Sodium
Hyponatremia under 135 mEq/L






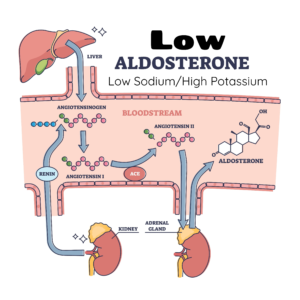


The D's of Hyponatremia
- Water retention such as in fluid overload and heart failure. More water, less sodium=Hyponatremia
- Pay attention to sodium level in heart failure! Low sodium due to dilution from fluid overload
Sweating such as in a fever. Are you losing sodium in your sweat? Now you have less sodium. Hyponatremia!
Loop diuretics: Furosemide. Remember where sodium goes water goes. One way diuretics work is by excretion of sodium. To make the body lose water, diuretics excrete sodium (which is followed by water). Sodium gets excreted = hyponatremia
- The story goes like this. On top of each kidney there is an adrenal gland that produces hormones. One of them is aldosterone, which works on the kidneys and regulates SODIUM and POTASSIUM.
- The goal of aldosterone is to increase sodium and decrease potassium.
- ⇑ Aldosterone =⇑ Sodium ⇓ Potassium
- ⇓ Aldosterone = ⇓ Sodium ⇑ Potassium
- Memorize this relationship. Please! Say it 3 times: Aldosterone’s goal is to ↑ Na+ and ↓ K+
- ⇓ Aldosterone = HYPONATREMIA
- Decreased is one of the D’s of hyponatremia
- Kidney disease makes sense. They help regulate sodium and if kidneys are not working, sodium will be abnormal.
- Liver disease clients become hypervolemic (increased water leads to dilutional hyponatremia)
- Easy right. Low intake of sodium
- However, low intake of sodium can also be related to hypotonic solutions administered in the hospital. Sometimes clients are given 0.45% normal saline and it dilutes sodium⇒Hyponatremia!
- 0.9% is isotonic. Anything < 0.9% is hypotonic (low salt or low NaCL)
- Antidiuretic hormone prevents you from peeing. Makes you hold water. Too much ADH, you retain water which dilutes sodium⇒Hyponatremia.
- Too much ADH = Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH).
- Remember S ↔ Submerged in water
- The opposite is true. Too little ADH leads to losing too much water/making lots of urine. With low or no ADH, nothing is stopping you making losing water/urine. This is called Diabetes Insipidus ⇒ Hypernatremia
- D ↔ Dry as the Desert
- Addison’s disease is adrenal insufficiency.
- Remember the adrenal gland. One of the hormones is aldosterone. With aldosterone insufficiency, sodium goes down.
- Clients with addison’s disease not only have low cortisol levels, but also low aldosterone.
- Low Aldosterone = hyponatremia
- ADDison’s ⇒ ADD hormone
- The opposite of Addison’s is Cushing’s Disease. Too much cortisol/Aldosterone. Yes, Cushing’s = Hypernatremia.
- ADDison’s = Hyponatremia (D’s of hyponatremia)
- Cushing’s = Hypernatremia
Not a D, but something that comes up frequently
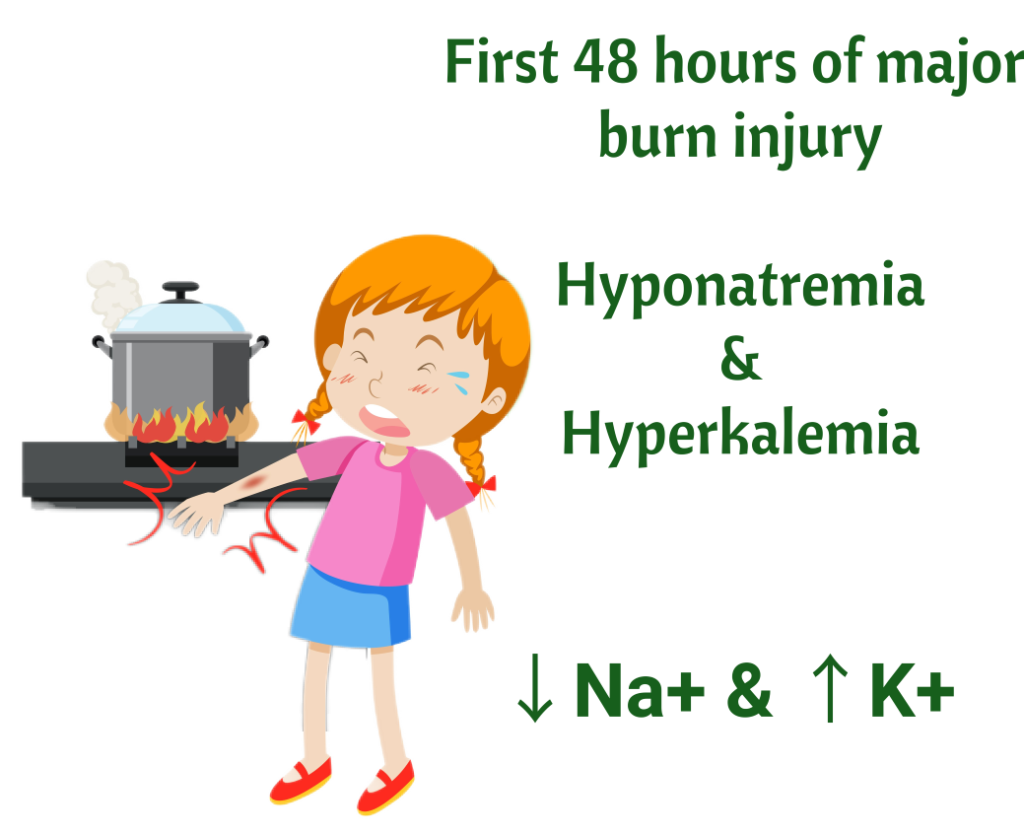
Memorize this! An important cause of hyponatremia is a Major Burn injury in the first 48 hours. ↑ Capillary permeability leads to sodium leakage from the plasma to the interstitial space, so serum sodium decreases! Also, potassium leaks from the intracellular space to the extracellular space and there is hyperkalemia.
Major Burns in the first 48 hours = hyponatremia and hyperkalemia.
Let's make sure you understand
Quiz Summary
0 of 1 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 1 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 1
1. Question
Type an X where it belongs!
-
Sodium High Low High or Low Aldosterone causes hyponatremia In Addison, is serum sodium high or low? SIADH is serum sodium high or low? Diabetes Insipidus, is serum sodium high or low? If too much ADH, serum sodium is high or low? In hemodilution, is serum sodium high or low? Would 0.45% NaCL cause high or low serum sodium In the first 48 hours of burn injuries is serum sodium high or low?
CorrectIncorrect -
Signs and Symptoms of Hyponatremia
S Stupor/Coma
A Anorexia
L Lethargy
T Tendon
L Limp Muscles (Weakness)
O Orthostatic Hypotension
S Seizures/Headaches
S Stomach Cramps

NCLEX Tips
Let's check what you know
Quiz Summary
0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-
If you are not sure about the answers go back and study.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- Current
- Review / Skip
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 10
1. Question
Select signs and symptoms of hyponatremia.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 10
2. Question
What is true of hyponatremia
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 10
3. Question
The nurse has completed the admission assessment of a client with hyponatremia. The physician has ordered 3% NaCl to corrrect the sodium imbalance. Which of the following is true about the correction of sodium in a hyponatremic client?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 10
4. Question
The nurse is caring for a client with head trauma. The client’s urine output is drastically decreased and the client is gaining weight. Which of the following is a priority assessment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 10
5. Question
Which of the following are electrolyte imbalances in adrenal insufficiency? Please make sure you know this!
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 10
6. Question
The client had a tumor removal from the pituitary gland and now has large amount of urine output. The client has been diagnosed with diabetes insipidus. Which of the following potential findings in a client with diabetes insipidus are of immediate concern to the nurse?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 10
7. Question
Which findings would the nurse expect in a client with addison’s disease?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 10
8. Question
Which findings would nurse expect in a client with hyponatremia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 10
9. Question
What electrolyte imbalance does the nurse expect in the first 48 hours after a major burn injury?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 10
10. Question
The nurse is caring for a client who is having a seizure. Which of the following electrolyte imbalances is likely the cause of the seizures?
CorrectIncorrect
Hypernatremia Over 145 mEq/L
S Skin flushed
A Agitation; Anxiety
L Low-grade fever
T Tachycardia
E Extreme Thirst
D Dry Mouth, ↓ Urine

Causes of HYPERnatremia




Addison's disease versus Cushing's syndrome

Cushing's Syndrome
- Cushing’s syndrome is too much adrenal hormone due to steroid therapy or an adrenal tumor that secretes cortisol. There is also high aldosterone (↑ sodium, ↓ potassium).
- Cushing’s disease is a rare condition thatis specific to a pituitary adenoma. The adenoma secretes too much ACTH leading to ↑ cortisol.
- Everything is high EXCEPT potassium
- Hypernatremia, hypertension, hyperglycemia and high weight
- Too much cortisol/steroids leads to osteoporosis, weak immune system, infection, and poor wound healing
- Hypokalemia is the only hypo

Addison's Disease
- Adrenal insufficiency. Need to ADD hormone= ADDison’s
- Low corticol/steroid/Low aldosterone.
- Everything is low except potassium
- Low energy and low hair (lol)
- Low blood pressure
- Low sodium
- Low weight
- Low blood sugar
- Hyperkalemia is the only hyper: connect to cardiac monitor and watch for tall peaked T waves on EKG.
Do you know the difference between hyponatremia and hypernatremia
Did you know that potassium and sodium have an opposite relationship. When sodium is low, potassium is high. Sodium High=Potassium Low. When thinking about this relationship always remember ALDOSTERONE! Aldosterone ↑ sodium, ↓ potassium

NCLEX-like case study. Click on the words “Nursing Notes” “Vital Signs” and “Labs” to view the whole medical record.
The client is a 54-year-old male with Addison Disease who has not taken steroids for the last 10 days. The client is confused and very weak. The client can barely open his eyes to answer questions. Lungs clear to auscultation in all lobes. All peripheral pulses 1+, CFT about 4 seconds. Hyperactive bowel sounds.
Temp 96.9 F, BP 90/54, HR 108, RR 15, Oxygen saturations on room air 96%
- Sodium 129 (normal 135-145 mEq/L)
- Potassium 5.6 (normal 3.5- 5.0 mEq/L)
- Chloride 94 (normal 95-105 mEq/L)
- Glucose 59 (normal 80-100 mg/dl)
