Disaster Triage, Prioritizing, and Delegation
4 Topics | 2 Quizzes
Neurological System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
MS, MG, and Guillain Barré
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The Cardiovascular System
12 Topics | 1 Quiz
Pulmonary System
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cushing Versus Addison Disease
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Thyroid Disorders
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Parathyroid Disorders
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
DI and SIADH
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Diabetes
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Burns
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Anemias, Aplastic Anemia, Polycythemia Vera, Thrombocytopenia and DIC
9 Topics | 1 Quiz
Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Oncological Emergencies
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Leukemias, Hodgkin’s Disease, and Multiple Myeloma
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
The GI system
16 Topics | 1 Quiz
Renal and Genitourinary Problems
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Infection and Isolation Precautions
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
NCLEX Pharmacology
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
TPN, IV Solutions, & Blood Products
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Lab Values
9 Topics
Stroke
Cerebral Vascular Accident (Stroke)
Risk Factors
| Modifiable | Non-Modifiable |
|---|---|
| Hypertension Hyperlipidemia Diabetes Obesity Stress Oral Contraceptives Anticoagulants such as aspirin and warfarin | Genetics Age Gender (Male) Ethnicity such as black/hispanic |
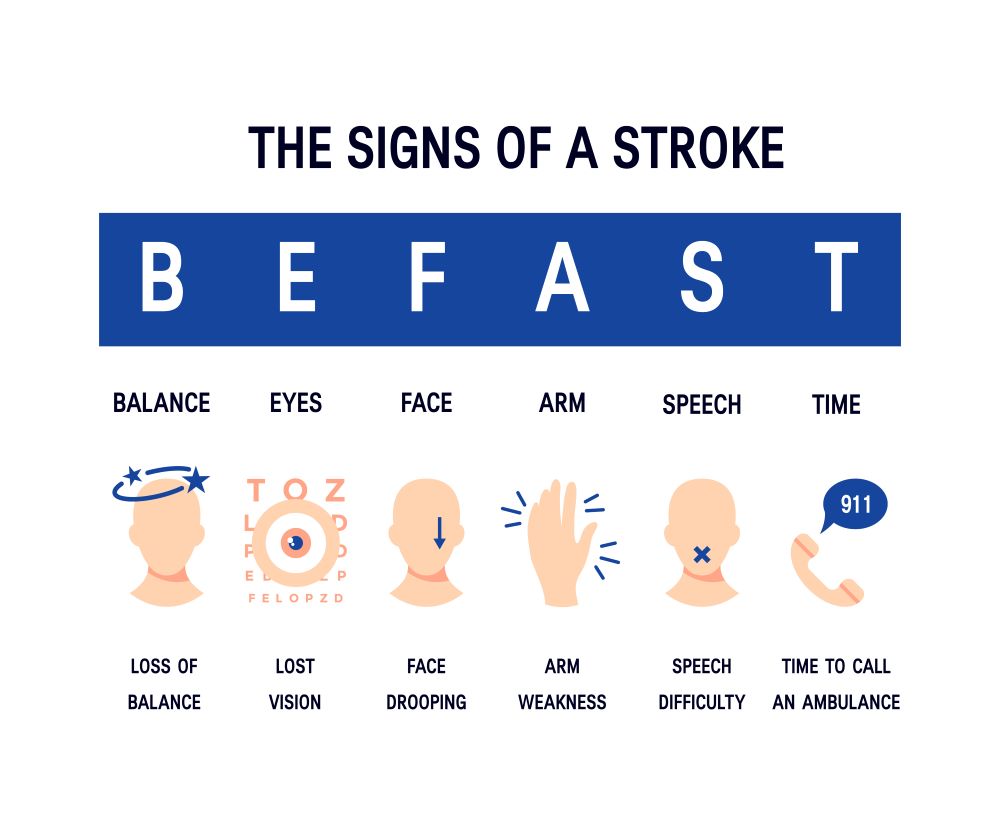
- TIAs or transient ischemic attacks revolves within 24 hours, usually within 30 minutes.
Ischemic vs Hemorrhagic Stroke
| Ischemic | Hemorrhagic | |
|---|---|---|
| What? | Thrombosis= clot that formed in the wall of an artery in the brain. Embolic: A clot that traveled to the brain such as in atrial fibrillation Blood flow is cut off due to ischemia 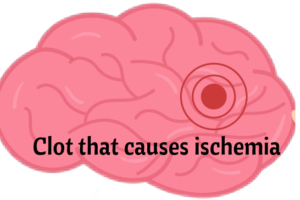 | Ruptured Artery Aneurysm that ruptured Uncontrolled hypertension The collection of blood in the brain can cause increased intracranial pressure. The treatment for a hemorrhagic stroke is to stop the bleeding and prevent ↑ ICP. 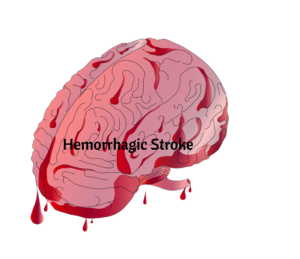 |
Treatment for an ischemic stroke
Fibrinolytics to break down the clot

Timing is everything
Give within 3 hours of onset of symptoms and within 60 minutes of arrival to the ER

Examples
Alteplase or tPA and Streptokinase

Indications for fibrinolytics
No recent hemorrhage or surgery, controlled BP, normal INR and platelets, and no recent anticoagulants. What is recent? Within 3 months.

Long Term Prevention
Meds such as Dabigatran (Pradaxa) which are given to clients with atrial fibrillation. Aspirin (antiplatelet medication).
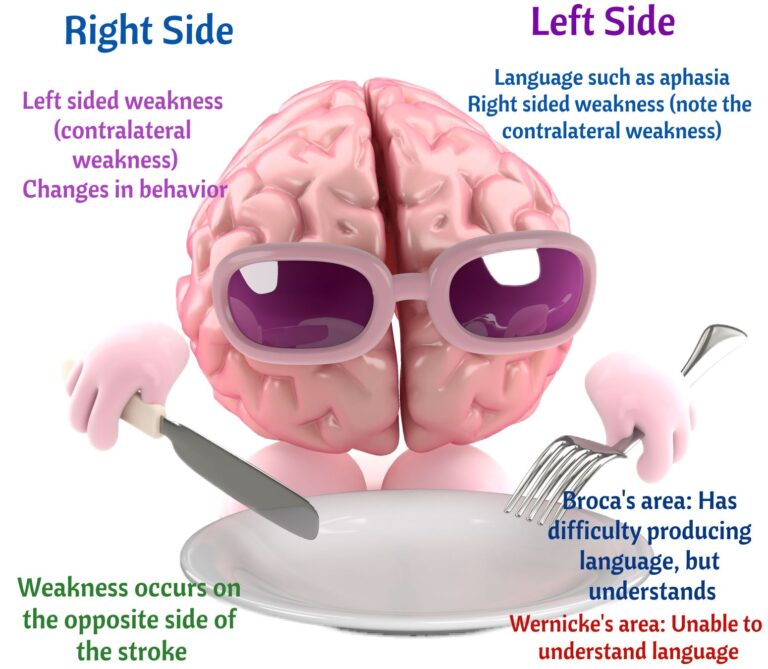
Nursing Interventions
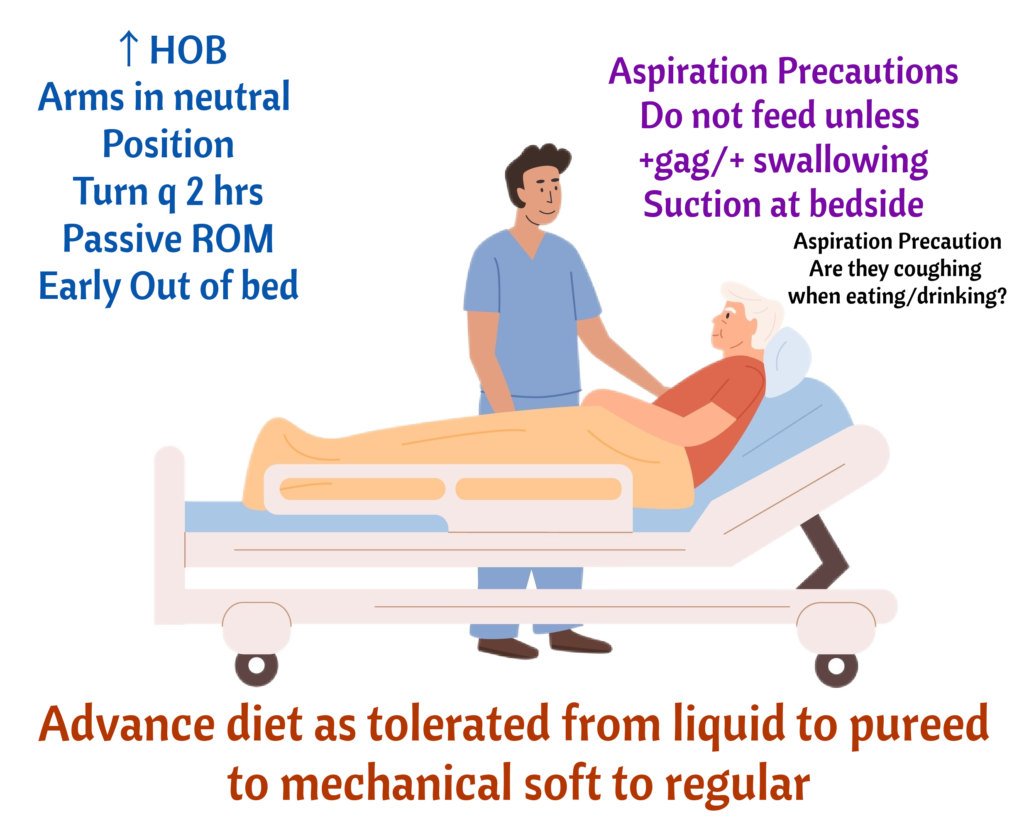
Must-Know
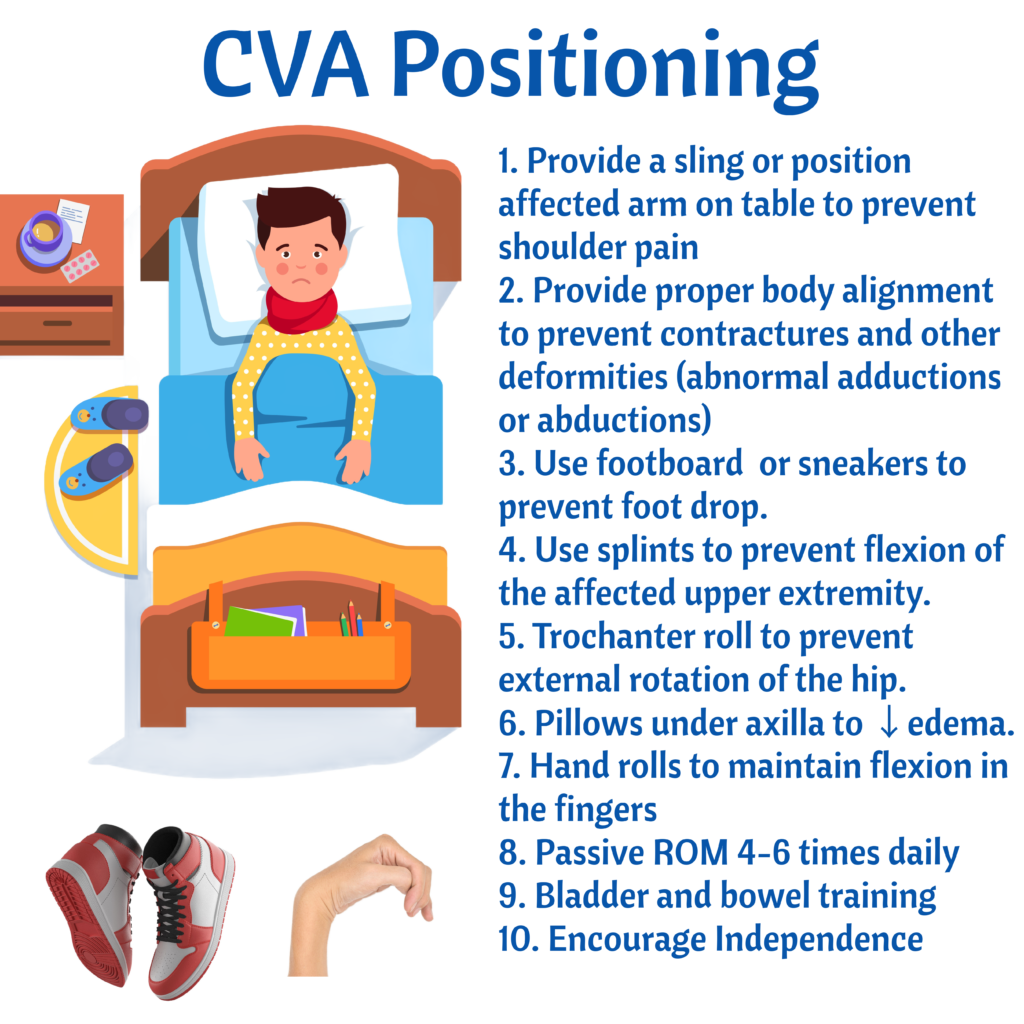
- Assess ABC: always priorities
- Stat CT scan: Take them to CT stat for diagnosis. Time is neurological function.
- Give thrombolytics such as alteplase
- Give antihypertensives such as atenolol. If BP is not controlled, the thrombolytics may cause hemorrhage.
