Iron Deficiency Anemia
/*! elementor – v3.12.1 – 02-04-2023 */
.elementor-heading-title{padding:0;margin:0;line-height:1}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title[class*=elementor-size-]>a{color:inherit;font-size:inherit;line-height:inherit}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-small{font-size:15px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-medium{font-size:19px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-large{font-size:29px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-xl{font-size:39px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-xxl{font-size:59px}
Know your normal values
Hypoproliferative Anemias = Decreased production of RBCs
/*! elementor – v3.12.1 – 02-04-2023 */
.elementor-widget-image{text-align:center}.elementor-widget-image a{display:inline-block}.elementor-widget-image a img[src$=”.svg”]{width:48px}.elementor-widget-image img{vertical-align:middle;display:inline-block} 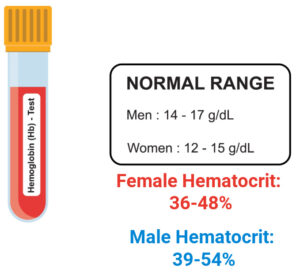
Iron Deficiency Anemia
/*! elementor – v3.12.1 – 02-04-2023 */
.elementor-accordion{text-align:left}.elementor-accordion .elementor-accordion-item{border:1px solid #d5d8dc}.elementor-accordion .elementor-accordion-item+.elementor-accordion-item{border-top:none}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title{margin:0;padding:15px 20px;font-weight:700;line-height:1;cursor:pointer;outline:none}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon{display:inline-block;width:1.5em}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon svg{width:1em;height:1em}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon.elementor-accordion-icon-right{float:right;text-align:right}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon.elementor-accordion-icon-left{float:left;text-align:left}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon .elementor-accordion-icon-closed{display:block}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon .elementor-accordion-icon-opened,.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title.elementor-active .elementor-accordion-icon-closed{display:none}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title.elementor-active .elementor-accordion-icon-opened{display:block}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-content{display:none;padding:15px 20px;border-top:1px solid #d5d8dc}@media (max-width:767px){.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title{padding:12px 15px}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon{width:1.2em}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-content{padding:7px 15px}}.e-con-inner>.elementor-widget-accordion,.e-con>.elementor-widget-accordion{width:var(–container-widget-width);–flex-grow:var(–container-widget-flex-grow)}
Patho
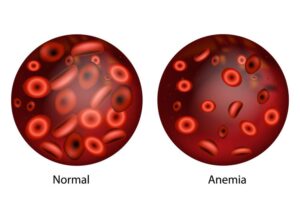
- Microcytic (note that the cells are not just less in number, but smaller)
- Red Blood Cells are small in size
- small cells have a lower capacity to carry oxygen.
- Decreased oxygen explains most of the symptoms of anemia (e.g., fatigue and shortness of breath
- Serum Ferritin < 10 (normal 12-300) (Ferritin is the protein that contains the iron in the RBC).
- ⇓ RBC production
- 2/3 of iron in Hgbs ⇒ less RBCs⇒Less Hgb⇒less iron
- Poor intake of iron and poor diet
- Vegetarian diet
- Inability to absorb iron (e.g. bariatric surgery or Celiac disease
- Blood loss
- Women and elderly are at risk
- Pregnancy

- Severe symptoms: smooth, red tongue and brittle and ridged nails

- Increase intake of iron
- red meat
- Organ meat
- egg yolks
- kidney beans
- leafy green veggies
- Iron-fortified cereals
- Oysters and tuna
- Seeds
- Fish
- Adequate rest
- Avoid coffee or tea since inhibit absorption of iron.
- Iron Supplement

- Liquid iron: drink with a straw and brush teeth afterwards.
- DO NOT take iron with calcium (milk or antacids) because it ⇓ absorption.
- Iron names (ferrous sulfate, ferros gluconate, ferrous fumarte)
- May be given IV as well!

