Neurovascular Assessment
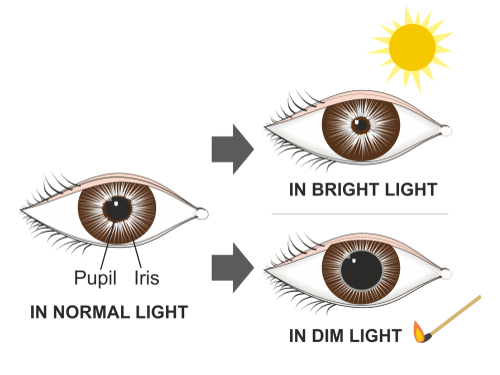
Pupillary Reaction
Shine a light and pupils constrict. Remove the light and pupils dilate. PERRLA = pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation. Size of pupils 2-6 mm. Pupillary reaction is mainly assessing CN III.
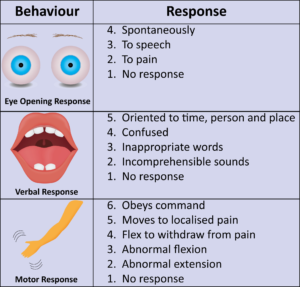
Glasgow Coma Scale
Minimum score = 3 (Severe neurological impairment). Maximum score = 15 (fully alert client). < 8 = Unconscious client.
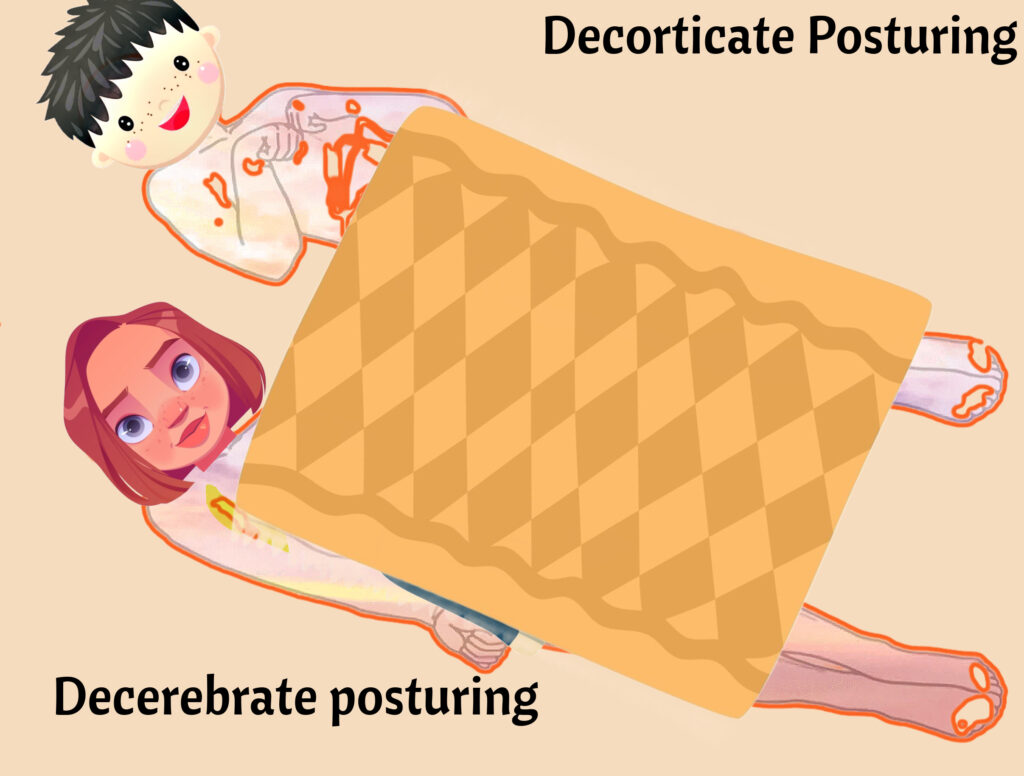
Posturing
Decorticate posturing is a reflex pose that causes the legs to become rigid and straight, while the arms flex upward and hold tensely to the chest (core of the body). DECORTICATE THE ARMS TO THE COR. Decerebrate posturing causes extremities to extend and hold rigid. Decerebrate has many “E”s so thing “arms EXTEND.” Decerebrate posturing = SEVERE brain damage.

ICP
The pressure inside the skull increases, leading compression of brain. Commonly occurs in clients with traumatic brain injury
Preventing ICP
Coughing, Sneezing, Suctioning, Agitation, valsalva Maneuver (bearing down), Vomiting, Avoid fever; ↑ brain oxygen needs., Avoid Rectal thermometers, Lumbar punctures (lead lead to brain herniation), Prevent shivering

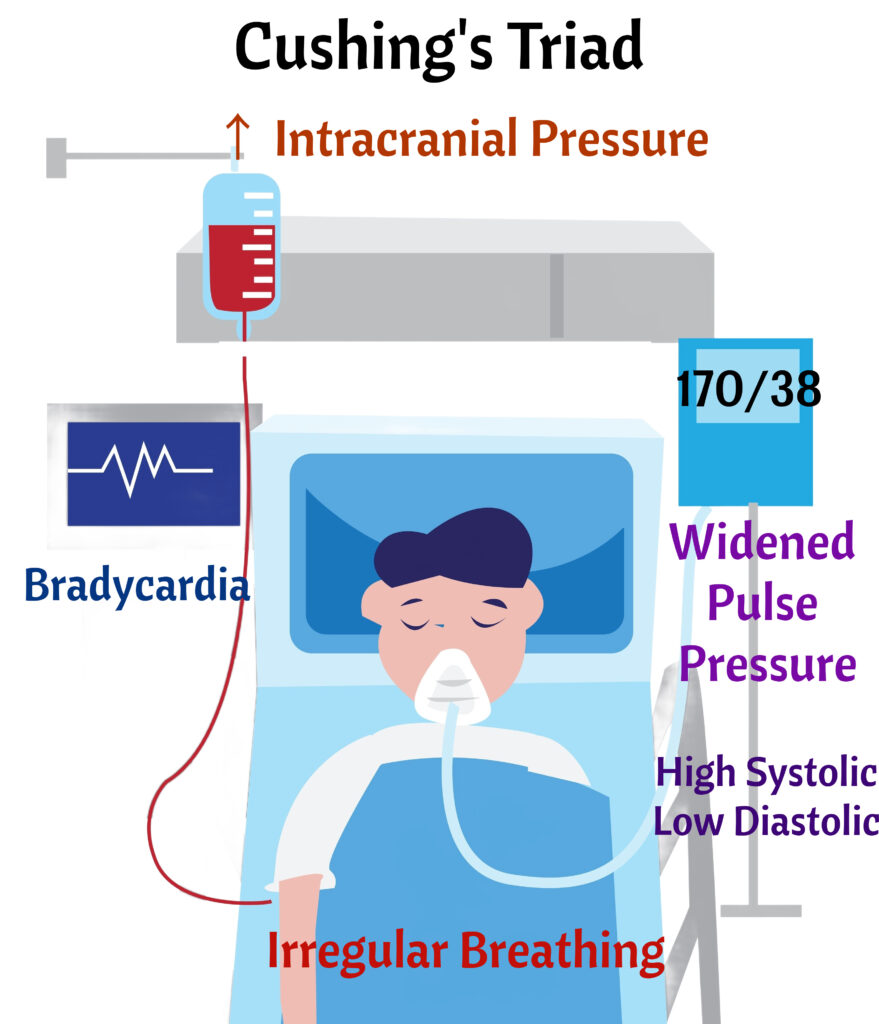
Symptoms
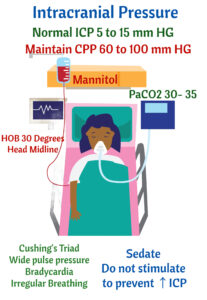
Bradycardia, Cheyne-Stokes breathing, Increased pulse pressure. Cushing Triad: 190/50= wide pulse pressure (Pulse pressure = 190-50=140). HR 50 = bradycardia. RR 9= abnormal breathing.
Treatment
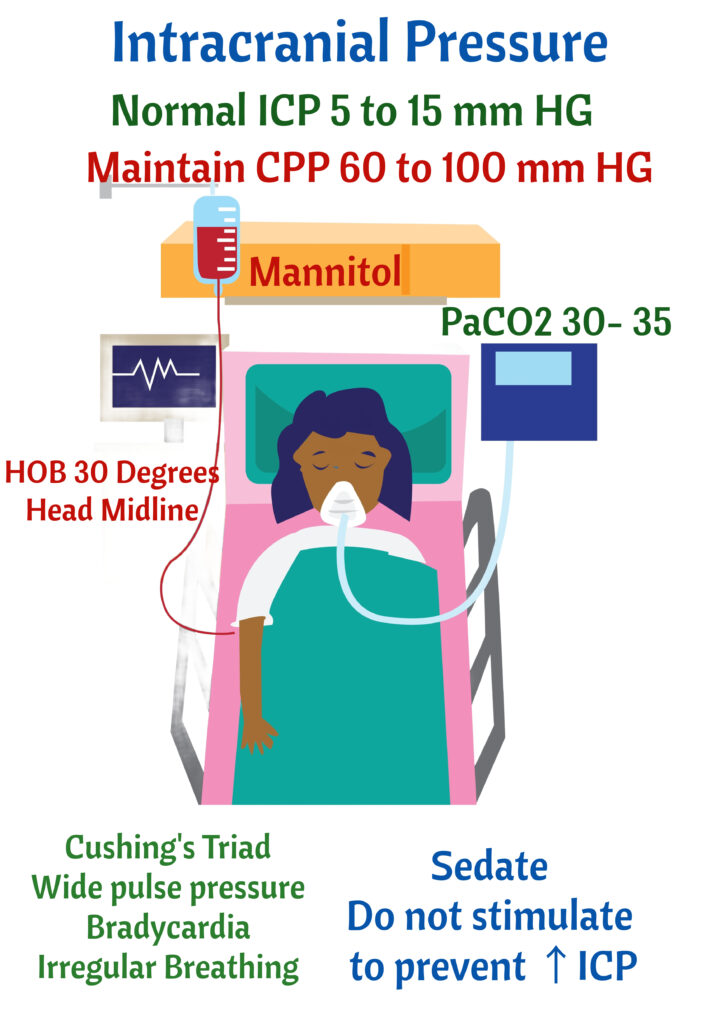
Midline position of the head. Placing HOB 15-30 degrees. Prevent flexion of the neck and flexion of the hips. Keep PaCO2 between 30-35 mm Hg. Elevated PaCO2 causes vasoconstriction ⇒⇑ICP. Maintain normal ICP 5 to 15 mm Hg. ICP monitor is inserted in lateral ventricle. Maintain a cerebral perfusion pressure 60 to 100 mm Hg
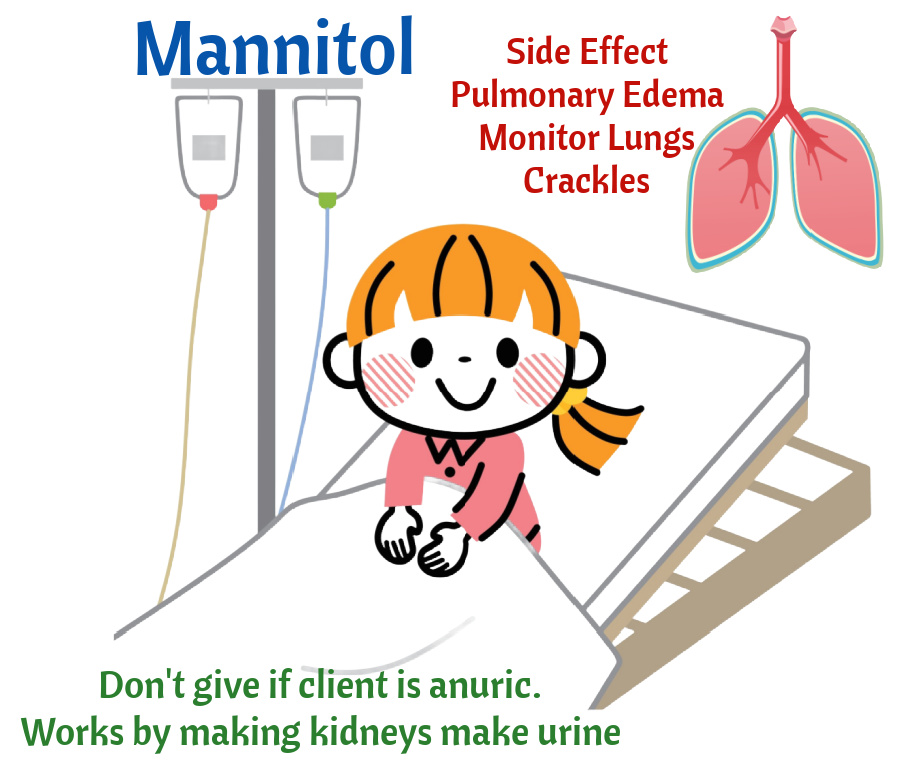

- Mannitol will remove water from the brain and take it to the vessels.
- Mannitol will cause kidneys to make more urine
- Major side effect: Pulmonary edema. Monitor for lungs for crackles. Remember Mannitol takes fluid from the brain and takes it to the vessels. Vessels take fluid to the heart/lungs.
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = (2(DBP) + SBP)/3
- Example: 120/70
- (2(70) + 120)/3 =87
- Cerebral Perfusion Pressure = MAP – ICP
- Example if ICP is 12 and MAP 87
- CPP = 87 – 12 = 75
ICP Symptoms again
- Vision changes (blurred vision or diplopia). This is due to papillledema (swelling of the optic nerve).
- Changes in LOC
- Cheyne Stokes respirations
- Headache
- Pupil changes
- Abnormal posturing.
- Seizures
- Vitals: Increased BP with widenining pulse pressure, bradycardia, and decreased respirations. This is Cushing’s triad.
- In children: bulging fontanels, high-pitched cry, and irritability
Treatment
- Assess neuro status
- Prevent overhydration
- HOB 15 to 30 degrees.
- Keep head midline
- Antiseizure medications
- Steroids to decrease inflammation
- Mannitol (watch for heart failure/pulmonary edema)
- Avoid narcotics or medications that depress breathing.

Oculocephalic reflex. The absence or abnormal response of the Doll’s eyes reflex can be indicative of neurological dysfunction, especially in the brainstem. If the eyes do not move in the opposite direction when the head is turned, it may suggest impairment in the brainstem, potentially due to injury or pathology.
The 12 Cranial Nerves

Olfactory (I) Nerve:
Have the client smell a familiar smell

Oculomotor (III)
Eye movement & pupil constriction

Trigeminal (V)
Face sensation and motor movement. Ask to clench teeth for motor

Optic (II) Nerve:
Visual acuity and Visual fields. Snellen Chart

Trochlear (IV) Nerve
Vertical eye movement. Follow finger

Abducens (VI)
Lateral Eye movement. Test III, IV, and VI together. Follow finger in an "H" pattern.

Facial (VII) Nerve
Facial expression. Taste on anterior 2/3 of tongue

Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Swallowing/Gag reflex. Taste on posterior tongue

Accessory (XI)
Shoulder/neck muscle strength. Shrug shoulders against resistance.

Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
Hearing and balance

Vagus (X) Nerve
Throat sensation, gag reflex, check for hoarseness. rise of palate (say "ah")


