MI & Angina
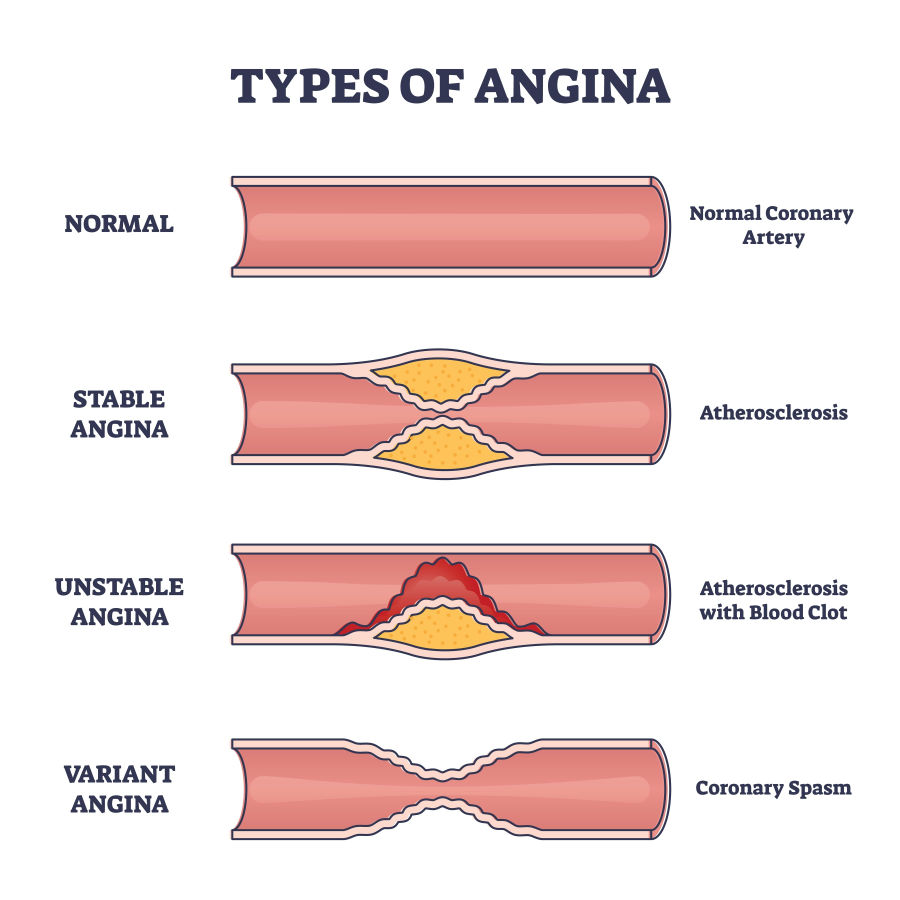
Angina
Long-term interventions
Modify risk factors (↑ cholesterol), Control HTN & DM, Angiogram to open up blocked coronaries or heart surgery

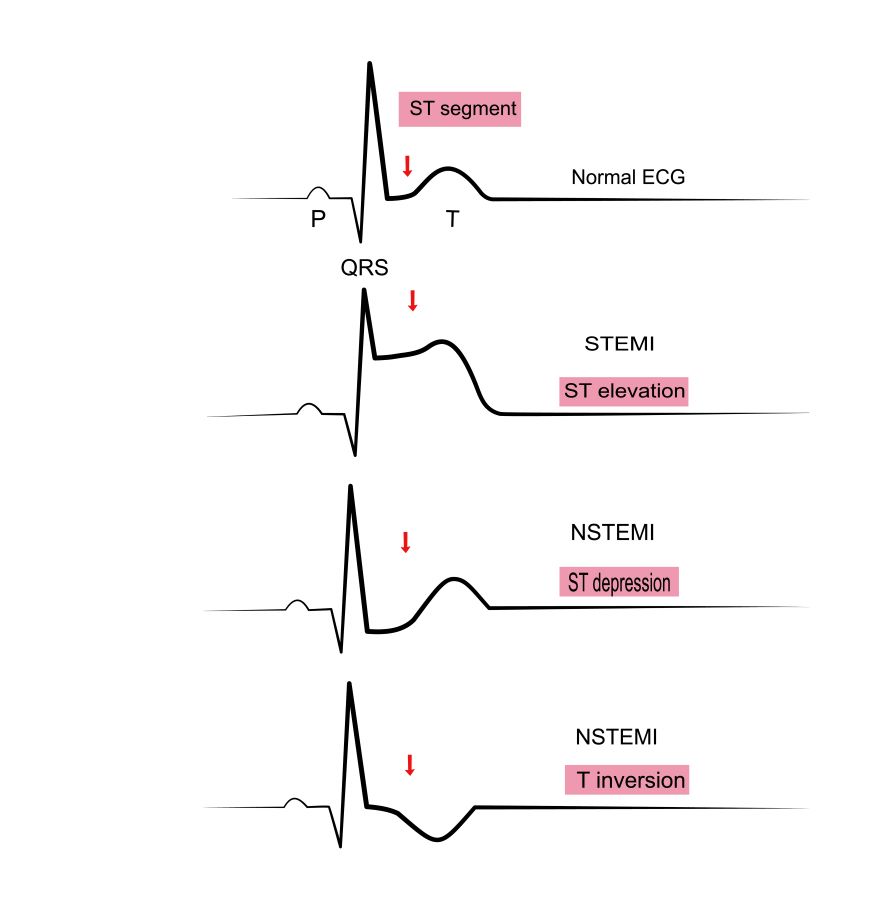
EKG Changes
None or transient ST segment changes.
Nursing Priorities
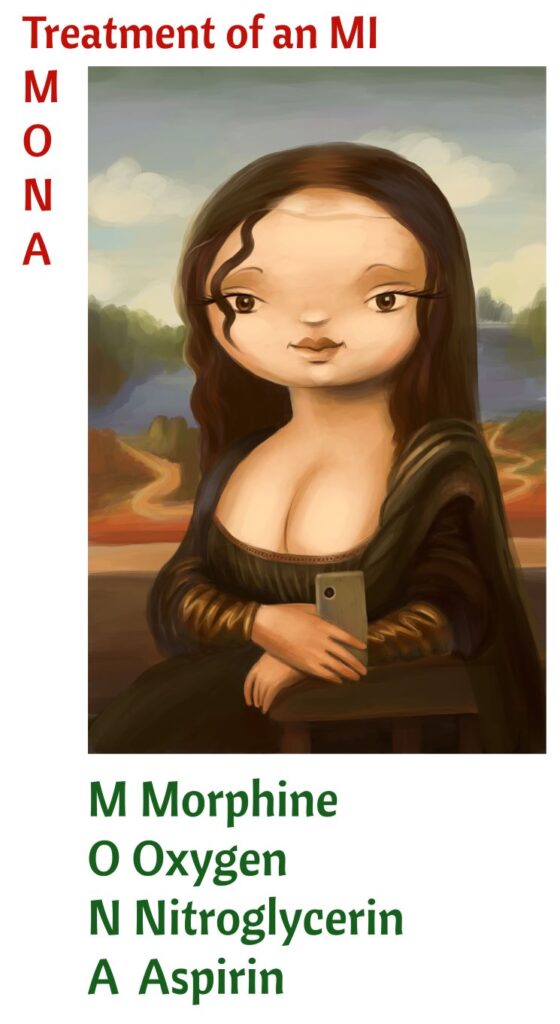
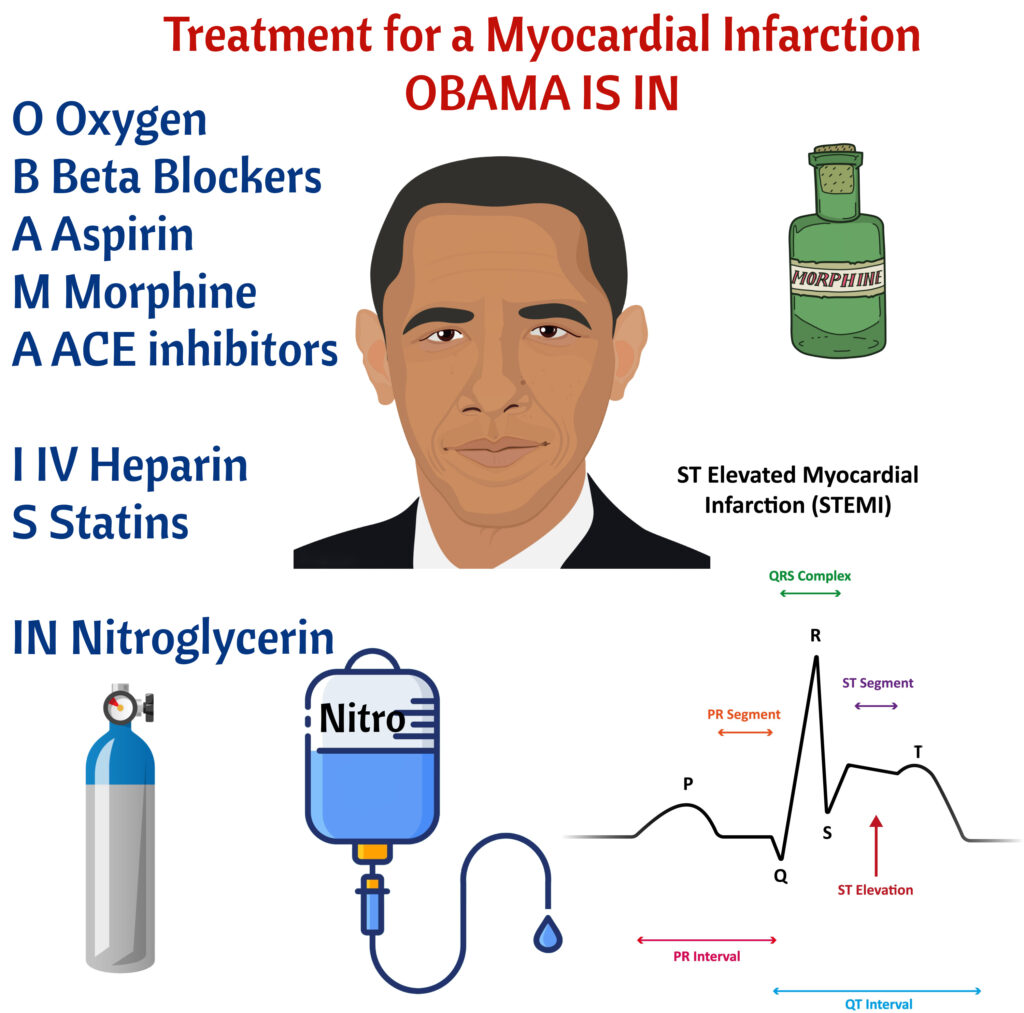
Educate client to rest and take nitroglycerin. At hospital, MONA (morphine, oxygen, nitroglycerin, and aspirin). Work up for MI
Myocardial Infaction
Symptoms
Substernal crushing pain unrelieved by nitroglycerin. Occurs at rest. In women, vague symptoms.
Interventions
ICU, MONA (Morphine, Oxygen, Nitro, Aspirin). Reperfusion therapy with fibrinolytics. Take to cath lab within 90 minutes. Heart surgery if indicated
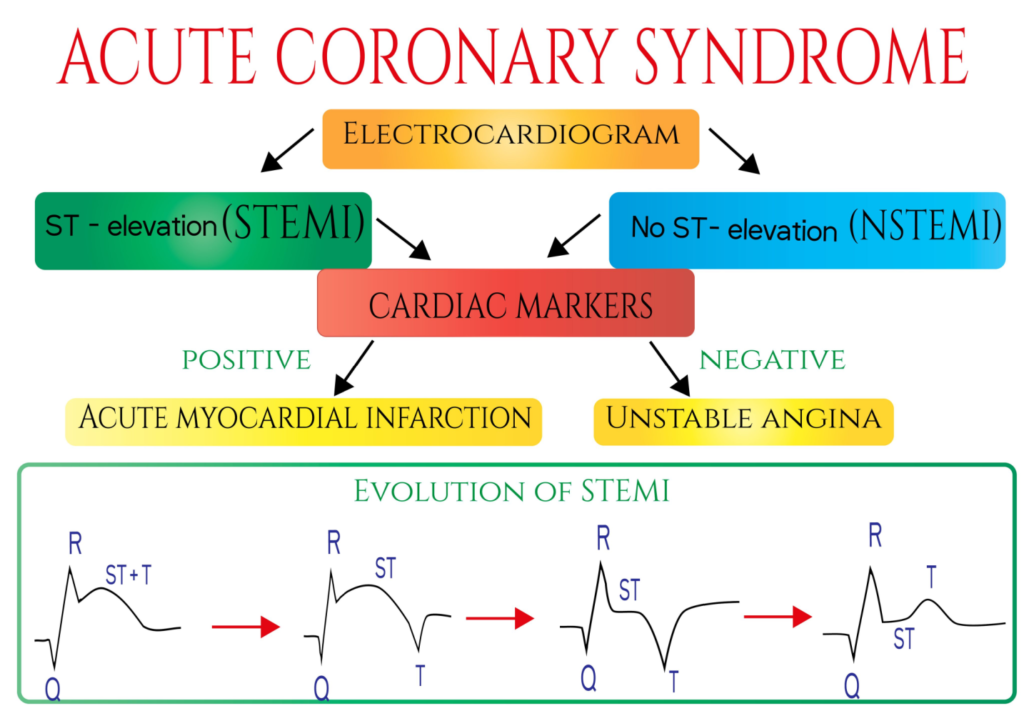
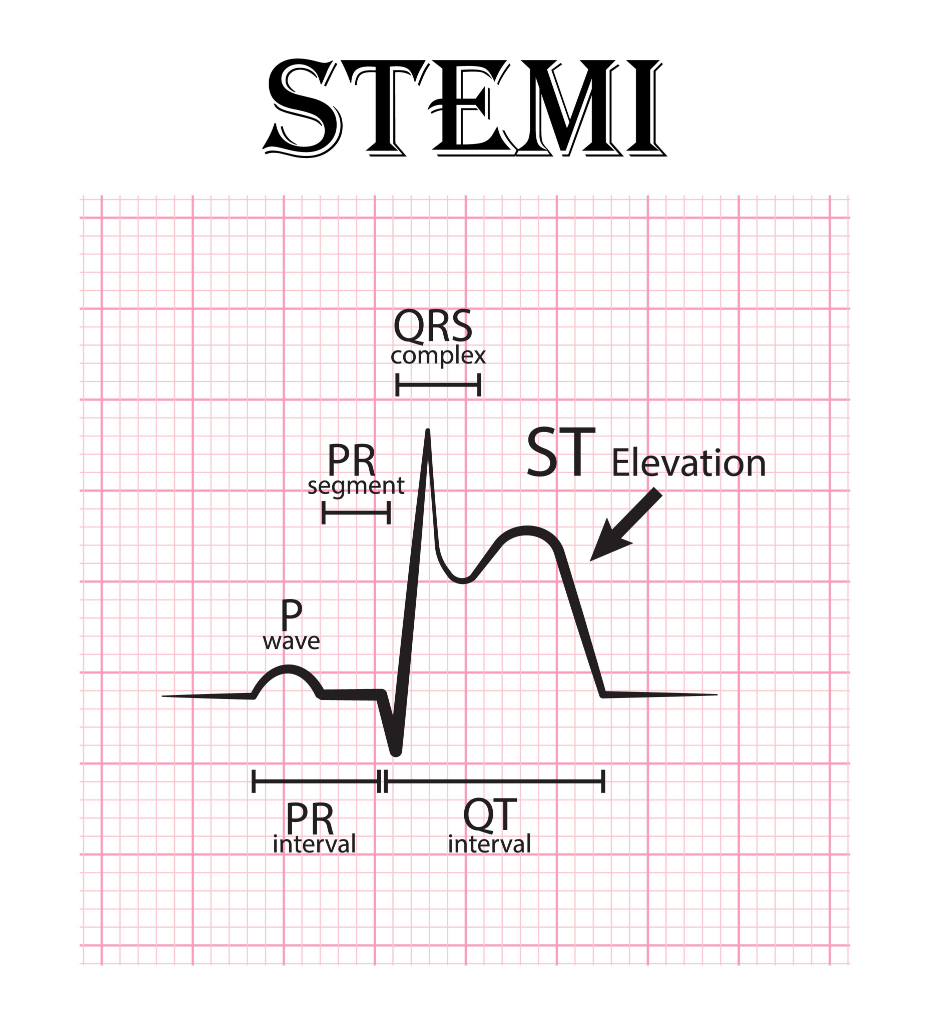
EKG Changes
ST elevation or NSTEMI (No ST-Elevation Myocardial Infaction) and elevated cardiac enzymes
Priorities
Pain relief and Oxygen. Pain=heart damage. Identify unusual signs of MI (Indigestion or confusion in the elderly). Monitor for complications = arrhythmias #1 and heart failure.

Other Symptoms of a Myocardial Infaction
Symptoms last > 20 minutes. Pain radiates to jaw or left arm/shoulder. In women, symptoms can be vague- aching jaw, choking sensation, fatigue, insomnia, & dyspnea

Diaphoresis

Nausea/Vomiting

Changes in BP
Changes in HR

Cardiac Enzymes

- Cardiac anzymes are released in response to cardiac ischemia/infarction. They include CK-MD, myoglobin, Troponin T, and Troponin I.
- Troponin I and T = Myocardial Infarction= MOST SPECIFIC to the heart
- If troponin is elevated always think MI, MI, MI, MI
- Look at the table below and notice that Troponin stays elevated the longest.
- Takes a few hours for enzymes to go up. To diagnose a myocardial infarction, SERIAL ENZYMES are ordered. Cardiac enzymes are usually ordered every 8 hours x 3.
| Enzyme | Indication | Initial Rise | Peak | Back to Normal | Normal Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troponin | Hgh Affinity for myocardial injury | < 4 hours | 12 hours | Up to 10 days | < 0.6 mg/mL |
| CK-MD (Creatine kinase, myocardial muscle) | Myocardial Injury | 4 to 6 hours | 18 to 24 hours | 72 to 96 hours (3 to 4 days) | 0% to 5% of Total = 26 to 174 units/L |
| LDH (Lactate dehydrogenase) | Two types LDH₁ and LDH₂. Usually 1<2, but if 1>2, it indicates myocardial necrosis. Basic math, right? | 24 to 48 hours | 2-3 days | 4 to 5 days | 140 to 280 IU/L. Look for the flipped values 1>2 |
| Myoglobin | Less specific since it is found in both skeletal and cardiac muscle | < 2 hours | 8 to 10 hours | 24 hours | 25 to 72 ng/mL |
Drug Therapy for Angina Pectoris
| Nitrates | Calcium Channel Blockers | Beta Blockers | Antiplatelets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vasodilate to ↓ ischemia and pain. e.g sublingual nitroglycerin that is given x 3 at 5-minute intervals. If pain doesn't go away, client must call 911 (MI) | Relax blood vessels to ↑ oxygen to heart and ↓ oxygen demand/workload. e.g. the -pines such as amlodipine and nifedipine | ↓ myocardial oxygen demand e.g., metoprolol, labetalol yes, the -lol NCLEX Alert: mask that effects of hypoglycemia and cause depression | Prevent platelet aggregation and thrombosis Aspirin/clopidogrel |
Quiz Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 1 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
For each client finding, put an X to specify whether it is a modifiable or non-modifiable risk factor for heart disease.
-
Factors Modifiable Non-Modifiable Stress Family History Gender and Ethnicity Diabetes and hypertension Smoking Age Excessive alcohol use
CorrectIncorrect -
This is a drag and drop exercise.
- Aortic= 2nd intercostal space to the right of sternal border
- Pulmonic = 2nd intercostal space to the left of sternal border
- Erb’s point =the third intercostal space close to the left sternal border
- Tricuspic = 3rd intercostal space to the left of sternal border
- Mitral = left side of the sternum, 5th intercostal space at the midclavicular line
NCLEX Favorites
The client experiences angina and takes one sublingual Nitroglycerin. After the sublingual nitroglycerin, the client experiences a headache. The nurse recognizes that the client is most likely experiencing which of the following?
NCLEX favorite: A common and expected side effect of Nitroglycerin is a headache. Just take tylenol. Of course, if the client has other side effects (shortness of breath) along to headache, seek medical help.
The ER nurse is caring for a client who came in with chest pain rated 10 out of 10. After Morphine 4mg IVP, the pain goes down to 2/10. The results of the cardiac enzymes reveal an elevated creatine kinase, Troponin T & I, and myoglobin. The nurse recognizes that the client is most likely experiencing which of the following conditions?
Elevated cardiac enzymes= always MI
The nurse needs to listen to the apical pulse to administer Digoxin to an adult client with heart failure. Where should the nurse place the stethoscope?
5th intercostal space, left midclavicular line for adults. 4th interscostal space, left midclavicular line for children. This is a popular question where the NCLEX will ask you to click on the actual location on an image.
The client has been diagnosed with angina and has been discharged on Nitroglycerin paste. Which of the following demonstrates understanding of the discharge teaching?
All medications that affect Blood pressure cause orthostatic hypotension. Teach clients to get out of bed slowly. This is a big NCLEX favorite. Headache is a common side effect of Nitro. Just recommend client to take Tylenol. Nitroglycerin paste should be applied to clean hairless skin for better absorption.
The nurse develops a teaching plan for a client who is being discharged after having a myocardial infarction. Which of the following teaching points should the nurse include?
Nitroglycerin should be in a dark bottle, kept in a dark cool place at room temperature for 6 months. Aspirin is often prescribed: Side effects GI bleed (dark tarry stools) and Ototoxicity (ringing in the ears/hearing loss). Report to PCP. Clients can exercise as tolerated and in 4 to 8 weeks resume sexual intercourse.
The client asks the nurse, "My cardiologist told me that I don't have coronary artery disease, but spasms of my coronary arteries that cause chest pain?" The nurse recognizes that the condition that the client is most likely experiencing is which of the following?
Variant angina (Prinzmetal angina) isn't due to coronary artery disease but spasms of the coronary arteries, which reduces blood flow to the myocardium. Stable angina is the most common type of angina. It occurs with activity. Refractory Angina is a type of angina that keeps occuring despite medication and lifestyle changes. Unstable angina is a medical emergency. It occurs at rest and does not go away with anti-anginal medications. Client must go to the ER because it may be an MI.
The clinic nurse is assessing a client who had a myocardial infarction a month ago. The client states, "Ever since my heart attack, I have been very depressed." The nurse reviews client's medication list. Other than the possible stress of having an MI, which of the following medications is the possible cause/exacerbation of the client's depression?
NCLEX Alert: Beta blockers' side effects: bradycardia, depression, mask effects of hypoglycemia, & impotence. Never give in cardiogenic shock because they will further depress myocardial contractility.
The ER nurse admits a client with severe chest pain that radiates to the left shoulder and jaw. The client is restless and diaphoretic. Which of the following physician's order should the nurse do first?
ABC. ABC. When prioritizing, always go for ABC. Plus the problem with an MI is decreased oxygenation to the myocardium. That is what causes chest pain.
A client with a myocardial infaction has been started on the antifibrinolytic alteplase. Which of the following findings during therapy requires follow up?
Anticogulants and Antifibrinolytics: Monitor for bleeding. Ecchymosis, bruises, epistaxis (nosebleed) need to be reported to the MD.
The nurse is caring for a client with a myocardial infarction. The physician has ordered a Nitroglycerin drip. Which of the following is essential for the administration of this medication?
NCLEC Alert: Nitroglycerin drip: IV pump and Blood pressure monitoring. A bolus a Nitroglycerin can kill a client from the profound hypotension. And of course, headache as a side effect.
After a myocardial infarction, the client develops cardiogenic shock. Which of the following assessment findings that the nurse anticipate? Select all that apply
Please select 6 correct answers
The nurse monitors the client with a myocardial infarction for which of the following common complications.
That's the number one complication! NCELX Alert
Click on the titles to view the rest of the partial medical record
The client is 60-year-old African American male with a history of hypertension, diabetes, smoking of 1 pack of cigarettes per day, who is admitted to the ER with chest pain unrelieved by Nitroglycerin x 3
Client is alert and oriented. Client complains of chest pain rated 7 out of 10. Pain radiates to jaw and left arm. Patient states “I feel like I have a brick on my chest”. Skin moist but warm.
Temp 98.5 °F BP 110/55, HR 100 BPM, Respiratory rate 20. Oxygen saturation 93% on room air.
- Metoprolol 100mg po QD
- Glipizide 5mg po daily

Time's up

