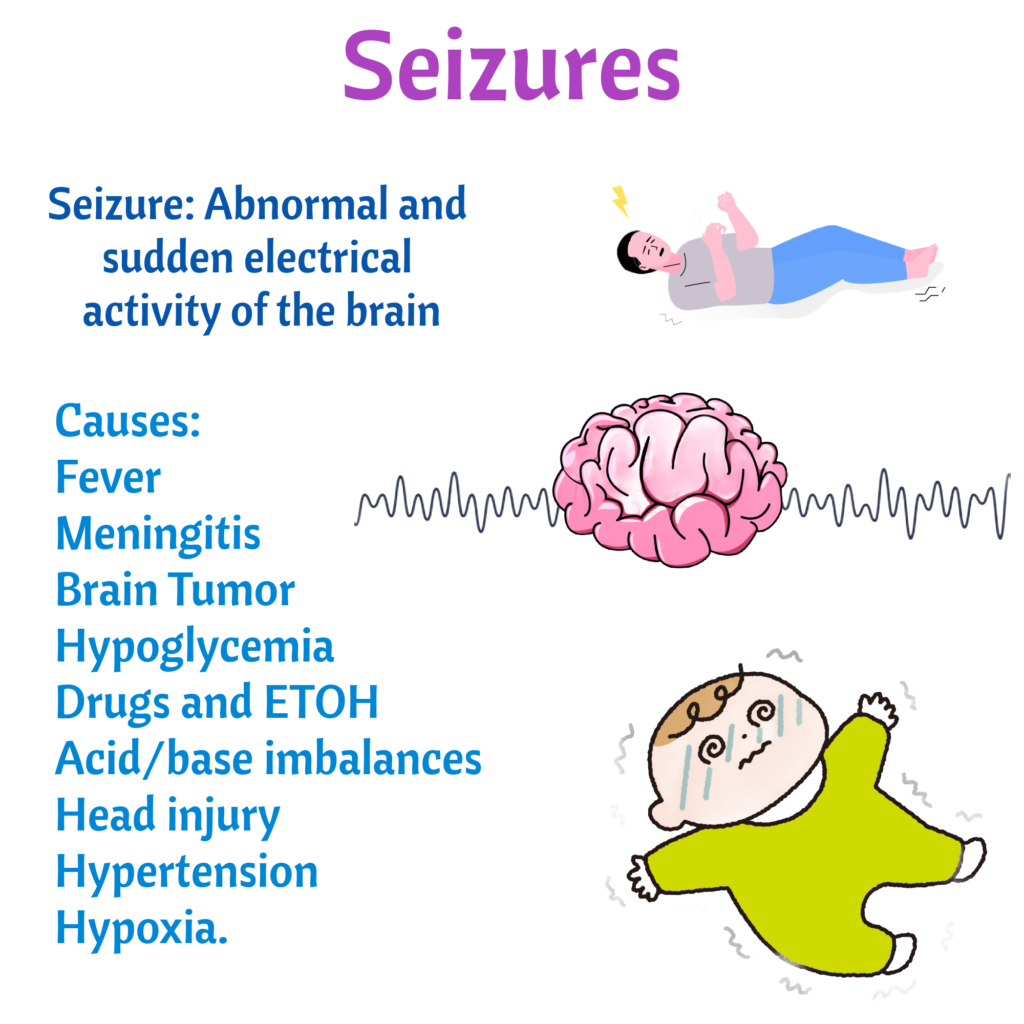
Seizures
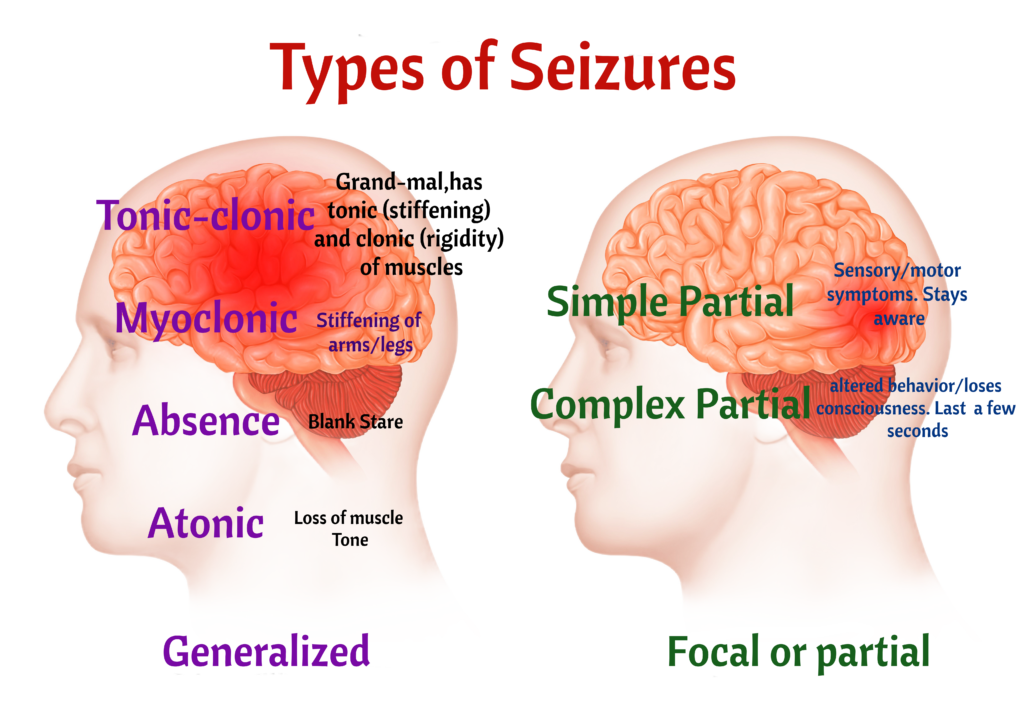
Generalized seizures: These seizures affect the entire brain and can cause a loss of consciousness, muscle spasms, and convulsions.
Focal seizures: Also known as partial seizures, these seizures only affect one part of the brain. They can be simple (no loss of consciousness) or complex (loss of consciousness).
Absence seizures: These seizures are typically seen in children, and they cause a brief loss of consciousness that lasts only a few seconds. Blank stare. Smacking of lips. Twitching of mouth.
Myoclonic seizures: These seizures cause sudden, jerky movements in the arms and legs.
Atonic seizures: These seizures cause a sudden loss of muscle tone, often resulting in a person falling to the ground.
Tonic-clonic seizures: Also known as grand mal seizures, these seizures are the most recognizable type and involve convulsions, muscle rigidity, and loss of consciousness.
Status Epilepticus: A medical emergency. Life-threatening if not corrected. A continual grand mal seizure without a recover period. Treatment: Diazepam or Lorazepam to stop the seizure followed by Phenobarbital or phenytoin.
Causes
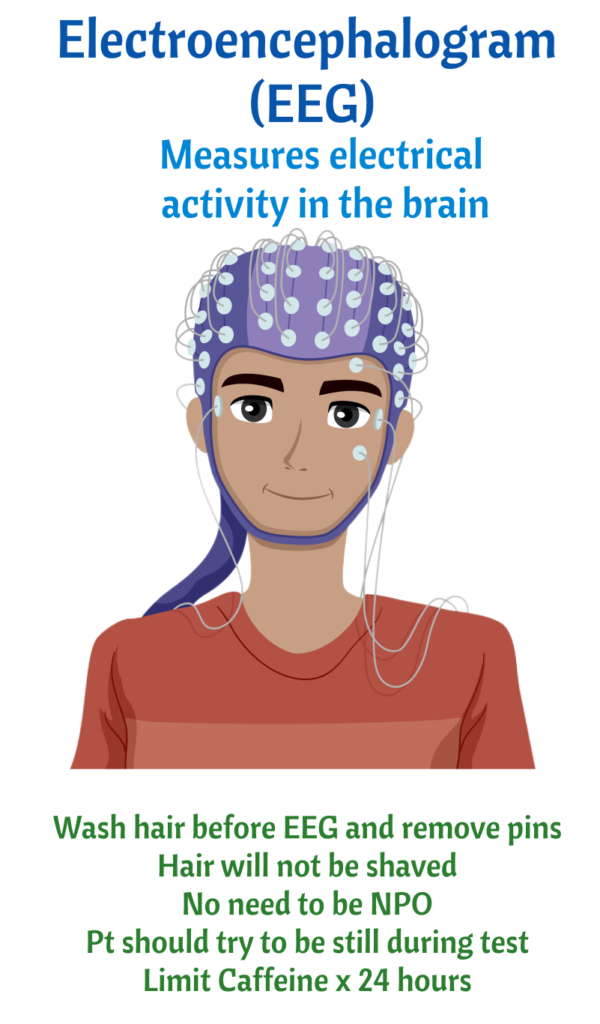
Types
Triggers
- Hormone shifts such as mentruation
- Poor sleep
- Dehydration
- Seizures
- Emotional stress
- Flashing lights
- Caffeine
- Non-compliance with meds
- Alcohol
- Hypoglycemia
- Head Trauma
Aura
- Auras are partial or focal seizures that sometimes happen before a more severe seizure occurs.
- Déjà vu- the sense that something has happened before.
- Impending doom.
- Fear
- Seeing spots in visual field
- Intervention: lay client down on their side with pillow under head. The big one may be coming.
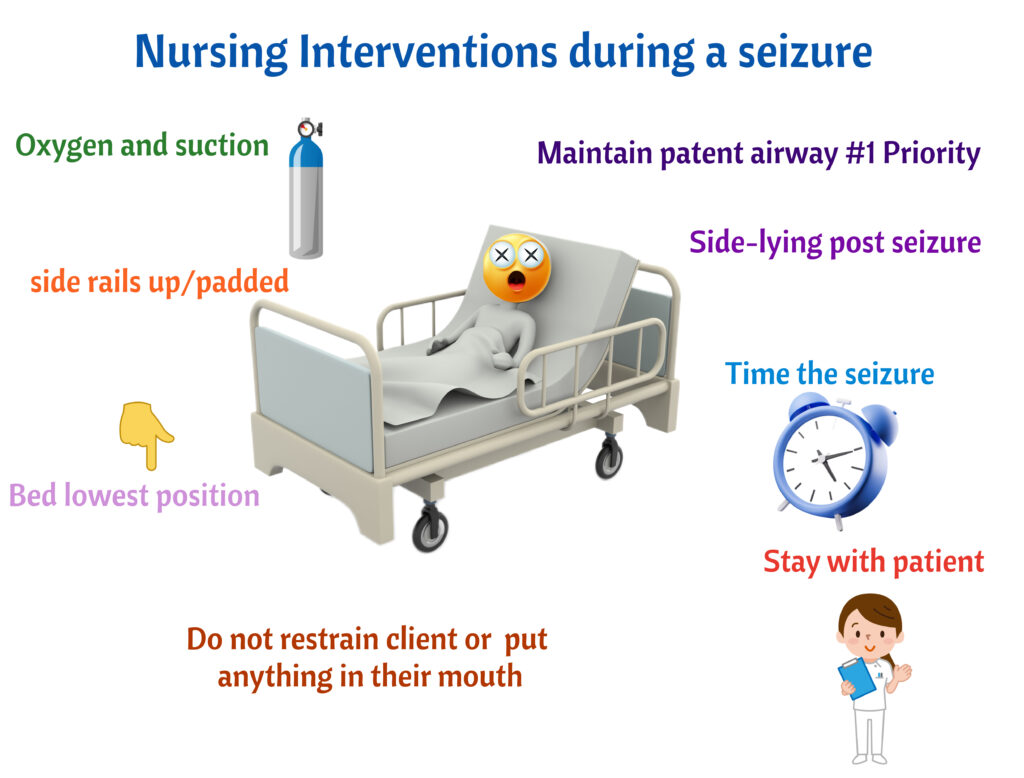
Priorities during a seizure, again

- #1 Priority is to maintain patent airway. Turn client on his side
- Have Oxygen and suction at the bedside
- Do not put anything inside the client’s mouth
- Do not restrain the client (NEVER)
- Stay with the client
- Loosen clothing
- Side rails padded/ Keep only 2 siderails up.
- Bed in the lowest position
- Time the seizure. Note any loss of consciousness, aura, or incontinence.
- Side-lying post seizure
After a tonic/clonic seizures
- Ok to let the client sleep
- Position side-lying
- May need to orient to environment since clinet may be confused (in a post-ictal state).
Never
- Again: Do not restrain client
- Again: Do not put anything in the client’s mouth. No tongue depressor.
Interventions/Treatments
- If seizures lasts > 5 minutes, call 911
- Seizure medications
- Seizure precautions
- Ketogenic diet: high fat and low carbohydrates. Used in pediatrics.
Phenytoin
- Normal level 10 to 20 mcg/ml
- Levels should be checked regularly
- Do not take with milk products or antacids because they affect Phenytoin absorption
- Monitor for rashes ( Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)= painful rash/blisters)
- Teach good oral care since it may cause gingival hyperplasia (an overgrowth of gum tissue)
- If level low, initiate seizure precautions
- Do not mix with D5W. It will precipitate.
- Agranulocytosis (Low WBCs). Watch for infection
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelets). Watch for bleeding.
Phenobarbital
- 10 – 30 mcg/mL . Some sources use 10-40
- Toxicity: Hypotension and CNS depression.
Lorazepam or Diazepam
- Lorazepam and diazepam are benzodiazepines.
- Flumazenil is the antidote

Time's up

Time's up
