What should you DO FIRST?
What is the most important intervention or what should you do FIRST? Oh no! Some long reading! Please read.
What intervention/assessment should you DO FIRST? This is one of the most difficult questions on the NCLEX or any nursing test since most of the time all of the available choices are interventions/assessment that need to be done. Let’s go through some rules that can help you choose the right answer:
- It is almost never call the doctor. Unless it is something like a potassium= 2.8 mEq/L and you need replacement orders or a patient has a new cast and toes feel cool to touch (perfusion is compromised).
- If they provide you with an assessment, likely the answer will be an intervention. For example, the most important intervention for a client with severe respiratory distress is to have the intubation tray at the bedside/have the client intubated, not assess the client. You were already told that the client is in respiratory distress.
- If you are told that the patient has a narcotic overdose, you know what is wrong, right? Now intervene. Give the patient some narcan. Don’t waste time checking pupils or listening to breath sounds. If the patient is not breathing due to the overdose, do you really think that Oxygen will help.
- If they do not tell you the assessment of the problem, the answer may be assess FIRST. For example, a patient tells you that his or her arm is hurting. You would need to assess first. Choose assessment. You need to know what’s wrong FIRST! Why is the arm hurting. Is it swollen? Was it hurt?
- Always think! What is the most important thing I should do for the patient to save his life or solve his problem: An assessment or an intervention?
- Again, do you assess or do you intervene?…..mmmm..Well, are they telling you what’s wrong? Or do you need to find out?

Example: Your client has an opioid overdose. What action should you do first?
- Give Oxygen
- Give Narcan
- Assess Respiratory Status
- Check ABG
- The question reads: A client has an opioid overdose (heroin, morphine, or fentanyl). They have provided you with the assessment. You know what’s wrong. Now choose the intervention: NARCAN/NALAXONE. Do not choose assess respiratory status, give oxygen, or do an ABG. What is going to save your client’s life is to reverse opioid overdose with Narcan and nothing else.
- You enter a client’s room who was given ativan IV (Lorazepam), a benzodiazepine, and now he has very shallow breathing. What should you do FIRST? You know he is overdosed with a benzodiazepine (an assessment). Choose an intervention that will save the patient’s life. Give flumazenil (Romazicon).
NCLEX Tip: flumazenil (romazicon) reversal agent for bendodiazepines and Narcan for opioid overdose. Know this!

Take the time to learn these antidotes
Warfarin (Coumadin)=Vitamin K
Heparin= Protamine Sulfate
Digoxin= digibind
digoxine immune fab
Tylenol overdose=Acetylcysteine (mucomyst)
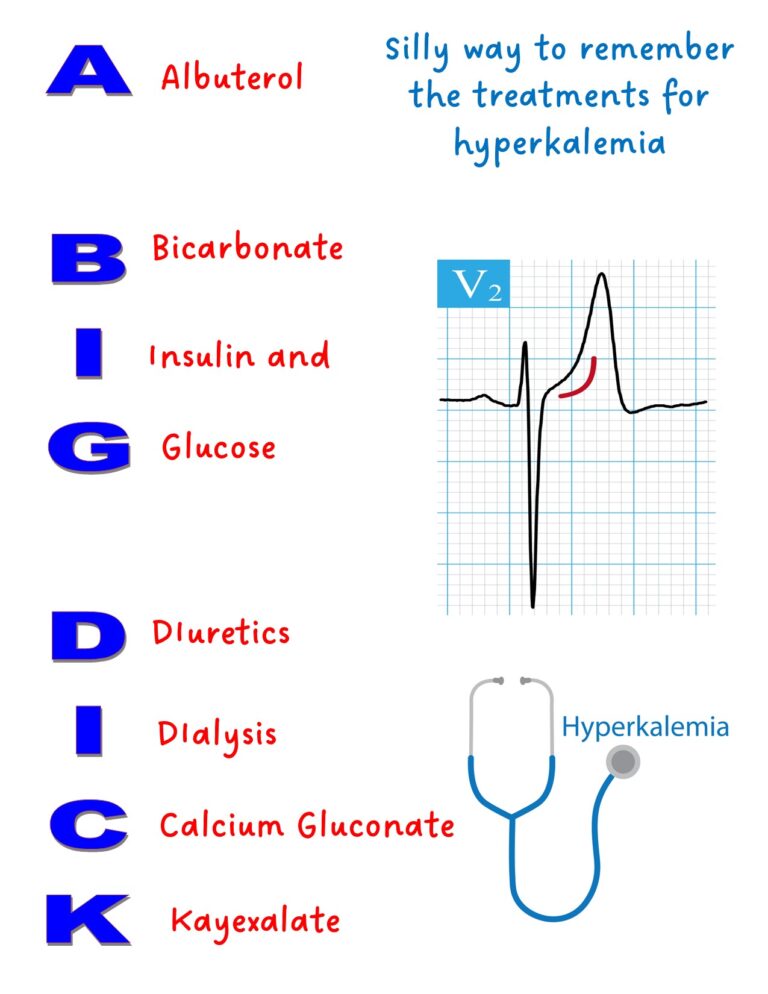
Hyperkalemia when dialysis not available immediately= Insulin and Dextrose, Kayexalate, Calcium gluconate, Albuterol, or Sodium bicarbonate.
Remembering the Treatments for hyperkalemia
If the question tells you what the problem is then choose an intervention.
If the question does not tell you the problem then choose an assessment.
Ask yourself: What would benefit the client the most?

What to do first if this happens.
Place client in left Trendelenberg
Sit up in bed to decrease blood pressure. Check for bladder distension or fecal impaction. Remove any noxious stimuli
Oxygen and Morphine always show up as choices. But you may also see nitroglycerin and aspirin.
Remember MONA- morphine, oxygen, nitroglyceirn and aspirin
Goal: Treat chest pain. Chest pain = myocardial ischemia/infarct
Assess for muscle weakness and check potassium levels.
Check potassium levels and digoxin levels. Hypokalemia potentiates digoxin toxicity. If a client has visual disturbances (e.g., seeing halos) always think digoxin toxicity. Normal digoxin level is 0.8- 2.0 ng/mL
Too much antidiuretic hormone. Patient retains fluid. Patient is hyponatremic (dilution from too much fluid). Ok to give sodium to his client. Priority is to restrict fluid.
Have the external/transcutaneous pacemaker at the bedside
Priority is to stop the infusion.
Report black-colored stools= GI bleeding
Priority is to check breathing. Remember that paralysis/weakness starts from the lower extremities and moves up the body. The client will go into respiratory arrest/distress as the breathing muscles become weaker/paralyzed.
Bedrest. If the client is dehydrated the priority is to give fluids. I saw a question in Saunders. Patient was unstable and tachycardic and the answer was keep in bed.
Check Blood sugar
Get intubation tray. Any patient in respiratory distress, get ready to intubate is almost always the answer.
Watch for nephrotoxic drugs/antibiotics/Contrast dye
Watch for electrolyte imbalances, especially hyperkalemia
Have tracheostomy tray at the bedside in case of airway closure due post operative edema.
Check for hypocalcemia, even in thyroidectomies. The parathyroid may have been damaged during surgery.
Two important signs of hypocalcemia: Chvostek’s and Trousseau’s sign
Let's practice your new knowledge!
Quiz Summary
0 of 9 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 9 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- Current
- Review / Skip
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 9
1. Question
The nurse enters the room of a 12 year-old client who is supine on the bed with his head turned to the side and has a continuous nosebleed. What should the nurse do FIRST?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 9
2. Question
You enter the room of a client with ativan overdose. What should you do FIRST?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 9
3. Question
A client is admitted with COPD exacerbations and has a blood gas with a pH=7.24 and a PCO2=69. What should the nurse do FIRST?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 9
4. Question
A client is having an allergic reaction while receiving a blood transfusion. What should the nurse do FIRST?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 9
5. Question
What should be the nurses priority for a postoperative client?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 9
6. Question
The nurse admits a client who is having a spontaneous abortion at 20 weeks. Which is the priority?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 9
7. Question
The nurse is caring for a client with a spinal cord injury who suddenly has an increase in blood pressure to 174/99 and a decrease in heart rate down to 45 bpm. The client is diaphoretic and complains of a severe headache. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform FIRST?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 9
8. Question
An agitated client received haldol and now he is having intermittent sustained involutary contractions of the muscles of the face, neck, and extremities. Which of the following actions should the nurse do FIRST?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 9
9. Question
The nurse enters a client’s room with COPD. The client’s respiratory rate is 8 breaths/min and the Oxygen saturation is 95% on 5L Nasal Cannula. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform FIRST?
CorrectIncorrect
