Myocardial Infarction
Assessment
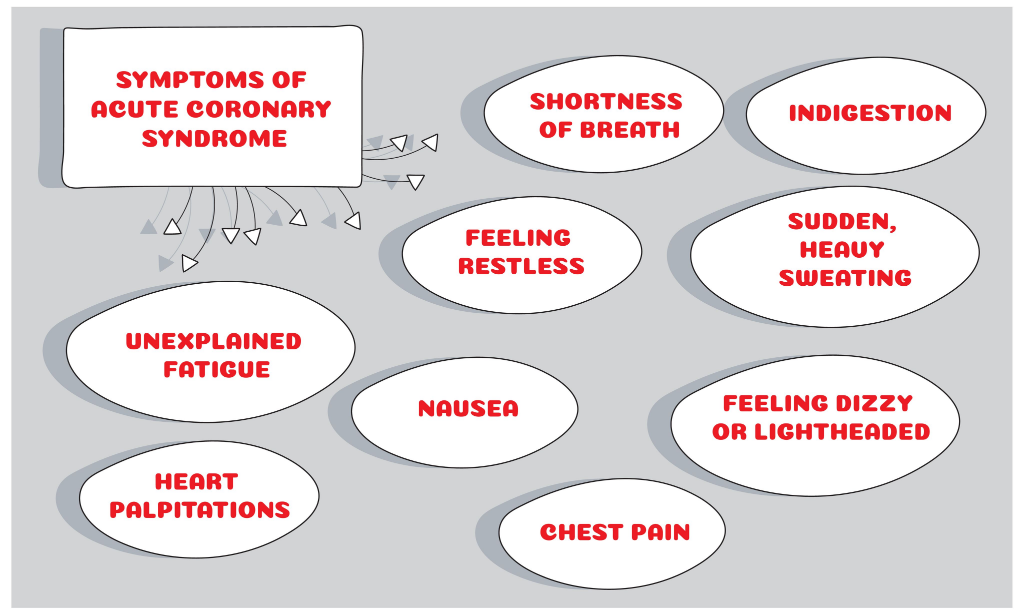
- Severe, substernal, crushing pain
- No relief with 3 nitroglycerins
- Occurs at rest
- Lasts > 20 minutes
- Client may experience changes in vital signs: hypotension, bradycardia, or tachycardia.
- Other symptoms: diaphoresis, anxiety, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, weakness, and dyspnea.
- In women: vague symptoms- aching jaw, choking sensation, fatigue, insomnia, and dyspnea.
Labs
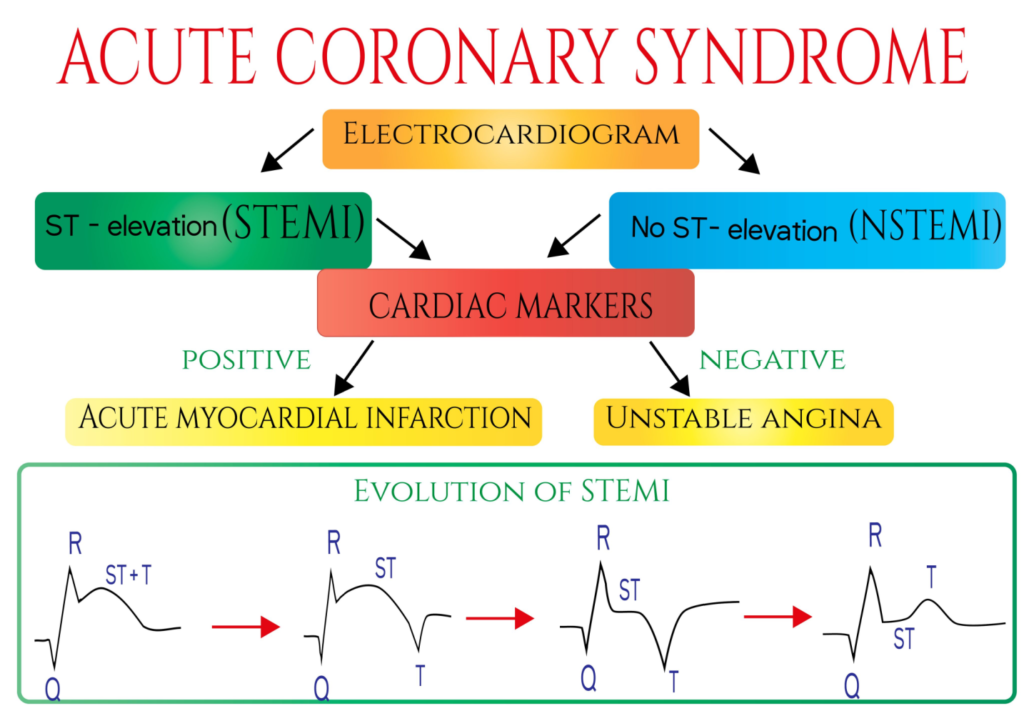
Elevated Cardiac Enzymes
- Elevated Troponin I
- Elevated CK (CK-MB)
EKG Changes
12-lead EKG may show
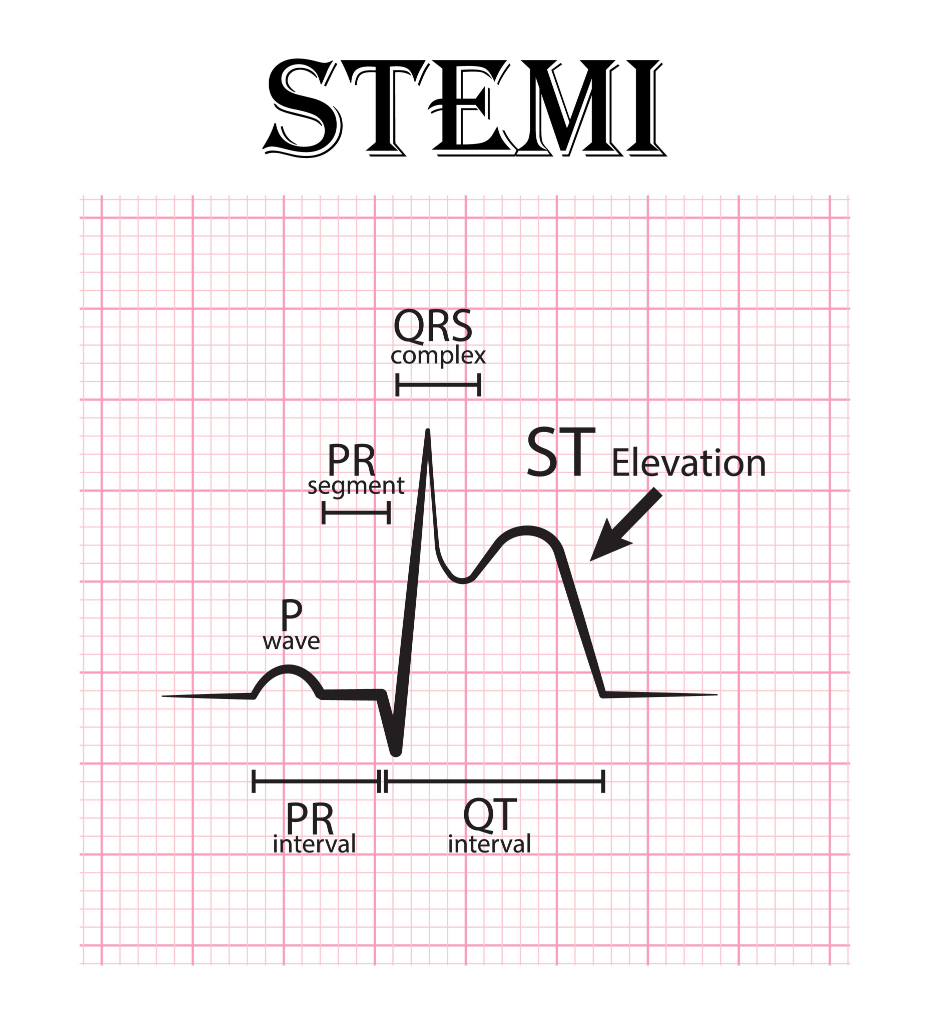
- ST-Elevation (ST-Elevation MI or STEMI)
- No ST-Elevation (NSTEMI)
Interventions
- Admit to intensive care unit
- Bedrest
- Oxygen
- Monitor vital signs, oxygen saturations and EKG
- Morphine to relieve pain (also vasodilates coronary arteries and relieves anxiety)
- Aspirin or plavix (antiplatelet medications)
- Vasodilators to relief pain (morphine and nitroglycerin)
- Beta blockers to decrease myocardial oxygen demand
- Reperfusion therapy with fibrinolytics if indicated
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Goal- in the cath lab within 90 minutes
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery if indicated
Nursing Priorities
- Initiate immediate treatment: Morphine, Oxygen, Nitroglycerin, and Aspirin or plavix. PAIN= Myocardial ischemia
- Identify unusually symptoms of MI- just shortness of breath or indigestion (no chest pain. Confusion in the elderly
- Know symptons of complications: heart failure, cardiogenic shock, and dysrhythmias.
- Prepare for fibrinolytic therapy, PCI, or CABG as indicated by physician.
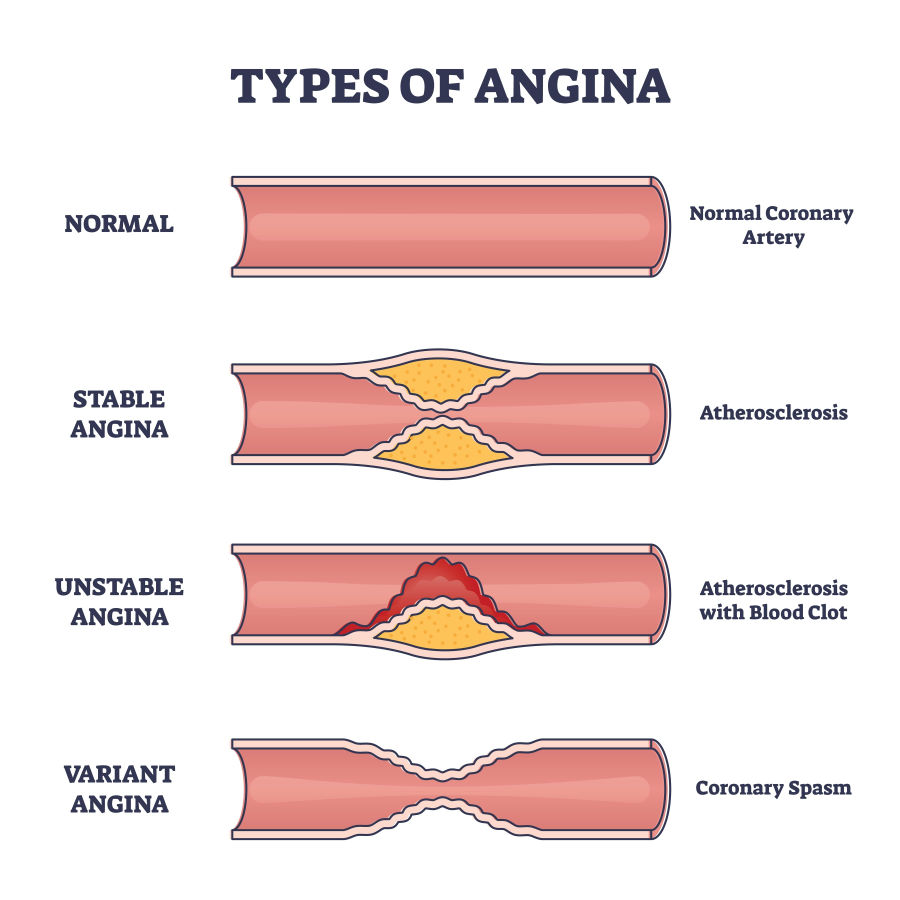
Angina
Assessment
- Chest pain varies in severity
- Pain may be similar to a myocardial infaction
- Difference: Relieved by nitroglycerin
- Difference: Occurs with activity and relieved by rest
- Difference: lasts < 5 minutes
- Other symptoms may be present: diaphoresis, anxiety, and dyspnea.
Labs
Management of risk factors to prevent MI
- Keep total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL
- Keep Triglycerides < 160 mg/dL
- Keep LDL < 160mg/dL
- Keep HDL > 45 mg/dL in men and > 55 mg/dL in women
EKG Changes
Non-Contributory
Interventions
- Long term: Control of modifiable risk factors (no smoking, weight loss, control diabetes, reduce stress, keep BP <140/90 mm Hg, treated elevated cholesterol)
- Short term: Oxygen, vasodilators such as nitroglycerin, beta blockers (metoprolol), antiplatelet medication (Aspirin), Calcium channel blockers.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention to open up blocked vessels
- Coronary artery bypass graft if unable to open blocked vessels with PCI
Nursing Priorities
Acute episode: Morphine, Oxygen, Nitroglycerin, and ASA or plavix.
Long-term: Educate on Modificable risk factors