Spina Bifida
Spina Bifida

- Prone with legs flexed to prevent injury to the sac
- Monitor sac for infection (meningitis)
- Measure head circumference (hydrocephalus)
- Monitor fontanelles (incerased intracranial pressure)

- Spina bifida is a congenital disorder characterized by incomplete closing of the spinal cord during development. It can lead to a range of physical and neurological complications, depending on spinal cord involvement.
- Abnormal hair growth over the spinal cord
- Hydrocephalus (accumulation of fluid in the brain)
- Leg weakness or paralysis
- Bladder control problems
- Trouble with bowel function
- Teach self-catheterizations. Will eventually develop latex allergy.

The nurse is caring for a newborn with a myelomeningocele. The nurse monitors the newborn for which of the following common complications?
Hydrocephalus occurs in about 90% of infants with Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele due to the blocked flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
The nurse educates a group of child-bearing age women about the best way to prevent spina bifida. Which of the following points should the nurse include?
Consuming folic acid during pregnancy has been found to reduce the risk of Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele by up to 70%.
The nurse is caring for an infant with spina bifida that has developed hydrocephalus. Which of the following procedures does the nurse anticipate that this infant will have?
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt placement is a common procedure used to manage hydrocephalus by directing the excess fluid from the brain ventricles to the peritoneal cavity.
The nurse demonstrates knowledge of Spinal Bifida Myelomeningocele when the nurse states that it primarily affects which of the following regions of the spine?
Spinal Bifida Myelomeningocele primarily affects the sacral region of the spine, which is the lowest part of the back.
A 3-month-old male baby is brought to the emergency department with a bulging fontanelle, vomiting, and irritability. A CT scan reveals an enlarged ventricular system, indicating hydrocephalus. The nurse anticipates that the most common cause of this baby's hydrocephalus is which of the following?
Congenital anomaly. Hydrocephalus is most commonly caused by a congenital anomaly in infants, such as a neural tube defect or brain malformation.
A 3-month-old male baby is brought to the emergency department with a bulging fontanelle, vomiting, and irritability. A CT scan reveals an enlarged ventricular system, indicating hydrocephalus. The nurse expects that this baby's hydrocephalus will be treated with which of the following procedures?
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt. In infants, hydrocephalus is usually treated by surgically implanting a ventriculoperitoneal shunt to drain excess CSF from the brain, as it can cause brain damage if left untreated.
A 2-year-old girl was diagnosed with spina bifida at birth. After corrective surgery, she was discharged with management plans and follow-up appointments. During one of her appointments, the child's mother expressed concerns over the child's delayed milestones, including the inability to crawl and walk. The nurse noticed that the child also had bowel and bladder incontinence, as well as signs of skin breakdown on her buttocks. What is the best intervention for this child?
Frequent repositioning helps to relieve pressure on bony prominences and prevent skin breakdown. This is especially important for clients with spina bifida who have limited mobility and may be restricted to a wheelchair or bed-bound.
Which of the following interventions is most effective for managing bowel and bladder incontinence in clients with spina bifida?
Timed voiding is a structured approach to toilet training that involves establishing a regular schedule of bathroom breaks. This helps to promote bladder control and reduce the risk of incontinence. Pelvic floor muscle exercises and the use of catheters may also be helpful interventions, but timed voiding is the most effective strategy for managing bowel and bladder incontinence in clients with spina bifida.
A 30-year-old woman gave birth to a newborn with myelomeningocele. The baby had a sac-like protrusion on the lower back that contained nerves and parts of the spinal cord. The baby was immediately transferred to the neonatal intensive care unit for specialized care. What is the priority intervention for this newborn?
The priority nursing intervention for a newborn with myelomeningocele is assessing for signs of infection, such as fever, drainage, redness, or swelling around the sac. This is important to prevent meningitis, which is a common complication associated with this condition. Administering IV antibiotics would be appropriate if an infection were present.
The NICU nurse admits a newborn with a myelomeningocele. Which of the following positions is the best for this newborn?
A neonate born with myelomeningocele (spina bifida) has a protruding spinal cord and the best position for the neonate is prone. This is to prevent any pressure on the myelomeningocele and reduce the risk of damage or rupture. The supine position increases pressure on the myelomeningocele, which can lead to complications such as hydrocephalus, respiratory distress or cardiac problems. The lateral position also puts pressure on the myelomeningocele and can worsen the condition, while the right lateral position does not offer any advantage over the other lateral positions. Thus, placing the neonate in a prone position with proper support can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Which of the following postures is an indication of decerebrate position in a patient?
The decerebrate position is characterized by extension of the upper extremities, pronation of the hands, and extension of the lower extremities. This abnormal positioning is indicative of damage to the brainstem, particularly the midbrain or pons. The patient may exhibit other signs such as altered consciousness, abnormal breathing patterns, and decreased motor function. It is important for the nurse to recognize this position as it indicates a serious neurological issue and immediate intervention is required to prevent further damage. Assessing and monitoring the patient's level of consciousness, respiratory status, and neurological responses are critical nursing interventions when observing decerebrate position.
Which of the following is a sign of decorticate position during a neurological assessment?
Decorticate position is a postural abnormality that indicates damage to the corticospinal tract. The position is characterized by upper extremity flexion and lower extremity extension. The arms are adducted and internally rotated, while the wrists are flexed and the fingers are flexed into a fist. The legs are internally rotated and extended. The decorticate position is caused by damage to the midbrain or upper pons and is often associated with anoxic brain injury, stroke, or traumatic brain injury.
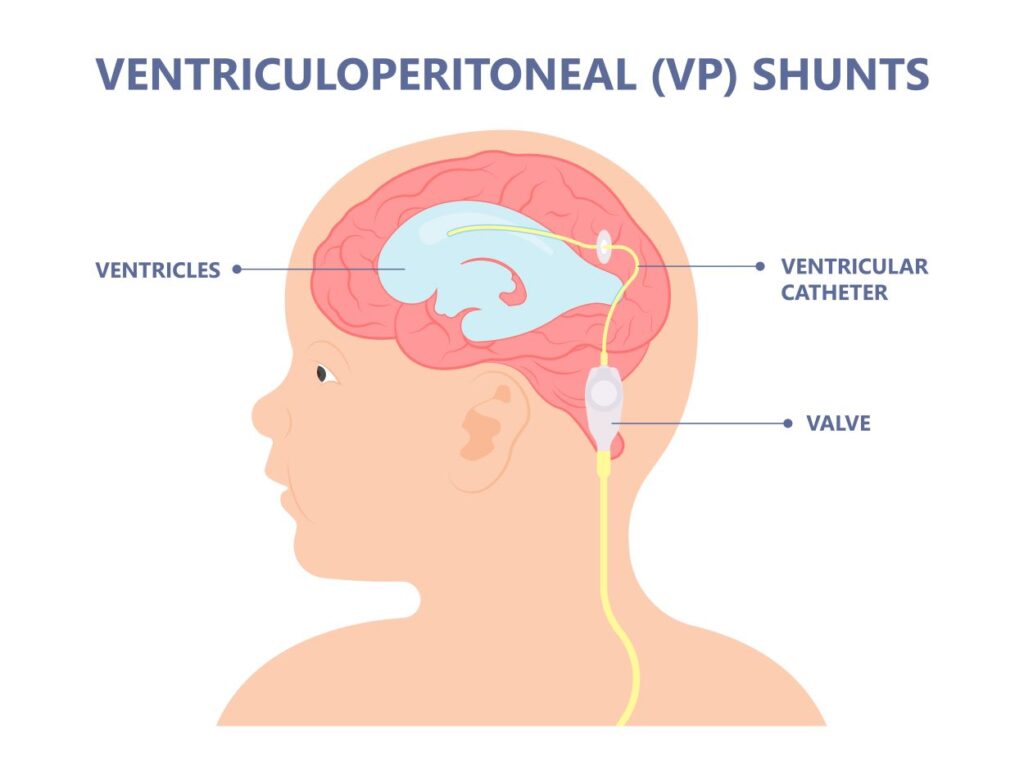
After a VP shunt
- Check vital signs and assess neuro status
- Position the child on the unoperated side to prevent pressure on the shunt valve
- Keep child flat to prevent rapid reduction of intracranial fluid
- HOB 15 to 30 degrees if signs of increased intracranial pressure
- Measure head circumference
- Monitor Intake and output
- Administer: diuretics, antibiotics, and anticonvulsants as prescribed
- Malfunctioning shunt: irritability, lethargy, and poor feeding (and signs of ↑ ICP)
- Monitor for infection
