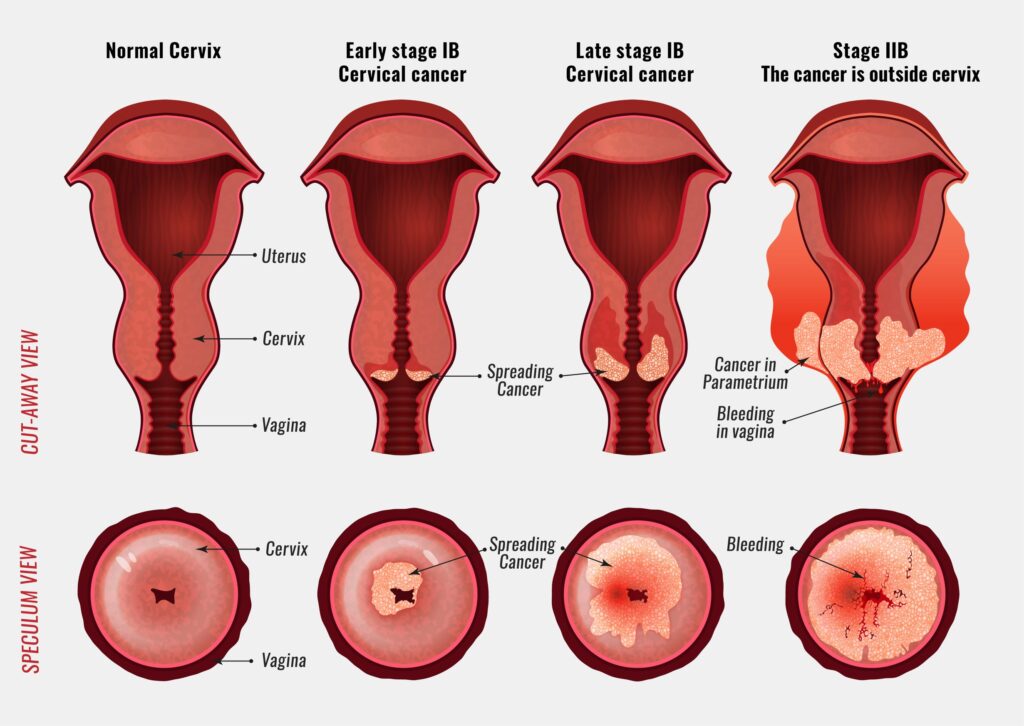
Cancer Staging
- Determines severity of cancer
- Helps determine treatment
- Helps determine metastasis
- stage 0 – in situ
- stage 1 – small- no metastasis
- stage 2 – has grown but no metastasis
- stage 3 – the cancer is larger. Metastasis to surrounding tissues/lymph
- stage 4 – Metastatic cancer to at least one other organ.