ordered
