Sickle Cell Anemia
/*! elementor – v3.12.1 – 02-04-2023 */
.elementor-heading-title{padding:0;margin:0;line-height:1}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title[class*=elementor-size-]>a{color:inherit;font-size:inherit;line-height:inherit}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-small{font-size:15px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-medium{font-size:19px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-large{font-size:29px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-xl{font-size:39px}.elementor-widget-heading .elementor-heading-title.elementor-size-xxl{font-size:59px}
Sickle Cell Anemia: Hemolytic Anemia: Increased destruction of RBCs
/*! elementor – v3.12.1 – 02-04-2023 */
.elementor-accordion{text-align:left}.elementor-accordion .elementor-accordion-item{border:1px solid #d5d8dc}.elementor-accordion .elementor-accordion-item+.elementor-accordion-item{border-top:none}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title{margin:0;padding:15px 20px;font-weight:700;line-height:1;cursor:pointer;outline:none}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon{display:inline-block;width:1.5em}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon svg{width:1em;height:1em}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon.elementor-accordion-icon-right{float:right;text-align:right}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon.elementor-accordion-icon-left{float:left;text-align:left}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon .elementor-accordion-icon-closed{display:block}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon .elementor-accordion-icon-opened,.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title.elementor-active .elementor-accordion-icon-closed{display:none}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title.elementor-active .elementor-accordion-icon-opened{display:block}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-content{display:none;padding:15px 20px;border-top:1px solid #d5d8dc}@media (max-width:767px){.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title{padding:12px 15px}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-title .elementor-accordion-icon{width:1.2em}.elementor-accordion .elementor-tab-content{padding:7px 15px}}.e-con-inner>.elementor-widget-accordion,.e-con>.elementor-widget-accordion{width:var(–container-widget-width);–flex-grow:var(–container-widget-flex-grow)}
Patho
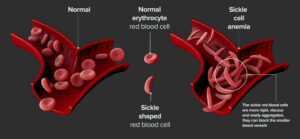
- Sickle cell disease: formation of abnormal hemoglobin called HbS (more than 40% of RBCs are HbS in sickle cell disease
- HbS cells are sickled in shape, rigid, sticky and clump together, obstructing blood flow and causing hypoxia and ischemia.
- Very painful

- To have the disease, both parents must be carriers
- You can have the sickle cell trait, carry only one gene, and have a very mild form of sickle cell.
- Mostly in african-americans.
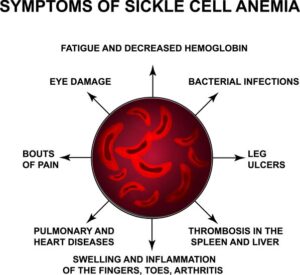
- Very painful due to low oxygen from obstructed blood flow.
- Symptos of anemia: Shortnes of breathe and hypoxia, Tachycardia, weakness and pallor.
- Organ damage: renal failure, spleen and liver.
- Sores
- Dactylitis: swelling of hands and feet
- Seizures
What precipitates a sickle cell crisis
- Hypoxia
- Dehydration
- Infections
- Immobility
- pregnancy
- Alcohol
- Extreme temperatures
- Exercise
- Emotional stress
- Anethesia/surgery
- Blood becomes thick, cells clump leading to no blood flow and tissue hypoxia, which causes the pain.

- Hydration makes blood thinner, increasing organ perfusion and decrease pain from hypoxia
- Prevent Infection: handwashing, monitor temp and WBC. May need prophylactic antibiotics to prevent pneumonia and strep.
- Do not elevate HOB > 30 ° to prevent pulmonary embolism (remember that blood is thick and can clot)
- Monitor extremities for poor blood flow (temp, color, CFT, pulses, check pulse ox of fingers and toes if possible)
- Keep room temp moderate
- Hydroxyurea: chemotherapy agent that ⇓ cells from sickling
- RBC transfusion
- Stem cell transplant

- Limit stress
- Prevent infection
- hydrate
- vaccinate
- do not smoke
- avoid high altitudes
- avoid over-exertion

