Mechanical Ventilation & Oxygen Delivery
/*! elementor – v3.12.1 – 02-04-2023 */
.elementor-heading-title{padding:0;margin:0;line-height:1}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title[class*=elementor-size-]>a{color:inherit;font-size:inherit;line-height:inherit}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-small{font-size:15px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-medium{font-size:19px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-large{font-size:29px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-xl{font-size:39px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-xxl{font-size:59px}
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
/*! elementor – v3.12.1 – 02-04-2023 */
.elementor-widget-image{text-align:center}.elementor-widget-image a{display:inline-block}.elementor-widget-image a img[src$=”.svg”]{width:48px}.elementor-widget-image img{vertical-align:middle;display:inline-block} 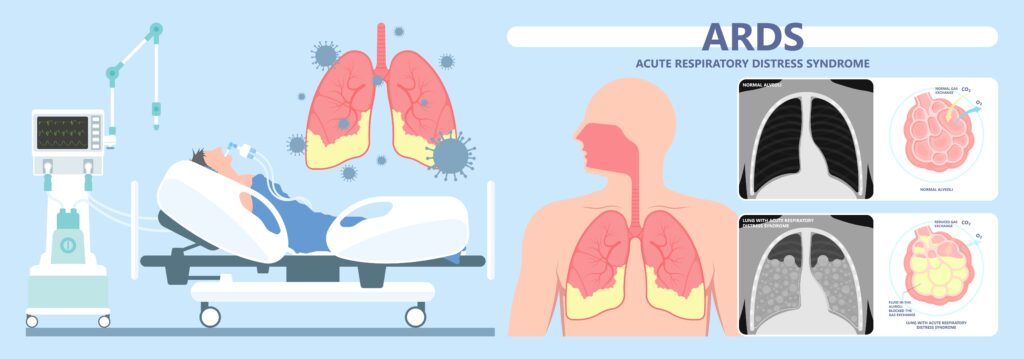
- Fluid in the alveoli blocks gas exchange. Yes, Gas exchange #1 problem, in case anyone asks you.
- Cardinal sign and symptom of ARDS is HYPOXEMIA. A common NCLEX ?
- This is a sick client that will be eventually be intubated and may go into multiple organ failure.
Endotracheal Tube
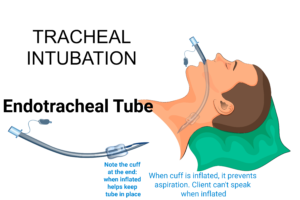
- Endotracheal tube used for mechanical ventilation
- To maintain patent airway. Patent airway is always the #1 priority in all NCLEX questions.
- If client still needs an ET tube (needs mechanical ventilation) more than 10-14 days, a tracheostomy is performed. Why? Protect vocal cords.
- Confirm ET tube placement with a chest xray. Priority after intubation? Get a chest xray!
- ET tube cuff pressure should be checked every 8 hours and should be < 20 mm Hg.
- Priority: get x ray after intubation. It must be important if mentioned again.
- Potential problem: Stomach intubation: breath sounds over stomach.
- Potential Problem: ET Tube in right main bronchus = no breath sounds on the left side because ET tube is in the right side of lung.
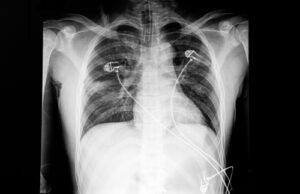
- Can you see the ET tube in this xray?
- Anyways, remember that when suctioning, you must insert suction catheter withOUT suction and apply suction as you remove catheter. Suction regulator should be set at 120-140 mm Hg. Suction < 15 seconds. NCLEX
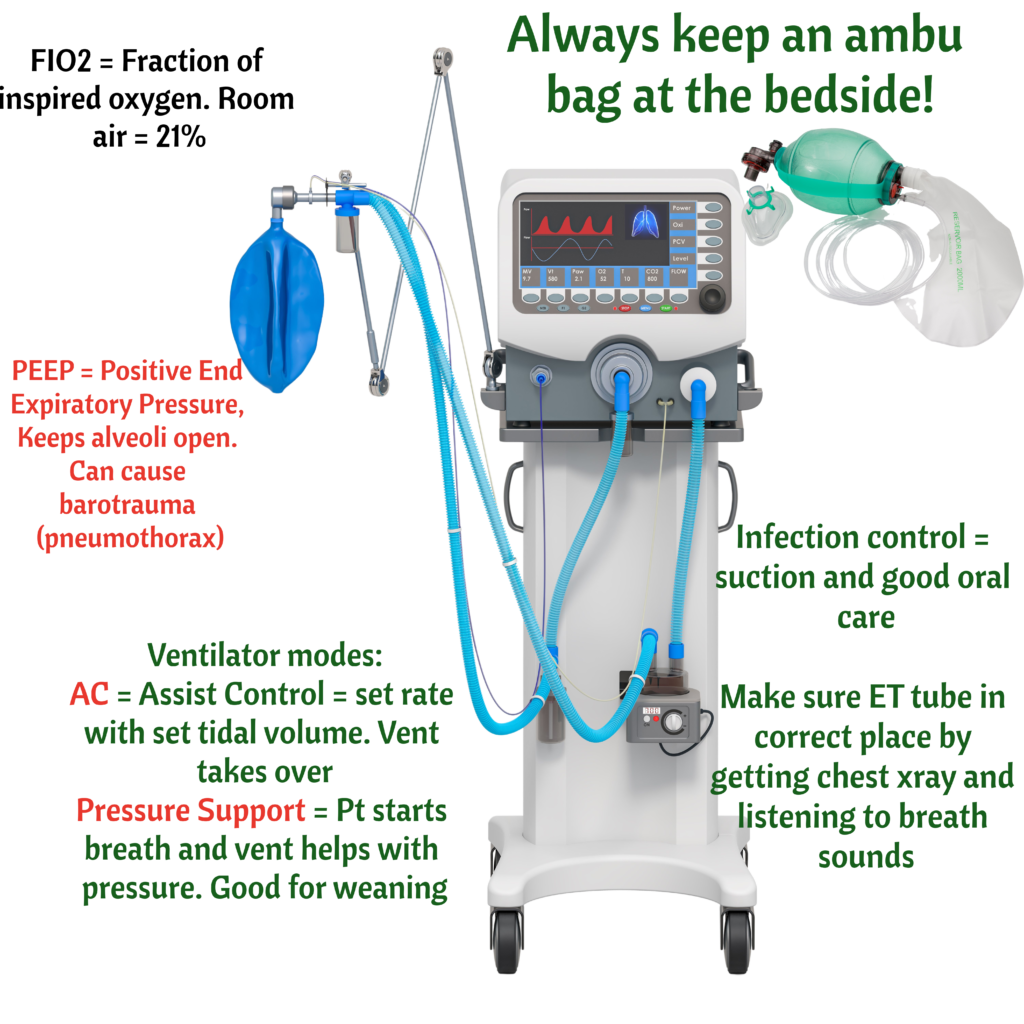
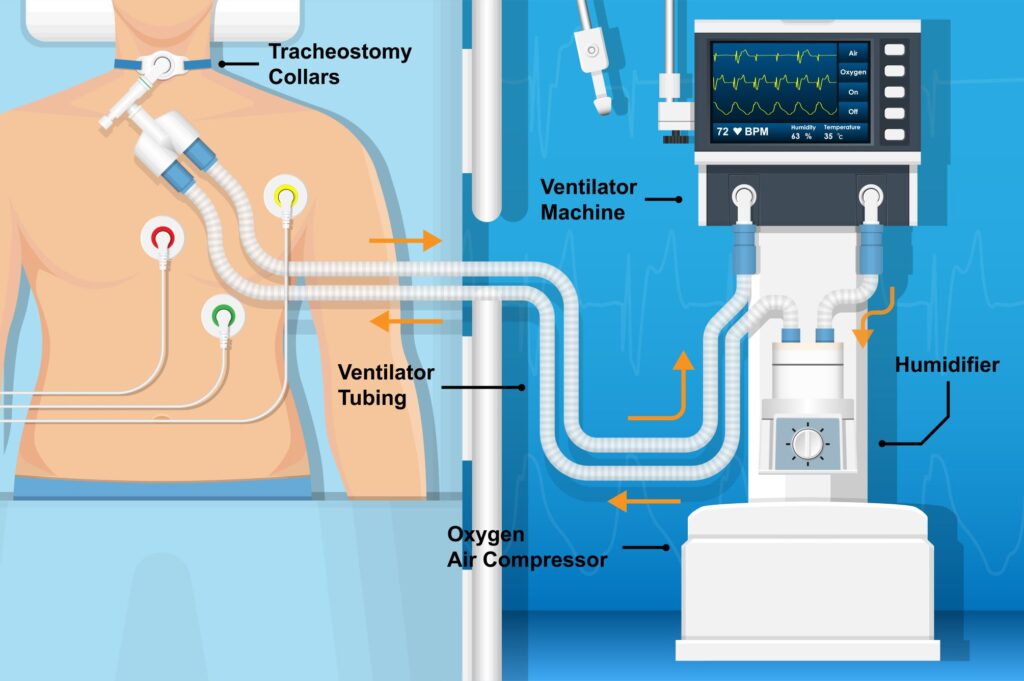
- It the tubing becomes disconnected = LOW PRESSURE ALARM. Makes sense, ventilator working against no pressure
- If there is an obstruction, lots of water in the tubing, or client has lots of secretions = HIGH PRESSURE ALARM. Makes sense, ventilator working against resistance/pressure.
- Remember that ventilators use humidified air which condenses into water.
- Finally, if the ventilator is going off and you have no idea what is happening, the answer both on the NCLEX and in practice is to check the client. Look at the client. Never troubleshoot any equipment without looking/assessing the client. AMBU BAG the client. Repeat after me, AMBU BAG, AMBU BAG (ahh, and make sure ambu bag is connected to oxygen)
What is Ventilation?
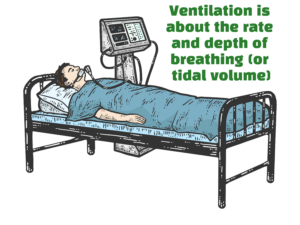
- Fast rate (⇑ Respiratory rate) and increased tidal volume blow off more CO2 leading to HYPERVENTILATION or decreased PCO2.
- Here is a hyperventilation ABG: pH 7.52, PCO2 30, HCO3 22. Respiratory alkalosis! Yes, Hyperventilation = low pCO2 = respiratory alkalosis
- Hypoventilation = low rate and/or low tidal volume, leading to high PCO2. Here is a hypoventilation ABG: pH 7.32, PCO2 55, HCO3 23. Respiratory acidosis! Retaining pCO2
- Ready! To get rid of pCO2, you either breathe faster or breathe deeper.
- Tidal volume is a measure of the amount of air a person inhales during a normal breath

