Disaster Triage, Prioritizing, and Delegation
4 Topics | 2 Quizzes
Neurological System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
MS, MG, and Guillain Barré
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The Cardiovascular System
12 Topics | 1 Quiz
Pulmonary System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cushing Versus Addison Disease
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Thyroid Disorders
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Parathyroid Disorders
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
DI and SIADH
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Diabetes
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Burns
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Anemias, Aplastic Anemia, Polycythemia Vera, Thrombocytopenia and DIC
9 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Oncological Emergencies
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Leukemias, Hodgkin’s Disease, and Multiple Myeloma
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The GI system
16 Topics | 1 Quiz
Renal and Genitourinary Problems
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Infection and Isolation Precautions
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
NCLEX Pharmacology
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
TPN, IV Solutions, & Blood Products
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Lab Values
9 Topics
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis
Affects young women and old men
Patho
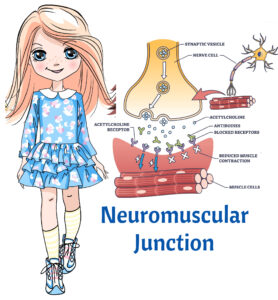
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor are attacked by antibodies
- Acetylcholine cannot attach to receptors, which leads to MUSCLE WEAKNESS
Weakness

- #1 Symptom is severe muscle weakness that worsens with activity and improves with rest.
Early Signs
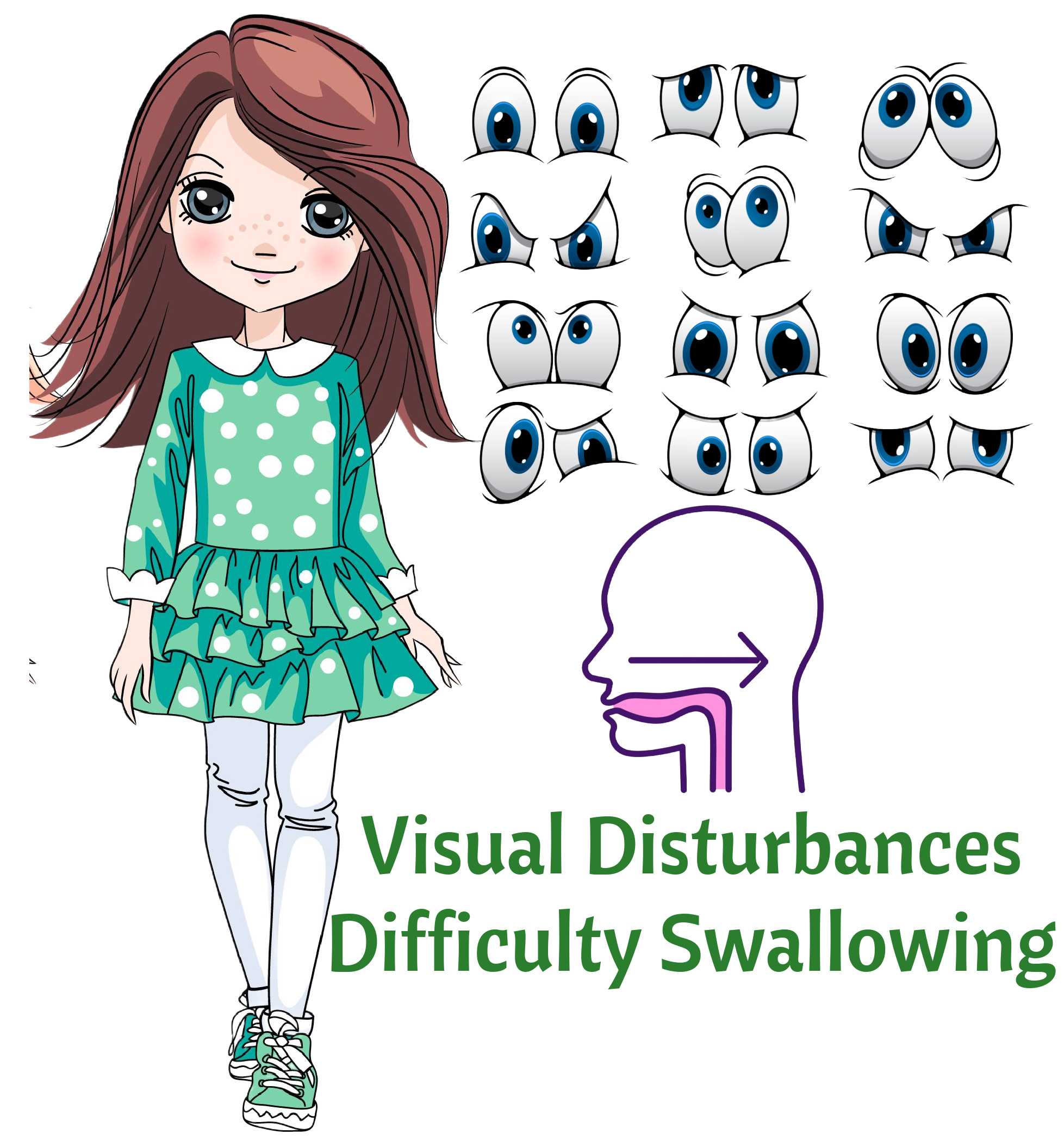
- Early Signs: Difficulty Swallowing and Visual Disturbances
Priority

- Watch for respiratory arrest
- Have suction and tracheostomy & endotracheal tube at the bedside
Symptoms

WEAKNESS
W Weakness
E Eyelid drooping (Ptosis)
A Appearance (No expression)
K Keeps choking/gagging
N No Energy
E Extraocular movements (double vision)
S Slurred Speech
S Shortness of Breath
Treatment
- Cholinergics or Anticholinesterases: Prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine to ↑ acetylcholine in Myasthenia Gravis.
- E.g., Pyridostigmine Bromide (Mestinon). Major side effect: muscle cramps! NCLEX
- Give at the SAME TIME everyday. Set alarm if necessary to prevent muscle weakness.
- Thymectomy
- Corticosteroids (Prednisone)
- Plasmaphresis
Myasthenic Crisis
- Not enough medication
- Exacerbation when muscles that controls breathing are too weak leading to respiratory failure.
- Other CAUSES: Stress, surgery, or infection.
Cholinergic Crisis
- Too much medication or cholinergics
- Receiving to much anticholinesterase medication leading to muscles becoming overworked or weak!
- Anticholinesterases = Cholinergics
- Cholinesterases are enzymes that breakdown acetylcholine (↓ available acetylcholine). By blocking cholinesterases (giving anticholinesterases), you ↑ acetylcholine, which is necessary for muscle contraction.
Tensilon Test
- Determines if myasthenic crisis or cholinergic crisis.
- Give Edrophonium (Tensilon), short-acting Pyridostigmine.
- Client gets better = Myasthenic crisis. Needed more medication
- Client gets worse= Cholinergic crisis. Getting too much medication.
- Pyridostigmine= long-acting used to treat MG
- Edrophonium = short-acting. Too short-acting to be used as treatment.
Nursing Interventions
- Monitor Breathing #1
- High risk for Aspiration (thick liquids, small bites)
- Assess swallowing
- Assess vision: High risk for falls
- Major activities and meals in the morning when energy is at its highest (NCLEX)
- Best food: Easy to chew such as clam chowder and mashed potatoes. Avoid steaks and veggies (hard to chew).
- Antidote for cholinergics: Atropine (memorize)
- Pyridostigmine give 1 hour before eating for better strength to eat.
Priority

Cholinergic Drugs
- Physostigmine
- Neostigmine
- Pyridostigmine
- Edrophonium (Tensilon)
- Rivastigmine
- Donepezil
- Galantamine
Uses of Cholinergic Drugs
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Glaucoma
- Paralytic ileus
- Urinary retention
- Myasthenia gravis
This is what happens when you overmedicate a client with myasthenia gravis

Do you know that there are also anticholinergic drugs
Cholinergics
- Pupillary constriction (affects vision)
- Diarrhea
- Bronchoconstriction
- Urination
- Diaphoresis, lacrimation, & increased secretions
Anticholinergics
- Pupillary dilation (blurred vision)
- Constipation
- Bronchodilation
- Urinary retention
- Dry mouth/decreased sweating. Dry Dry Dry
Learn their differences. Memorize how they are opposites. Right now!
- Atropine (increases heart rate and dries up secretions)
- Belladonna alkaloids (Treats stomach cramps/spasms)
- Benztropine (Cogentin)(Treats extrapyramidal symptoms)
- Flavoxate (Urispas) (Treats bladder spasms)
- Glycopyrrolate (dries up secretions)
- Ipratropium (Atrovent) (respiratory drug that bronchodilates)
- Oxybutynin (Ditropan XL)
- Propantheline (Pro-banthine) (Treats excessive sweating and urinary incontinence)
- Tiotropium (Spiriva) (Respiratory drug that bronchodilates)
- Tolterodine (Detrol) (Treats incontinence/overactive bladder). Decreased sweating is a side effect, but usually not used to treat excessive sweating.

