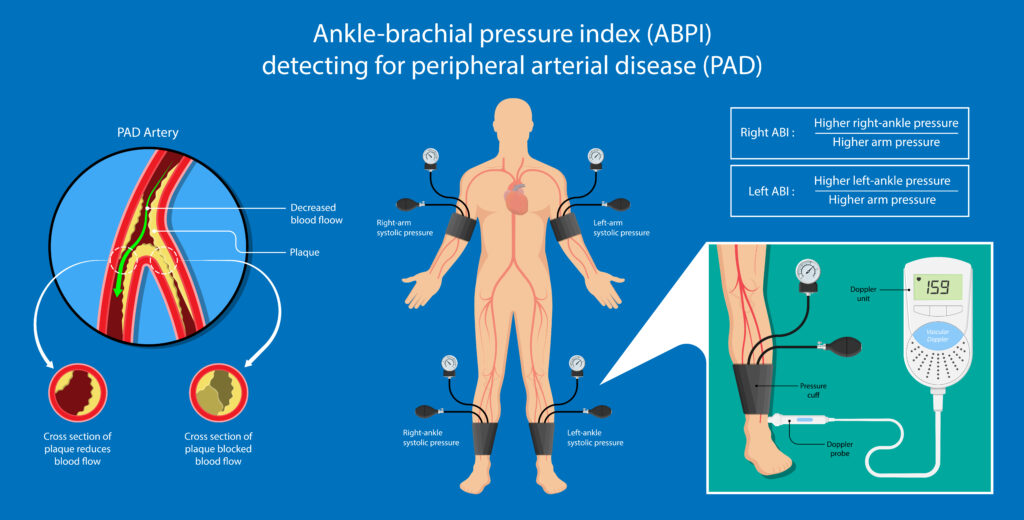
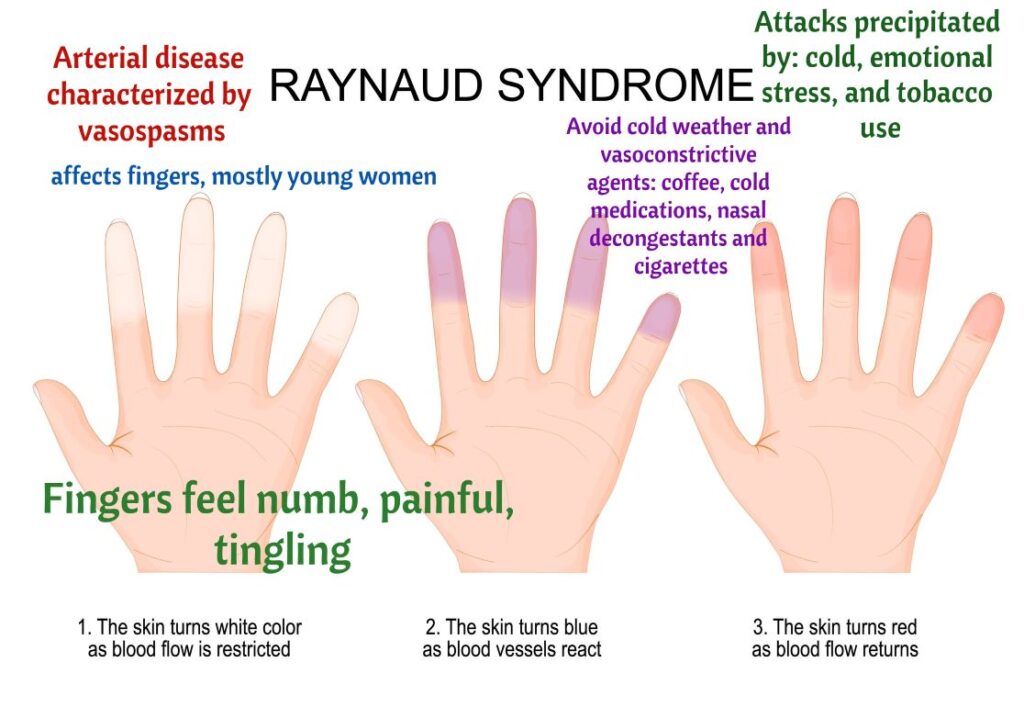
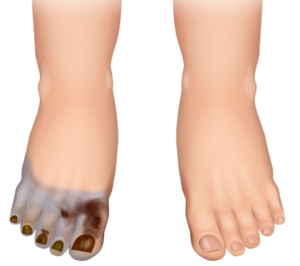
Peripheral Artery Disease
Pain
Sharp, intermittent claudication. You walk and pain occurs, you stop and pain goes away
Pulse
Pulse is decreased or absent. Remember there is no or ↓ arterial blood flow
Edema
No edema due to no or decreased blood flow
Temp & Color
Extremity is Pale, HAIRLESS, and skin is thin due to ↓ blood flow.
Position
Dangle legs to ↑ blood flow. Let gravity do its thing
Treatment
No smoking, aspirin, vasodilators, good skin care, avoid tight shoes & surgery such as femoral-popliteal bypass.