Disaster Triage, Prioritizing, and Delegation
4 Topics | 2 Quizzes
Neurological System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
MS, MG, and Guillain Barré
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The Cardiovascular System
12 Topics | 1 Quiz
Pulmonary System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cushing Versus Addison Disease
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Thyroid Disorders
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Parathyroid Disorders
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
DI and SIADH
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Diabetes
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Burns
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Anemias, Aplastic Anemia, Polycythemia Vera, Thrombocytopenia and DIC
9 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Oncological Emergencies
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Leukemias, Hodgkin’s Disease, and Multiple Myeloma
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The GI system
16 Topics | 1 Quiz
Renal and Genitourinary Problems
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Infection and Isolation Precautions
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
NCLEX Pharmacology
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
TPN, IV Solutions, & Blood Products
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Lab Values
9 Topics
NCLEX Must-Knows
NCLEX Alert: Flashcards
- Antidote for Benzodiazepines
- Do not give Flumazenil to clients with ↑ ICP or status epilepticus, it will aggravate the problem.
- ICP will increase even more
- Seizures/epilepsy will get worse
- Dilute with NS only. It will precipitate in D5W
- Give slow to prevent cardiac dysrhythmias. Give about 50mg/minute or less.
- Causes birth defects if given in pregnancy.
- For pregnancy, use phenobarbital for seizures instead.
- Phenytoin decreases effectiveness of birth control.
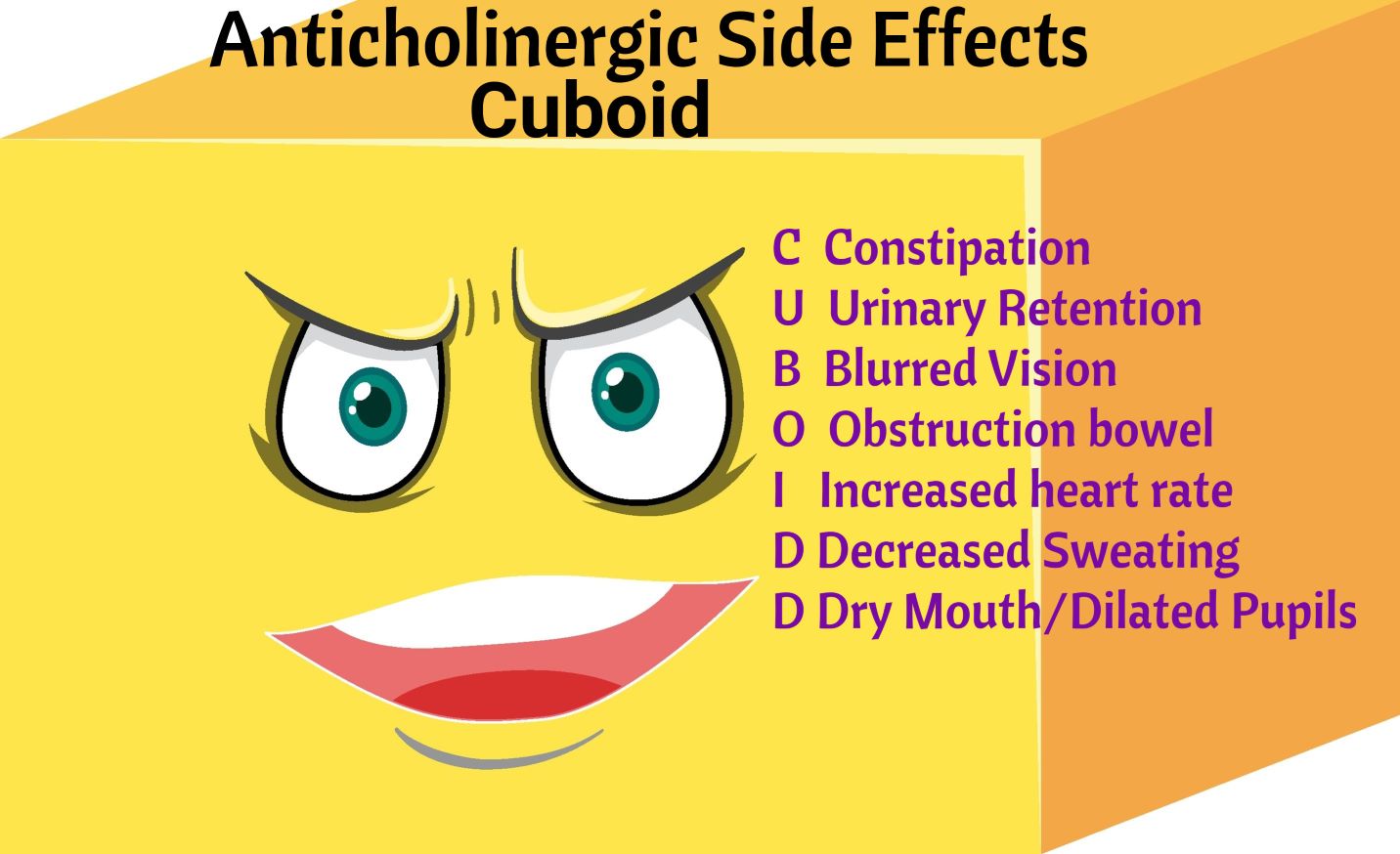
- Never stop anticholinergics abruptly because symptoms of parkinsonism will occur: rigidity, tremors, bradykinesia, akinesia, shuffling gait, and masked facies.
- Anticholinergics
- atropine
- benztropine
- glycopyrrolate
- scopolamine
- trihexyphenidyl
- diphenhydramine
- flavoxate
- oxybutynin
- orphenadrine
- Treats Parkinson’s Disease
- Do not take with MAOI to prevent hypertensive crisis
- Atropine is an anticholinergic
- When doing an edrophonium/Tensilon test, you must have it ready.
- Tensilon test: Determines whether a client with myasthenia gravis is having a myasthenic crisis or a cholinergic crisis.
- Tensilon or edrophonium is a cholinergic medication.
- If after receiving edrophonium, the client gets better (less weakness), the client is having a myasthenic crisis and needs more medication.
- If after receiving edrophonium, the client gets weaker, the client is having a cholinergic crisis or getting too much medication.
- Atropine must be ready to be injected in case the client has a severe cholinergic crisis after receiving edrophonium.
Atropine is an Anticholinergic and this is what it does. Notice that it increases heart rate
Edrophonium is a cholinergic and this is what it does

- A cholinergic
- Bethanechol is used for urinary retention because it causes urination

- Do not give if the client has a urinary obstruction or stricture. The bladder will explode.
- Stop 48 hours prior to a procedure with iodinated contrast to prevent lactic acidosis
- Monitor for respiratory depression. This is the priority concern.
- Do not give to clients with hepatic disease or alcoholism.
- Antidote is Acetycysteine
- Avoid in children under 15 to prevent Reye’s syndrome (encephalopathy and liver failure)
- Monitor platelets
- Drug of choice to prevent heart attacks and strokes.
- Give with a full glass of water
- Drink lots of water to prevent crystalluria
- Urine output must be good
- Do not give if client develops a rash.
- Notify MD
- One example is Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim)
- Rifampin, a tuberculosis medication, will cause urine, saliva, sputum, sweat, teeth, and tears to turn a reddish-orange to reddish-brown color.
- It is a harmless side effect.
- Will stain clothes permanently
Examples:
- Baclofen
- Carisoprodol
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Dantrolene
- Metaxalone
- Primary concern is safety since they cause drowsiness: High risk for falls
- Monitor liver function test since they are hepatotoxic
- Do not take with aspirin to prevent elevation of uric acid
- Encourage client to take acetaminophen for pain instead.
- Urinary antispasmodic agents increase bladder capacity, delay the desire to void, decrease the frequency and urgency to urinate, and reduce pain caused by difficulty in urination.
- Examples: Oxybutynin, flavoxate, and tolterodine.
- These medications are anticholinergics
- Notice how anticholinergics cause urinary retention. So if a client has an overactive bladder (peeing here and there), a drug that causes some urinary retention can be useful.

- Treat Angina
- Vasodilate coronary arteries
- Number one side effect is headache. Expected since brain vessels are also dilated
- Check expiration date because if expired, they do not work.
- Monitor for hypotension
- Educate client to report must pain since it could be rhabdomyolysis
- Treatment for hyperthyroidism
- Causes agranulocytosis.
- Report fever, sore throat or any signs of infection
- Use propylthiouracil during the first trimester then can switch to Methimazole to prevent birth defects.
Some commonly prescribed sulfonylureas include:
- glyburide (Micronase)
- glimepiride (Amaryl)
- chlorpropamide (Diabinese)
- glipizide (Glucotrol)
- tolazamide (Tolinase)
Watch for disulfiram-type reaction if taken with alcohol.
Alcohol consumption results in diaphoresis, palpitations, facial flushing, nausea, vertigo, hypotension, and tachycardia. These symptoms are known as the disulfiram-alcohol reaction and discourages alcohol intake.
Educate client about the following toxicities:
- Cause hepatotoxicity
- Nephrotoxicity
- Neurotoxicity
- Ototoxicity
- Treat Osteoporosis
- These include: Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill. Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill.
- Can cause esophagitis
- Take early in the morning for full glass of water and remain sitting or standing
- Do not eat anything for at least 30 minutes
- Can be absorbed into the systemic circulation especially in permeable areas of the skin such as perineum, eyelids, face and neck.
- Less likely to be absorbed in palms and soles of feet.
- Super teratogenic
- Causes fatal fetal abnormalities
- Strictly no pregnancy
- Must be on birth control
- Stains teeth
- Give using a straw
- Brush teeth after administration
- Do not use Meperidine in pediatrics due to the risk of normeperidine-induced seizures
- In adults, be careful when giving large doses.
- Remember Meperidine and Seizures!
- Given to promote labor
- Discontinue for:
- Uterine contraction frequency < 2 minutes
- Uterine contraction duration > 90 seconds
- Fetal distress
- Cyclophosphamide is used in the management and treatment of neoplasms, including multiple myeloma, sarcoma, and breast cancer.
- Causes Hemorrhagic cystitis
- Increase fluid intake
- As cancer drugs destroy cancer cells, uric acid is released.
- Allopurinol is given to decrease uric acid levels.
- Also used in gout to prevent elevation of uric acid.
- Not for acute gout.
- Used to treat the symptoms of asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, and other lung diseases.
- Toxicity occurs at levels > 20 mcg/ml.
- Signs of toxicity: Nausea, Vomiting, Restlessness, nervousness, tremors, palpitations, tachycardia, seizures and even death.
- These are short acting insulins that can be given IV
