Seizures
Generalized seizures: These seizures affect the entire brain and can cause a loss of consciousness, muscle spasms, and convulsions.
Focal seizures: Also known as partial seizures, these seizures only affect one part of the brain. They can be simple (no loss of consciousness) or complex (loss of consciousness).
Absence seizures: These seizures are typically seen in children, and they cause a brief loss of consciousness that lasts only a few seconds.
Myoclonic seizures: These seizures cause sudden, jerky movements in the arms and legs.
Atonic seizures: These seizures cause a sudden loss of muscle tone, often resulting in a person falling to the ground.
Tonic-clonic seizures: Also known as grand mal seizures, these seizures are the most recognizable type and involve convulsions and loss of consciousness.

A tonic-clonic seizure, or grand mal seizure, affects both sides of the brain and leads to unconsciousness and convulsions. It starts with a stiffening of the body for up to 20 seconds, followed by jerking movements that can last up to 2-5 minutes. Breathing may stop or become irregular.

An absence seizure, also referred to as petit mal seizure, is characterized by a short-lived loss of consciousness that can last up to 15 seconds.
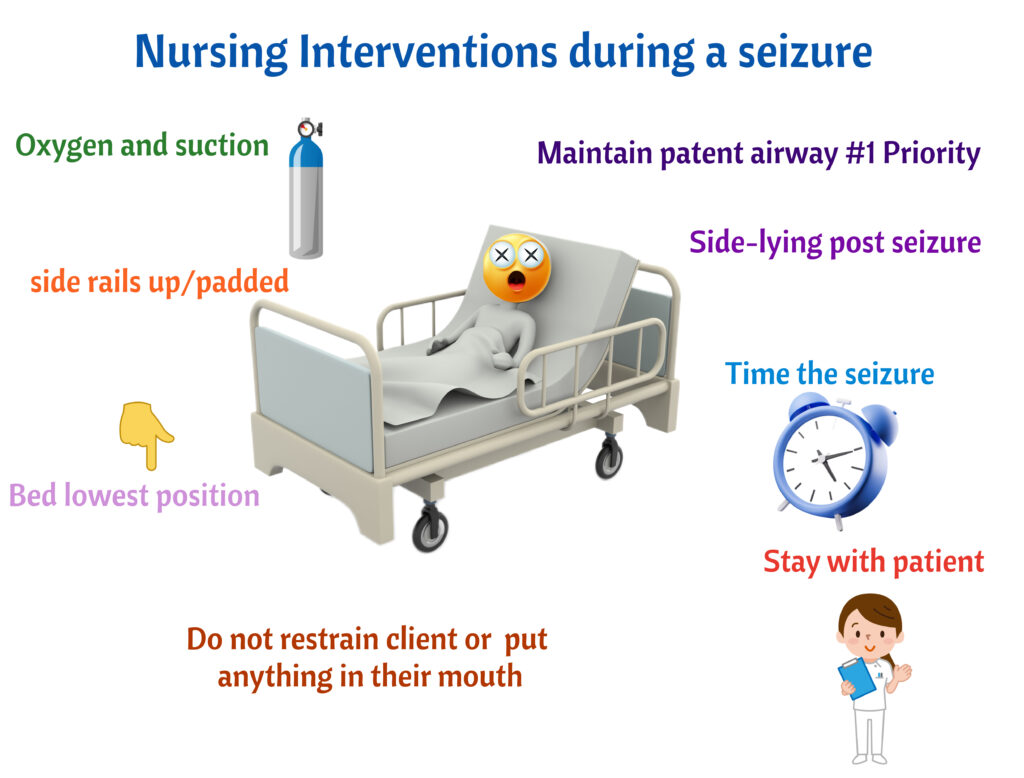
Priorities during a seizure, again

- #1 Priority is to maintain patent airway
- Have Oxygen and suction at the bedside
- Do not put anything inside the child’s mouth
- Do not restrain the child
- Stay with the child
- Side rails padded/ Keep only 2 siderails up.
- Bed in the lowest position
- Time the seizure
- Side-lying post seizure

Time's up

Time's up
Famous NCLEX Medication : Phenytoin
They have me on phenytoin (Dilantin) IV for my seizures. Please follow these precautions:
- Give it to me slowly. About 1 to 3 mg/kg/min or 50mg / minute, whichever is slower, to prevent cardiovascular side effects
- Check my Phenytoin levels (10 to 20 mcg/ml).
- Give through a central line or large bore IV to prevent risk of extravasation/infiltration.
- Only mix with normal saline. Again, only normal saline. (Never D5W because it will precipiate, or any other medication).
- Use with caution if I have kidney or liver problems.
- Monitor my skin for rashes and hives because of the risk of Steven-Johnson Syndrome.
