Problems Caused by Kidney Failure
Electrolyte Imbalances
Sodium

Hyponatremia: Salt Loss

Hypernatremia: Salted
Potassium
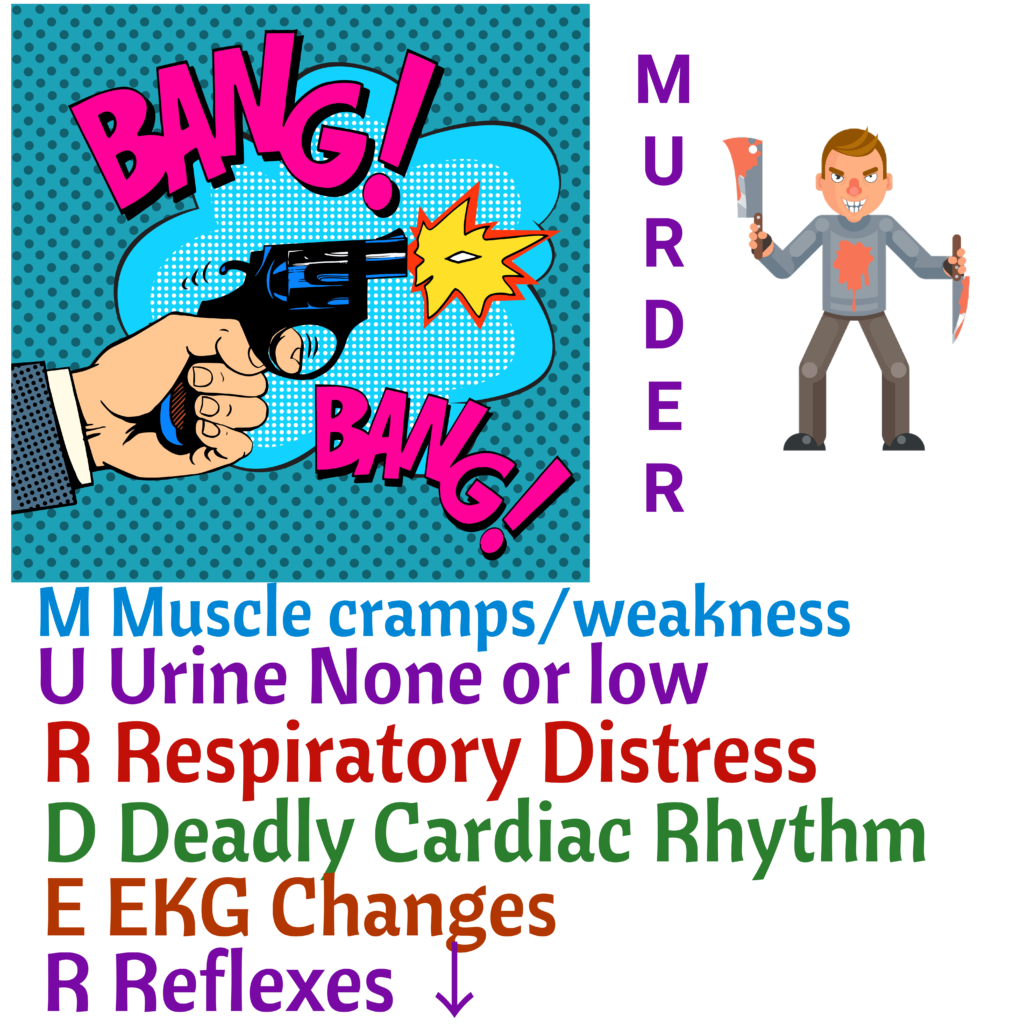
Hyperkalemia: Murder
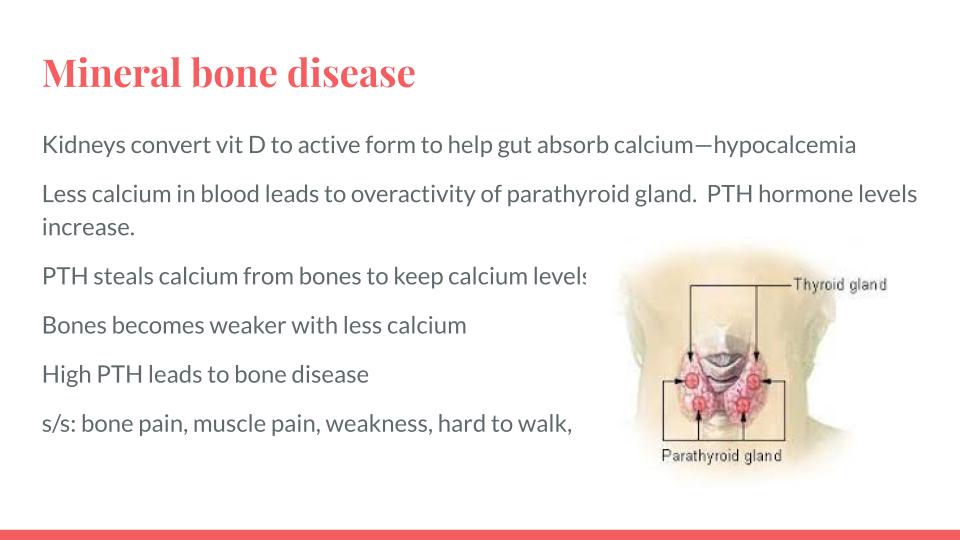
Calcium
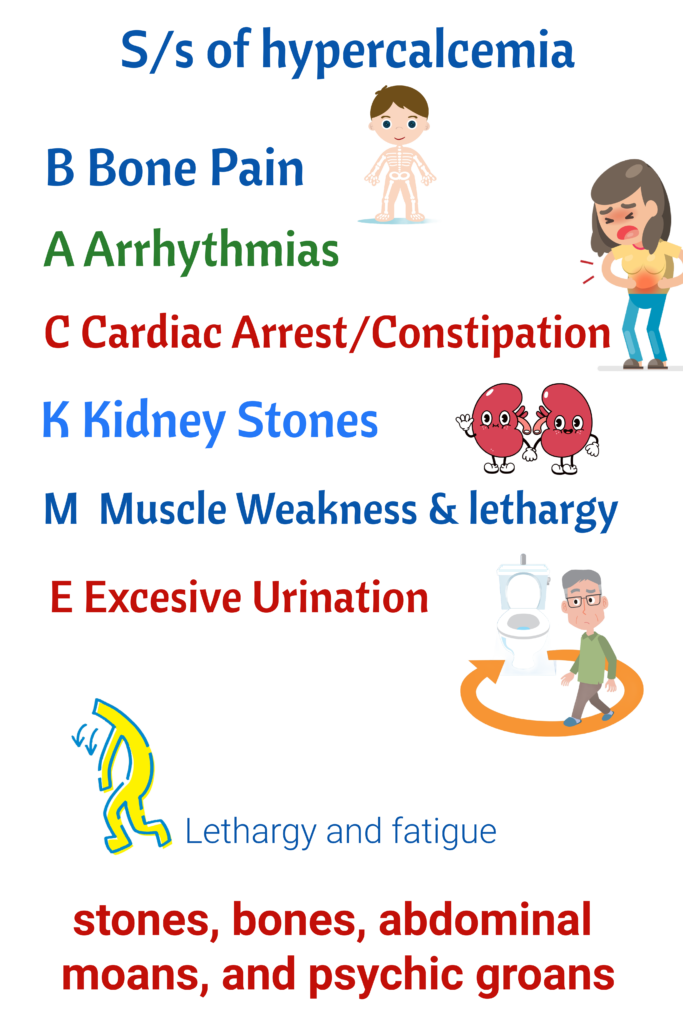

Phosphorus
Hypophosphatemia


- If calcium and phosphorus are high at the same time, the two minerals can bond, and sharp calcium phosphate crystals ay form in the eyes, skin, lungs, heart, joints and bloock vessels. Patients can lose fingers, limbs, and even die due to calciphylaxis (calcium phosphate crystals that block vessels).
- Dialysis doesn’t remove phosphorus and patients must take phosphorus binders such as calcium acetate (phoslo) and Sevelemer (Renvela) with every meal.
What is your role
- Report symptoms to the nurse
- Verify that the patient is getting the right dialysate
- Mix the dialysate correctly
- Start treatments only when water system and dialysates are correct/working properly.
Uremia and its symptoms
- Uremia is a build-up of wastes in the blood.
- Edema (swelling)
- Trouble breathing
- Make less urine
- Foamy/bubbly urine
- Pruritis (itchiness)
- Ammonia Breath
- Metal taste
- Yellow skin
- Sleep problems
You can help if you learn the symptoms of uremia and if any of your patents have these symptoms, notify the nurse.
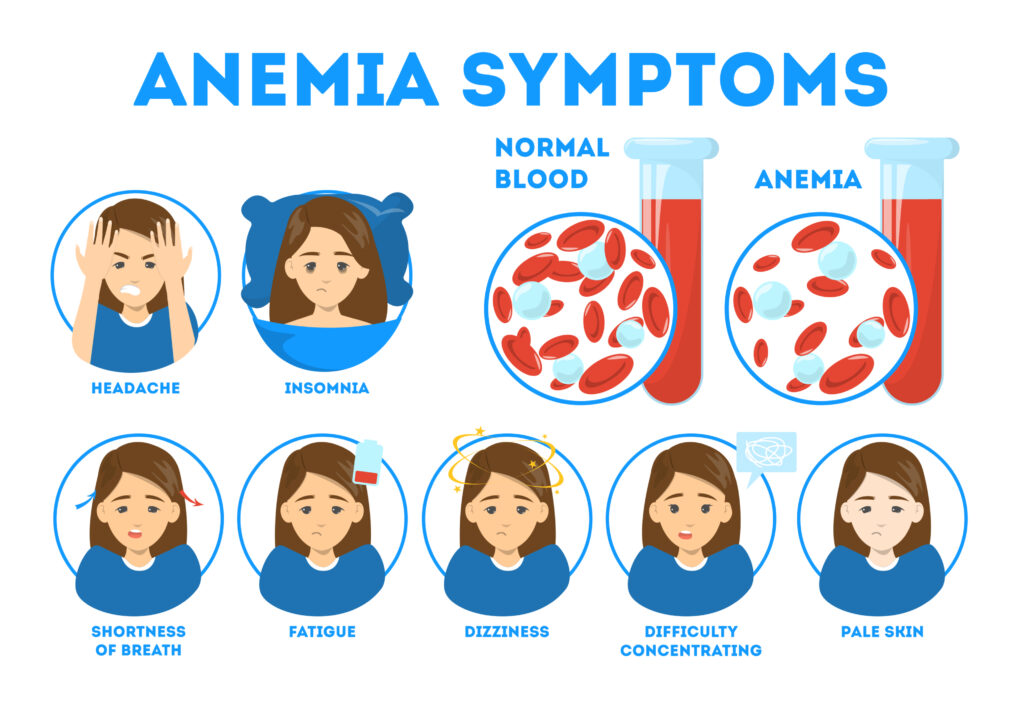
Your role in anemia managemet
- Rinse back as much as possible
- Report any bleeding/blood loss to nurse
- Encourage patients to come to all their treatments
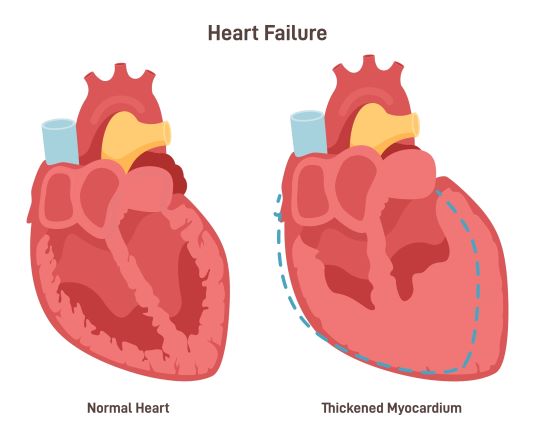
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- In left ventricular hypertrophy, the left ventricle becomes thick, fibrous, and loses it’s ability to contract effectively.
- Caused by anemia because the heart must pump harder to compensate and by aggressive fluid removal, which drops the blood pressure and weakens the heart.
Organ Stunning during standard in-center hemodialysis
- Stunning damage occurs when blood pressure drops during HD, a problem called intradialytic hypotension. (Intradialytic=during HD)
- This blood pressure drop causes ischemia (less blood flow to the tissues)
- The patient’s heart, brains, and the kidney function they have left are harmed by stunning (low blood pressure).
- Your role in organ stunning: report shortness of breath to the nurse, gentle removal of fluid, and dialysate that is slightly cooler than body temperature can help prevent organ stunning.
- When the rate of water removal (UF) is higher than the patient can tolerate, he or she can have small heart attackes during the treatment causing damage to the heart and LVH.
- Organ stunning can also damage the brain. People who do In-center HD and have drops in BP may not think as well and tend to have more depression.
- To prevent organ stunnning CMS requires that we keep ultrafiltration rate to < 13ml/kg/hr.
What is your role
Report SOB or chest pain to the nurse. Gentle fluid removal, Cool dialysate of 0.5 C below core temp.
Pericarditis
- Uremic toxins in the blood may elad to pericarditis (swelling of the sac around the heart).
- Symptoms: fever, dry cough, fatigue, hypotension, and irregular heart beat.
- Report any complaints to the nurse.
- If the patient has chest pain before the treatment, Do not start the treatment until the nurse sees the patient.
- Give patients their full treatment to prevent build up of toxins!


Neuropathy
- Patient’s may develop nerve damage in the hands or feet.
- It is most common in diabetics.
- Symptoms include: burning and pain in hands/feet, numbness like “pins and needles,” muscle weakness, trouble walking, erectile dysfunction.
- It is unknown why causes this neuropathy, but it is more common in patients with GFRs of < 12. It often improves when patients get long HD treatments during their sleep (noctural HD).
- Your role: notify the nurse of any patient complaints. Fall precautions.
