Simple Hemodynamics
- One question that always shows up is the knowledge that beta blockers and calcium channel blockers are contraindicated in cardiogenic shock because they decrease contractility.
- What increases contractility in cardiogenic shock? Dopamine, Dobutamine, and Epinephrine (aka vasopressors).
Hemodynamics
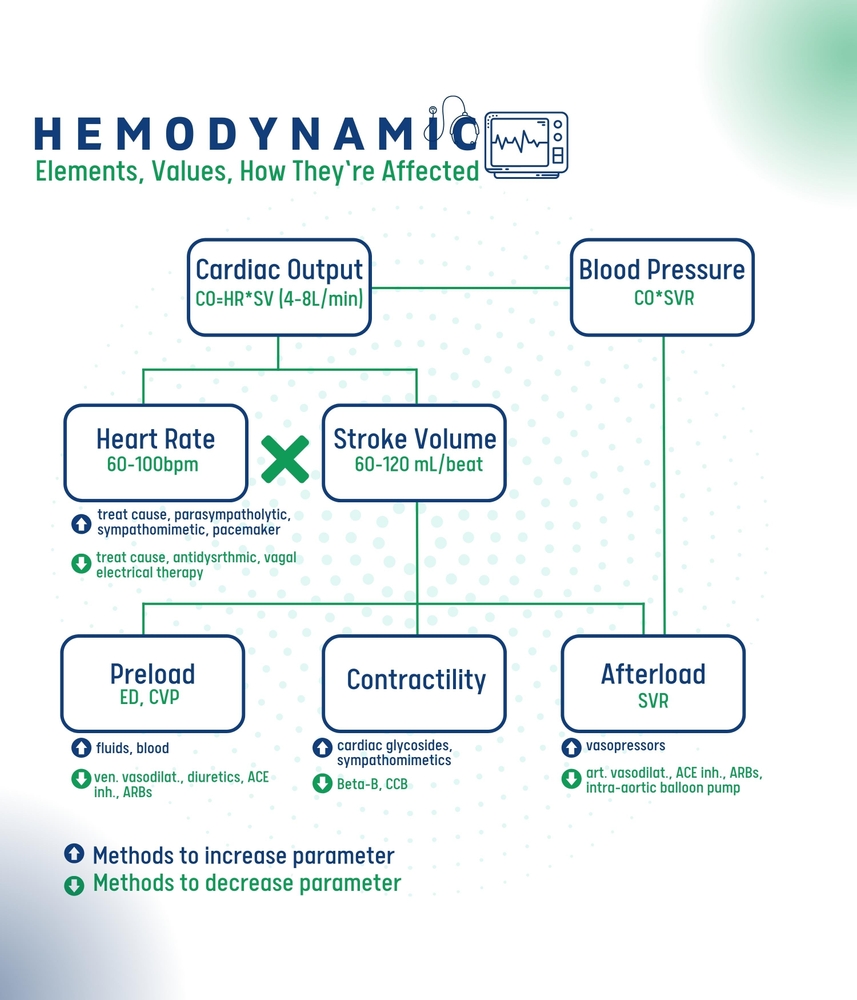
Cardiac output (CO) is the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one minute. It is calculated as HR X SV. Normal CO is around 4-8 liters per minute. Factors affecting CO include heart rate, preload, afterload, and contractility.
Cardiac Output
Preload is the volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole, before the next contraction. Afterload is the resistance the heart must overcome to eject blood into the systemic circulation. Contractility refers to the strength of the heart’s contractions.
Preload & Afterload
Central Venous Pressure (CVP) is the pressure in the vena cava near the right atrium, reflecting the amount of blood returning to the heart and the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. Normal CVP is 2-6 mmHg. Increased CVP may indicate fluid overload or right-sided heart failure.
